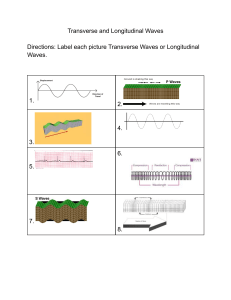
Note taking of General Wave properties and sound waves A wave is a source to transfer energy from one place to another. ● Energy transfers in the direction of a wave. ● Medium does not transfer in the direction of a wave. ● There are two types of waves. i) Longitudinal waves. ii) Transverse waves. ● Longitudinal waves have compressions and rarefactions ● In the longitudinal waves, particles vibrate parallel to the direction of motion of a wave. ● In the longitudinal waves, particles vibrate left right from a rest position. ● Sound waves are longitudinal waves. ● In the transverse waves, particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of motion of a wave. ● Transverse waves have crests and troughs. ● In the transverse waves, particles vibrate up and down from a rest position. ● All electromagnetic (Light, radio, X-rays, gamma rays, ultra violet, infrared) and water waves are transverse waves. ● Wave energy moves horizontally in both (transverse and longitudinal) waves. Compression is a region of high pressure. ● Rarefaction is a region of low pressure. ● Compression is shown by a crest. ● Rarefaction is shown by a trough. ● Distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions is a wavelength Wavefront is a straight line joining all the points on the same crest or trough of a wave. ● Wavefront makes it easier to see a lot of waves moving together. ● Wavefronts are always perpendicular to the waves. Waves front ● The amplitude of a wave is the maximum height of a wave from rest position. ● The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs is called a wavelength. ● Frequency is the number of waves passing a fixed point in one second.