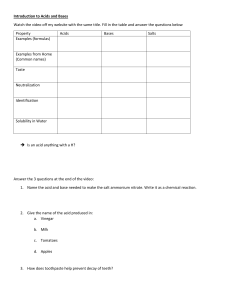
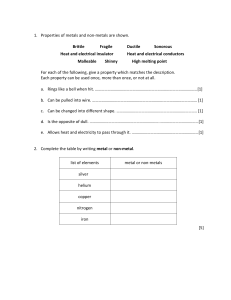
Unit 5 Acids, bases and salts CHARACTERISTIC REACTION OF ACIDS Pages 131-134 Ms. Rabiya Waheed CLASSROOM RULES STARTER What is the only letter in the alphabet that does not appear anywhere on the periodic table? Students will: Explain the reaction of acids with metals and carbonates. Describe the reaction of acids with alkalis and bases. • acids • salt • carbonates • hydrochloric acid • nitric acid • sulfuric acid • ethanoic acid • alkalis • bases Acids An acid is any substance that in water solution tastes sour. The pH will be less than 7. The solution contains an excess of hydrogen (H+) ions. What will be the color of acid with litmus paper? Reactions of acids There are 3 major chemical reactions in which all acids will take part: Acids will react with a reactive metal Acids will react with carbonates Acids will react with a base or alkali In all of the above reactions salt is one of the product. Salt- a compound made from an acid when a metal takes place of the hydrogen in the acid. Reaction of acids with metals Metals that are quite reactive can be used to displace the hydrogen from an acid safely. metal + acid salt + hydrogen ItItisisunsafe unsafeto totry trythis thisreaction reactionwith withvery veryreactive reactivemetals metals such suchas assodium sodiumor orcalcium. calcium. The Thereaction reactionisistoo tooviolent violent No reaction occurs with metals, such as copper which are less reactive than Lead. Reaction of acids with metals metal + acid salt + hydrogen Even with lead, it is difficult to see any reaction in a short time. Reaction of acids with metals The salt made depends on the acid used. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) always gives a chloride Nitric acid (HNO3) always gives a nitrate Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) always gives a sulfate Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) always gives an ethanoate Reaction of acids with carbonates All carbonates give off carbon dioxide when they react with acids. acid + metal carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide We have seen this in case of antacid tablets that occurs with effervescence due to carbon dioxide gas bubbles Reaction of acids with carbonates Carbon dioxide is prepared in the laboratory by reaction of acid with carbonates. Calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid to give calcium chloride (salt), water and carbon dioxide gas Workbook Pg 60 Students will: Explain the reaction of acids with metals and carbonates. Describe the reaction of acids with alkalis and bases. Reaction of acids with bases and salts A base will neutralize an acid, and as a result salt and water is formed. This is called neutralization reaction. Reaction of acids with bases and salts The salt produced in neutralization reaction depends upon the combination of reactants used. To make a particular salt, you choose a suitable acid and base to give the solution of salt. Reaction of acids with bases and salts Reaction of acids with bases and salts Base Nitric acid (HNO3) Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) Sodium Sodium hydroxide chloride (NaCl) (NaOH) Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) Sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) Potassium Potassium hydroxide chloride (KCl) (KOH) Potassium nitrate (KNO3) Potassium sulfate (K2SO4) Copper oxide (CuO) Hydrochloric acid (HCl) Copper Copper nitrate chloride (CuCl2) Cu(NO3)2 Copper sulfate (CuSO4) Q1. Name the reaction of acids we learnt today Q2. What is neutralization reaction? Q3. Write a word and symbol equation for any neutralization reaction Q4. Complete the following neutralization reactions Students will: Explain the reaction of acids with metals and carbonates. Describe the reaction of acids with alkalis and bases. Reaction of acids with metals Reaction of acids with carbonates Reaction of acids with alkalis and bases