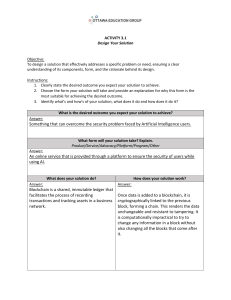
TRIBHUVAN UNIVERSITY Institute of science and technology A Project Proposal On Blockchain-Based Online Voting System Submitted to Department of Statistics and Computer Science Patan Multiple Campus In partial fulfillement of the requriments for Bachelor Degree in Computer science and Information Technology Submitted By: Hridesh Sapkota 25537 Roshan Ojha 25569 Sanam Timilsina 25580 Table of Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction to Blockchain 1.2 Decentralized Voting Using Blockchain 2 Literature Survey 2.1 Literature Survey on Online Voting System Using Blockchain 2.2 A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis on Scalable Blockchain Based Electronic Voting Systems 2.3 A Survey of Blockchain-Based E-voting Systems 2.4 Survey on Voting System Using Blockchain Technology 2.5 A Survey on Smart Electronic Voting System 3 Methodology 3.1 Requirement Identification 3.1.1 Existing System 3.1.2 Disadvantages of Existing Systems 3.2 Proposed System 3.2.1 Brief Explanation of Proposed System 3.2.2 Advantages of Proposed System Research 3.2.4 System Architecture 3.3 High Level Design of System 3.3.1 Hardware Requirements 3.3.2 Software Requirements 3.3.3 Use Case Diagram 3.3.4 Description of algorithms 4 Expected outcome 5 References 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction to Blockchain. Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger technology that ensures secure and transparent transaction validation across a decentralized network. Originating with Bitcoin, blockchain technology is now applied across various sectors including finance, supply chain, and voting. Its structure involves linking blocks of data with cryptographic hashes, creating an immutable and transparent system that resists tampering. 1.2 Decentralized Voting Using Blockchain. A decentralized voting system on the Ethereum blockchain offers a transformative approach to elections, enhancing security, transparency, and accessibility. By eliminating intermediaries and enabling anonymous, tamper-proof voting, such systems promise increased voter engagement and trust. This system allows global participation and provides real-time results, making elections more inclusive and efficient. 2 Literature Survey 2.1 Literature Survey on Online Voting System Using Blockchain This survey discusses the need for advanced security in online voting systems and explores various implementations across countries, highlighting issues in traditional systems like database manipulation. 2.2 A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis on Scalable Blockchain-Based Electronic Voting Systems. This review identifies scalability challenges in blockchain-based voting systems and examines solutions and research developments, offering guidance for future research and implementations. 2.3 A Survey of Blockchain-Based E-voting Systems This paper explores recent advancements in blockchain-based e-voting systems, focusing on security and privacy issues, and provides a comparative analysis of existing systems. 2.4 Survey on Voting System Using Blockchain Technology The survey highlights how blockchain technology can address problems in traditional voting, offering a secure and efficient online voting solution. 2.5 A Survey on Smart Electronic Voting System Using Blockchain Technology This survey discusses the implementation of blockchain in electronic voting systems in India, addressing security concerns and proposing a blockchain-based solution for enhanced transparency and reliability. 3 Methodology 3.1 Requirement Identification Requirement identification is the gathering of relevant requirement that will be used to develop a system. There are different methods to gather requirement which includes studying of existing system, interviews, questionnaires etc. 3.1.1 Existing System Traditional voting systems involve physical voting locations and manual counting, with electronic systems facing criticism over security vulnerabilities. 3.1.2 Disadvantages of Existing Systems Lack of transparency Vulnerability to fraud Slow results High costs Centralization Limited accessibility 3.2 Proposed System 3.2.1 Brief Explanation of Proposed System The proposed system utilizes Ethereum blockchain to ensure a secure, transparent, and immutable voting process. It employs smart contracts to facilitate anonymous voting and real-time results, enhancing the integrity of elections. 3.2.2 Advantages of Proposed System Decentralization Transparency Tamper-proof Global accessibility Real-time results 3.2.3 Objectives of the Proposed Research Security: Ensuring tamper-proof and transparent elections. Transparency: Allowing full visibility into the voting process. Accessibility: Increasing voter turnout by removing physical barriers. Efficiency: Reducing time and costs associated with traditional voting. Trust: Building confidence in the electoral process. 3.2.4 System Architecture The system architecture involves user authentication, role-based access, real-time vote recording, and result updates on the blockchain. Figure: System Architecture 3.3 High Level Design of System The high-level design of the Blockchain-Based Online Voting System includes a user interface for voters and administrators, allowing secure login and vote casting. Voter authentication is managed through secure registration and access control mechanisms like biometric verification or two-factor authentication. The system utilizes a blockchain network to ensure the immutability and transparency of the votes. Smart contracts are employed to automate election rules and vote tallying. Finally, the system provides real-time monitoring and secure storage of election data, ensuring a trustworthy and tamper-proof voting process. 3.3.1 Hardware Requirements Processor (2 GHz), RAM (4 GB), Disk Space (100 GB) 3.3.2 Software Requirements: Node.js, Web3.js, Truffle, Solidity, Ganache, Metamask, Python, FastAPI, MySQL. 3.3.3 Use Case Diagram Figure : Use Case Diagram 3.3.4 Data Flow Diagram Level 0 data flow diagram Figure : Level 0 Data Flow Diagram 3.3.1 Level 1 data flow diagram Figure : Level 1 Data Flow Diagram 3.3.1 Level 2 data flow diagram Figure : Level 2 Data Flow Diagram ER Diagram Figure : ER Diagram 3.3.5Description of algorithms The algorithm for the Blockchain-Based Online Voting System involves several key steps: 1. Voter Registration: Voters register securely, providing necessary identification and undergoing verification through mechanisms like biometric authentication or twofactor authentication. 2. Ballot Casting: After successful authentication, voters access the ballot through the system's user interface. Each vote is encrypted and digitally signed by the voter before being submitted. 3. Blockchain Recording: The encrypted vote is broadcast to the blockchain network, where it is added as a new transaction. The blockchain's consensus mechanism ensures that the vote is securely recorded and immutable. 4. Smart Contract Execution: Smart contracts within the blockchain automatically execute election rules, such as validating the vote, ensuring it's from a registered voter, and preventing double voting. 5. Vote Tallying: Once the voting period ends, the smart contract triggers the counting of votes. Since the blockchain is transparent, the tallying process is secure and can be verified by anyone. 6. Result Announcement: The final vote count is securely stored and made available for viewing, ensuring that the results are accurate and tamper-proof. 4 Expected outcome The expected outcomes are enhanced security, increased transparency, reduced election costs, improved trust in the process, and potentially higher voter participation through accessible online voting. 5 REFERENCES [1] “Blockchain-Based E-Voting System” by Friðrik Þ. Hjálmarsson, Gunnlaugur K. Hreiðarsson, Mohammad Hamdaqa, Gísli Hjálmtýsson, 2018 [2] “Blockchain-Based Electronic Voting System for Elections in Turkey” by Rumeysa Bulut, Alperen Kantarcı, Safa Keskin, Şerif Bahtiyar [3] “The Advantages and Disadvantages of the Blockchain Technology” by Julija Golosova, Andrejs Romanovs [4] A. Shanti Bruyn, “Blockchain an introduction. Research paper”, 2017. [5] Andrew Barnes, Christopher Brake and Thomas Perry “ Digital Voting with the use of Blockchain Technology”, 2016 [7] The Benefits Of Applying Blockchain Technology In Any Industry (https://www.forbes.com/sites/ilkerkoksal/2019/10/23/the-benefits-of-applyingblockchaintechnology-in-any-industry/?sh=48c9789a49a5 [8]What are the advantages of Blockchain? (https://omnitude.tech/what-are-the-advantagesofblockchain/) [9] Blockchain disadvantages: 10 possible reasons not to enthuse (https://www.enterprisetimes.co.uk/2018/10/15/blockchain-disadvantages-10possiblereasons-not-to-enthuse/) [10] Should we already be using blockchain as a voting system for elections? (https://www.corda.net/blog/should-we-already-be-using-blockchain-as-a-voting-systemforelections/)