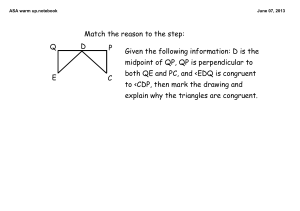
PROPERTIES OF CONGRUENT AND SIMILAR FIGURES Congruent Shapes • Two figures are congruent if one can be transformed into the other by translation, rotation, or reflection. • The lengths of sides (edges) and sizes of angles must be equal between the two shapes for them to be congruent. Examples Congruent Triangles Not Congruent Triangles Congruent triangles can be flipped, rotated and mirrored and will still be congruent. Examples Similar shapes Similar shapes are the same shape but they have different sizes. The corresponding sides are in the same ratio and the corresponding angles are the same. PROPERTIES OF CONGRUENCE 1.REFLEXIVE PROPERTY • any geometric figure is congruent to itself or any number is equal to itself. example: 5=5 2. SYMMETRIC PROPERTY describes a relationship between two elements where if one element is related to a second element, then the second element is related to the first one. e. example: If x=5, then 5=x 3. TRANSITIVE PROPERTY - REFERS TO A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THREE ELEMENTS. CONNECTS RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MULTIPLE ELEMENTS. EXAMPLE: IF A = B, AND B = C, THEN A = C THANK YOU!