Uploaded by
D.I.Y creativity
Organic Chemistry Solving Tips: Homologous Series & Polymers
advertisement

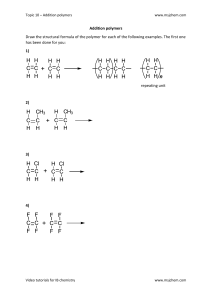
Organic Chemistry Topical Solving Tips Homologous Series & Isomerism ● Homologous series have the same general formula, chemical properties, and functional group. ● Isomers: compounds having the same molecular but different structural formulas. Reaction Conditions & Types ● Photochemical reactions need ultraviolet light (e.g., sunlight). ● Addition reaction: Double bond breaks, allowing new atoms to bond as each carbon atom that had a double bond gets a valency of one. ● Alkanes undergo substitution reactions or combustion. Proteins & Polymers ● Proteins have amine linkages called peptide linkages. ● Biodegradable materials can be broken down by microbes or decomposers. ● Natural polymers include cellulose, polysaccharides, DNA, and RNA. ● Condensation polymers release a small molecule (e.g., water). ● Amide linkage: Between dicarboxylic acid and diamine group. ● Ester linkage: Between dicarboxylic acid and diol group. ● Types of amide linkages: Nylon and proteins (peptide bonds). ● Types of Ester linkage: PET (polyethylene terephthalate). ● Synthetic polymers: Terylene, nylon. ● Proteins: Polymers from amino acids. Polymerization & Depolymerization ● Depolymerization: polymers can be converted back into using heat, acid catalysts, and enzymes. ● To make addition polymers, the double bond must be present in the monomers. ● Polyester is the type of compound formed when a dicarboxylic acid and a diol react. ● Polyamide is the type of condensation polymer formed when a dicarboxylic acid and diamine react. Reactions & Conversions ● Alcohol to carboxylic acid: Oxidation with acidified potassium manganate VII. ● Alkenes to alcohols: Hydration with steam, H₂SO₄, 300°C, 60 atm. ● Esters: Formed by the reaction of alcohols and carboxylic acids, releasing water. Crude Oil & Hydrocarbons ● Crude oil: oil extracted from the rocky layer. Also called petroleum and has fractions of various other compounds that can be separated by fractional distillation. ● Saturated compounds: Compounds containing all single carbon bonds. ● Hydrocarbons: Compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Fermentation & Ethanol Uses ● Fermentation conditions: Aqueous glucose, yeast, 37°C, no oxygen/air. ○ Advantages: Renewable source is glucose, doesn’t need high temp or pressure, and can be done on a small scale. ○ Disadvantages: Releases CO₂ as a pollutant and is slow. ● Ethanol is used as a solvent and as a fuel. Naming & Numbering Functional Groups ● The more the number of carbon, the higher the boiling point of a compound. ● After ethanol, in alcohols, we have to state the number of carbon on which the functional group is present. ● After propanol, in alkenes, we have to state the number of carbon atoms which has the functional group. ○ Start numbering with the closest side. Polymer Linkages & Structures ● Ester linkage between C double bond O and O. ● Amide linkage between C double bond O and NH group. ● PET is called terylene. ● Uses: ○ Teflon in non-stick pans. ○ PVC in pipes. ○ Polyethylene used to make shopping bags. ● Protein is the only condensation polymer in the syllabus made from one monomer. ○ To draw its monomer (amino acid), draw a box, put the carboxyl group on one and amine group on the other side. Observation-Based Answering Tips ● If a question comes about observation and carbon dioxide is released, don’t write “release of CO₂.” Instead, say effervescence or fizzing or bubbling as an observation. ● To determine the number of water molecules released in a polymer, count the number of amine or ester linkages. ● If a question comes to drawing two different alcohols containing 3 carbon atoms, you have to draw the propanol and its isomer.