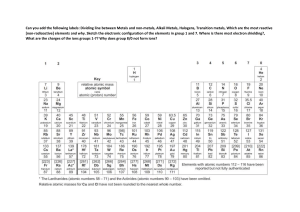
The Periodic Table: Groups and Periods The Periodic Table The periodic table is composed of elements arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Periods The horizontal rows on the periodic table are called periods. Groups • Columns on the periodic table are called groups. • Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. Three Types of Elements The periodic table contains three types of elements: metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Metalloids Nonmetals Metals Metals, Nonmetals, Metalloids • Metals – hard, shiny elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity. • Nonmetals – soft, brittle elements that are poor conductors of heat and electricity. • Metalloids – share some properties of metals and some properties of nonmetals. Groups of the Periodic Table • Elements are organized into groups (1-18). • Elements in the same group have similar properties. Alkali Metals (Group 1): Soft and shiny. Extremely reactive with water Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2): Hard, shiny metals. Very reactive. Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Transition Metals (Group 3-12): Strong metals that are ductile and malleable. Used to make common items like coins and tools. Transition Metals Boron Family (Group 13) Carbon Family (Group 14) Nitrogen Family (Group 15) Oxygen Family (Group 16) Carbon Nitrogen Halogens (Group 17): Extremely reactive elements that can form salts. Noble Gases (Group 18): Non-reactive group of non-metals. Neon Noble Gases Halogens Lanthanides (Elements 57-70) Actinides (Elements 89-102) Also known as the Rare Earth Metals. All metals, all solids, all radioactive. Lanthanides Actinides Detailed PowerPoint Notes