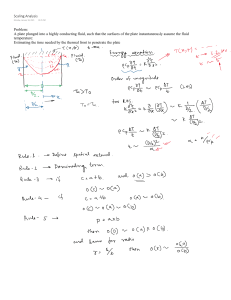
جامعة بيشة كلية الهندسة قسم الهندسة الكهربائية Sheet #1 – Introduction & Fluid Properties 1. Calculate the density, specific weight and weight of one litter of diesel fuel of specific gravity = 0.85. 2 2. If the velocity distribution over a plate is given by 𝑢 = 3 𝑦 − 𝑦 2 in which u is velocity in m/s at a distance y in m above the plate, determine the shear stress at 𝑦 = 0 and 𝑦= 0.15 𝑚. Take dynamic viscosity of fluid as 8 poises. 3. Calculate the dynamic viscosity of an oil, which is used for lubrication between a square plate of size 0.8 m x 0.8 m and an inclined plane with angle of inclination 30° as shown. The weight of the square plate is 300 N and it slides down the inclined plane with a uniform velocity of 0.3 m/s. 4. The space between two square flat parallel plates is filled with oil. Each side of the plate is 60 cm. The thickness of the oil film is 12.5 mm. The upper plate, which moves at 2.5 m/s requires a force of 98.1 N to maintain this speed. Determine the dynamic viscosity of the oil, and the kinematic viscosity of the oil if the specific gravity of the oil is 0.95. 5. A dimensionless combination of variables that is important in the study of viscous flow through pipes is called the Reynolds number, Re, defined as 𝑅𝑒 = 𝜌𝑉𝐷 𝜇 where, as indicated in figure, ρ is the fluid density, V the mean fluid velocity, D the pipe diameter, and μ the fluid viscosity. A Newtonian fluid having a viscosity of 0.38 N∙s/m2 and a specific gravity of 0.91 flows through a 25-mm-diameter pipe with a velocity of 2.6 m/s. Determine the value of the Reynolds number 6. The velocity distribution for the flow of a Newtonian fluid between two fixed wide, parallel plates 3𝑉 𝑦 2 sown in Figure is given as 𝑢 = 2 (1 − (ℎ) ) where V = 1m/s is the mean velocity for fluid of viscosity 0.38 Pa.s and h = 0.1 m. Determine: (a) the shearing stress acting on the bottom wall, and (b) the shearing stress acting on a plane parallel to the walls and passing through the centerline (midplane). Dr. Ali M.A. Attia No excuses just facts جامعة بيشة كلية الهندسة قسم الهندسة الكهربائية 7. The compressed air tank has a volume of 200 liters. Air at temperature of 30 °C and atmospheric pressure of 101.325 kPa (abs) is to be compressed. Determine when the tank is filled at gage pressure of 3 bar the density and the weight of air in the tank. 8. A jet aircraft flies at a speed of 250 m/s at an altitude of 10,700 m, where the temperature is -54 °C. Determine the ratio of the speed of the aircraft, V, to the speed of sound, c at the specified altitude. Assume k = 1.40 9. Pressures are sometimes determined by measuring the height of a column of liquid in a vertical tube. What diameter of clean glass tubing is required so that the rise of water at 20 °C in a tube due to capillary action (as opposed to pressure in the tube) is less than h = 1.0 mm? 10. Calculate the pressure rise for a 2 mm diameter water drop. Use σ = 73 mN/m. 11. Determine the largest diameter of sewing needle that can be supported by water to “float” on top of water. Assume that the needle material is stainless steel with SGss = 7.7. Dr. Ali M.A. Attia No excuses just facts