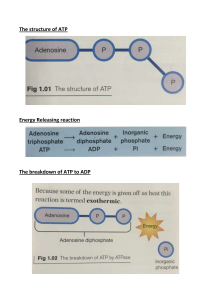
Name______________________________________________________ Period____________ Date_______________ Sameroff Objectives: Do Now SWBAT determine how to make water safe to drink. SWBAT describe several ways people use water. Activity #1 Activity #2 Exit Ticket DO NOW 1. Have you ever gotten sick from drinking impure water? Do you know someone who has? _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VOCABULARY-Define the words below using your worksheet. Physical Water Scarcity ACTIVITY #1 Why is clean water necessary for life? Record your answers in the bubble map below. THINK, PAIR, SHARE What do you think the phrase “eat water” means? In what ways do you think you “eat” water every day? Allow students 2–3 minutes to record their thoughts. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1 ACTIVITY #2 Answer questions 3-8 based on information from the map in Figure 2. 3. Name the countries or global areas that are experiencing physical water scarcity. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What would you predict the climate to be in these areas and why? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Name the countries or global areas that are experiencing economic water scarcity. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Name the countries or global areas that are not experiencing any water scarcity. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What do you predict the difference in per capita income (average income per person) would be between regions with plenty of water and regions with economic water scarcity? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2 ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. The southwestern United States is typically characterized as having a dry, arid climate. Why might this region be shown as having plenty of water even if it is dry and arid? ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3 DIRECTIONS: Read below with your partner, switching who is the reader and who is the summarizer each paragraph. The cloud should contain the MAIN IDEA of each paragraph. 4 ATP or adenosine triphosphate is the main energy-carrying or energytransferring molecule of all living things. In cellular respiration, the energy in the food you eat is released and used to power the cell and its functions. ATP is the molecule that accepts the energy from the food when it is broken down and transfers it to where it is needed in the cell. In photosynthesis, light energy is first captured by chlorophyll and transferred to ATP that then goes to power the process of making glucose. ATP is the energy “currency” of the cell. When a cell needs work to be doe it must spend its ATP. ATP is made up of three subunits: an adenine molecule, a ribose sugar and 3 phosphate groups. “Adenosine” is the term used for the molecule formed when adenine is bonded to ribose. When two phosphate groups are attached it is called ADP (adenosine diphosphate). The useable energy in ATP is stored in the last “high-energy” bond holding on the third phosphate group. The energy that is released during the formation of ADP is used to perform cellular work or a specific function. ADP does not have enough energy to perform cellular work so it must be turned back into ATP by adding a phosphate group back on. The energy needed to “reenergize” ATP by adding a phosphate comes from the chemical breakdown of the food we eat (cellular respiration) or from light energy (photosynthesis). Energy is stored in the bonds of glucose during photosynthesis. During cellular respiration, energy is made available (released) from the breakdown of glucose (food) and is used to change ADP to ATP. It is estimated that humans use almost their body weight in ATP each day to keep their cells functioning. In fact, a cell can use about 2 trillion molecules of ATP per second!! Where does all of the ATP come from? You guessed it; it is recycled over and over again from ADP. Just like rechargeable batteries. Part A: Chemical Structure of ATP 1. In cellular respiration what is the food you eat used for? ________________________ 2. What is ATP made up of? 5 _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe the term adenosine. _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Where is the useable energy in ATP stored? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ DIRECTIONS: Use the word bank below to fill in the missing words. ADP 5. glucose group energy ATP ATP is the _______________ “currency” of the cell. 6. The useable energy in ATP is stored in the last “high-energy” bond holding on the third phosphate ___________________. 7. During cellular respiration, energy is made available (released) from the breakdown of _________________ (food) and is used to change ADP to ATP. 8. It is estimated that humans use almost their body weight in _________ each day to keep their cells functioning. 9. You guessed it; it is recycled over and over again from _________. Just like rechargeable batteries. Regents Questions 1. What is the function of ATP in living things? a. provides energy for cells b. stores genetic information c. provides structure in the nucleus 2. The basic building blocks of a protein are a. glucose molecules b. amino acids c. Hormones d. fat 3. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? 4. What are the abiotic factors that characterize a forest ecosystem? A) light and biodiversity B) temperature and amount of available water C) types of procedures and decomposers D) pH and number of heterotrophs Heterotrophs and Autotrophs The energy to make ATP from ADP comes from food (glucose). Organisms get food in one of two ways. Heterotrophs get food by consuming (eating) other organisms. 6 Autotrophs use the energy in sunlight to make their own food. Photosynthesis is the process that uses light energy to produce food molecules DIRECTIONS: Complete the table comparing two types of organisms. Autotrophs and Heterotrophs Type Description Examples Autotrophs Heterotroph THINK, PAIR, SHARE Suppose that you ate a hamburger on a wheat roll with lettuce, tomatoes, and onions for lunch. As you ate, you took in food molecules from plants and animals. Explain why all the energy in the food molecules of this hamburger could be traced back to the sun. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ What is ATP and what is its role in the cell? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7 1. What are the reactants of the photosynthesis reaction? A. chlorophyll and light C. carbohydrates and oxygen B. carbon dioxide and water D. high-energy electrons and air 2. What are the products of the light-dependent reactions? A. chloroplasts and light C. oxygen and ATP B. proteins and lipids D. water and sugars 3. Where do the light-independent reactions occur? A. stroma C. chlorophyll B. thylakoids D. mitochondria 8 9