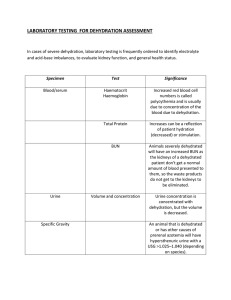
DEHYDRATION Occurs when more water and fluids leave the body than enter. Even low levels of dehydration can cause headaches, lethargy and constipation. Human body is roughly 75% water without this water it cannot survive water is found inside cells within blood vessels and between cells. Types of Dehydration Isotonic Dehydration Loss of water with normal dissolved particle balance Causes: fluid loss from stomach, intestines, kidneys, skin Hypertonic Dehydration Loss of more water than sodium Results in high sodium levels and cell shrinkage Hypotonic Dehydration Loss of more sodium than water Results in low sodium levels and cell swelling Inadequate Fluid Intake Diarrhea Vomiting Fever Excessive Sweating Increased Urination Signs and Symptoms Initial Responses: Thirst and decreased urine output. Concentrated, yellow urine. Advanced Symptoms: Dry mouth and eyes, lack of tears, halted sweating. Muscle cramps, nausea, vomiting, heart palpitations. Light-headedness, especially when standing, and weakness. Severe Dehydration: Cool, clammy skin, confusion, and weakness. Risk of coma, organ failure, and death. Diagnosis of Dehydration Physical Signs: Low blood pressure when standing, faster heart rate, reduced blood flow to extremities. Tests: Blood tests to check electrolyte levels (sodium, potassium) and kidney function. Urine tests to determine dehydration level and check for bladder infections. Treatment of Dehydration 1 Fluid and Electrolyte Replacement: Replace lost fluids and electrolytes. Use oral rehydration solutions (ORS) for infants and children. Severe Cases: Emergency treatment with intravenous (IV) fluids and salts. Note: The approach depends on age, severity, and cause of dehydration. Complications Seizures Electrolyte imbalance due to severe dehydration Brain Swelling (Cerebral Edema) Serious condition from severe dehydration Kidney Failure Long-term or severe dehydration impacts kidney function Shock Hypovolemic shock from significant fluid loss Coma Extreme dehydration can cause loss of consciousness Death Fatal without prompt treatment Thank you for listening