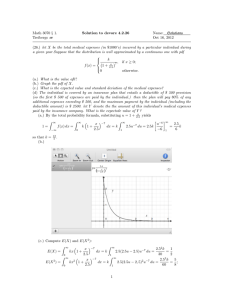
COST SHEET OF PEARL BISCUIT FOR THE YEAR ENDED 2018-19 Particulars Units(Kg) Amount Opening stock of raw materials 1000 10000 Add: Purchases of raw material Sugar Wheat Flour Iodized Salt Yeast Wheat bran Edible Vegetable oil Preservatives Less: Closing stock of raw material 200 400 500 150 250 500 400 20000 4000 2500 15000 2500 3000 12000 (3000) Raw material Consumed Amount 68500 68500 Add: Direct Labour/ Wages 20000 Direct Expenses 60000 PRIME COST 80000 148500 Add: Factory Overheads Indirect Labour 20000 Depreciation on Machinery 4000 Works Overheads 125000 Cost Of maintenance 22000 Other Factory Expenses 10000 Supervisor’s Salary 50000 Power and Fuel 25000 FACTORY/WORKS COST 256000 404500 Add: Office & Administrative Overheads Depreciation on furniture Office Rent Salary to staff Office and general expenses Telephone Expenses Electricity and Lightings Printing and stationary COST OF GOODS SOLD Add: Selling & Distribution Overheads Sales Commission Salary of Salesman Carriage Outward Sales Expenses 25000 12000 25000 55000 20000 15500 15000 120000 400000 250000 12000 167500 572000 782000 COST OF SALES 1354000 PROFITS 46000 SALES 1400000 Now let us look at the cost that are included in Direct material Particulars Sugar Amount 20000 Wheat Flour Iodized Salt 4000 2500 Yeast Wheat bran 15000 2500 Edible Vegetable oil Preservatives 3000 12000 What is the reason behind choosing this particular company and product? The decision to go with this business was made since it is well-established, earning well in the market, and generating an average annual profit over 120 percent of total of its cost. Because it has the largest market share and the majority of sales in the food and beverage business, I choose to make BISCUIT AS my product. Step wise process through which the product is developed After gathering all the raw materials, everything goes into a mixer to be combined. The dough is then kneaded and placed in the oven to bake. Kneading converts the protein to gluten . Mix only until the ingredients come together into combined mass After that, it undergoes a quality and flavour inspection. It then moves on to packing. It then receives final packing and is prepared for market. • It then travels to reputable distributors for additional sales. Departments that were set up for manufacturing are: 1. Purchase Department : The buy department, where purchase requisitions are created and issued to suppliers, is the first and most important department to be established. 2. Material Handling Department: Material handling is the movement protection storage and control of materials and products throughout manufacturing warehousing distribution consumption and disposal. 3. Production Departments: The most crucial department in the entire organisation, as you could guess from the name, is where the entire manufacturing process is carried out. The product is then forwarded to quality control at this point. 4. Quality Control Department: All quality products travel to the packing department after having their quality evaluated here using a variety of tests. If any product doesn't meet requirements, it is thrown here. 5. Packaging Department:. Here, the finished item is brought for packaging and labelling before being dispatched to the distribution department. 6. Distribution Department: The bundled item is now carefully wrapped and delivered to distributors for further product distribution. 7. Customer Care and Complain Department: Here, carefully hired staff members with strong communication skills are on hand to provide customer care, address any inquiries from clients, and address grievances from clients. Cost associated with the production of raw materials Sugar - 200 units x 100 = 20000 Wheat flour-400 units x 10 = 4000 Iodized Salt -500 units x 5 = 2500 Yeast - 150 units x 100 =15000 Wheat bran - 250 x 10 = 2500 Edible vegetable oil -500 units x 6 = 3000 Preservatives -400 units x 30 =12000