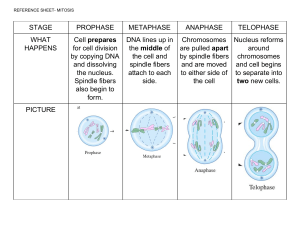
CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS FLAP BOOK – LIST OF EVENTS INSTRUCTIONS: Cut out each of the 24 list of events below. Each depicts events that occur during interphase and mitosis. After cutting, sort and arrange these events under the correct flap in your cell division and mitosis flap book so that each event is properly matched to the correct stage of cell division. 1. Nuclear membrane has completely disappeared. 2. Spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids apart at the centromere and drag them to opposite poles. 3. The nucleolus has disappeared. 4. Spindle apparatus has disassembled and the spindle fibers dissolve. 5. Nucleoli begin to reform within nuclei. 6. Centriole pair replicates. 7. Nuclear membranes begin to reform around separate (but identical) sets of chromosomes. 8. Spindle fibers have moved the duplicated chromosomes so that they line up at the midline (equatorial plate) of the cell. 9. Duplicated chromosomes are at their most condensed during this stage. 10. The cell elongates. 11. Duplicated chromosomes begin to condense and thicken. 12. Nuclear membrane further dissolves. 13. DNA replicates to create duplicated chromosomes. 14. Nucleolus begins to disappear. 15. The cell begins cytokinesis by forming a cleavage furrow to divide the cytoplasm. 16. The spindle apparatus (mitotic spindle) is fully formed. 17. Centriole pairs begin to migrate to opposite poles. 18. Centriole pairs are almost fully migrated to opposite poles. 19. Spindle fibers begin to form. 20. Chromosomes begin to decondense and lengthen. 21. Nuclear membrane begins to dissolve. 22. Spindle fibers attach to duplicated chromosomes. 23. Duplicated chromosomes are further condensed. 24. Centriole pairs are fully migrated to opposite poles. Interphase Prophase 17) Centriole pairs begin to migrate to opposite poles. 21) Nuclear membrane begins to dissolve. 19) Spindle fibers begin to form. 11) Duplicated chromosomes begin to condense and thicken. 14) Nucleolus begins to disappear. Prometaphase 18) Centriole pairs are almost fully migrated to opposite poles. 12) Nuclear membrane further dissolves. 3) The nucleolus has disappeared. 23) Duplicated chromosomes are further condensed. 22) Spindle fibers attach to duplicated chromosomes. Metaphase 24) Centriole pairs are fully migrated to opposite poles. 16) The spindle apparatus (mitotic spindle) is fully formed. 8) Spindle fibers have moved the duplicated chromosomes so that they line up at the midline (equatorial plate) of the cell. 1) Nuclear membrane has completely disappeared. 9) Duplicated chromosomes are at their most condensed during this stage. Anaphase 2) Spindle fibers pull the sister chromatids apart at the centromere and drag them to opposite poles. 10) The cell elongates. Telophase CELL DIVISION AND MITOSIS: ANSWER KEY 6) Centriole pair replicates. 13) DNA replicates to create duplicated chromosomes. 15) The cell begins cytokinesis by forming a cleavage furrow to divide the cytoplasm. 7) Nuclear membranes begin to reform around separate (but identical) sets of chromosomes. 4) Spindle apparatus has disassembled and the spindle fibers dissolve. 20) Chromosomes begin to decondense and lengthen. 5) Nucleoli begin to reform within nuclei.