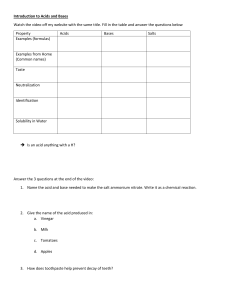
Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS NATURE OF ACIDS AND BASES Suggested Problems: 27,29,35,37,43,47,51,55,61,69,75,79,85,95,97,103,107,111,115,121 28. Write the dissociation reaction and the corresponding Ka equilibrium expression for each of the following acids in water. a. HCN b. HOC6H5 c. C6H5NH3+ 34. Use Table 14.2 to order the following from the strongest to the weakest base. ClO2-, H2O, NH3, ClO4- 2013 Page 1 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14 Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS 40. At 40°C the value of Kw = 2.92 x 10-14. a. Calculate the [H+] and [OH-] in pure water at 40°C. b. What is the pH of pure water at 40°C? c. If the hydroxide ion concentration in a solution is 0.10 M, what is the pH at 40°C? 44. Fill in the missing information in the following table. pH Solution a pOH [H+] 9.63 3.9 x 10-6 M Solution b 0.027 M Solution c Solution d 2013 Acidic, Basic, or Neutral? [OH-] 12.2 Page 2 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14 Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS OF ACIDS Remember that Appendix 5.1 in your textbook contains a table of common Ka values. 48. Calculate the pH of each of the following aqueous solutions. a) 0.10 M HCl b) 5.0 M HCl c) 1.0 x 10-11 M HCl 54. Calculate the pH of each of the following 0.250 M acids. a) HOC6H5 b) HCN 2013 Page 3 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14 Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS 62. Calculate the pH of a solution that contains 1.0 M HF and 1.0 M HOC6H5. Also calculate the concentration of OC6H5- in this solution at equilibrium. 70. One mole of a weak acid HA was dissolved in 2.0 L of solution. After the system had come to equilibrium, the concentration of HA was found to be 0.45 M. Calculate Ka for HA. 2013 Page 4 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14 Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASES AND POLYPROTIC ACIDS 78. Calculate [OH+] and pH for each of the following. a) 0.00040 M Ca(OH)2 b) 25 g KOH in 1.0 L of solution 84. For the reaction of hydrazine (N2H4) in water, H2NNH2(aq) + H2O(l) ↔ H2NNH3+(aq) + OH-(aq) Kb = 3.0 x 10-6. Calculate the concentrations of all species and the pH of a 2.0 M solution of hydrazine in water. 2013 Page 5 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14 Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS 96. Arsenic acid (H3AsO4) is a triprotic acid with Ka1 = 5 x 10-3, Ka2 = 8 x 10-8, and Ka3 = 6 x 10-10. Calculate [H+], [OH-], [H3AsO4], [H2AsO4-], [HAsO42-], and [AsO43-] in a 0.20 M arsenic acid solution. 2013 Page 6 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14 Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF SALTS 100. Arrange the following 0.10 M solutions in order from most acidic to most basic. See Appendix 5 for Ka and Kb values. CaBr2, KNO2, HClO4, HNO2, HONH3ClO4 104. Calculate the pH and the concentrations of all species present in a 0.25 M solution of ethylammonium chloride (C2H5NH3Cl). 2013 Page 7 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14 Name:_______________________________ Date:_________________ Hr:____ AP CHEMISTRY Ch 14 – Acids and Bases PRACTICE PROBLEMS 108. Consider a solution of an unknown salt having the general formula BHCl, where B is one of the weak bases in Table 14.3. A 0.10 M solution of the unknown salt has a pH of 5.82. What is the actual formula of the salt? 112. Are solutions of the following salts acidic, basic, or neutral? The relevant Ka and Kb values are found in Tables 14.2 and 14.3. a. KCl b. NH4C2H3O2 c. CH3NH3Cl d. KF e. NH4F f. CH3NH3CN 2013 Page 8 of 8 mrluzio.com/apchem14