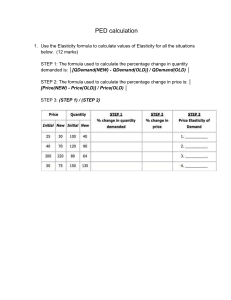
UNIVERISTY OF BOTSWANA FACULTY OF SOCIAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS TEST 1 - 2023/2024 COURSE CODE: ECO 313 DURATION: 75 MINUTES DATE: 15/SEPT/2023 TITLE OF THE PAPER: ENGINERING ECONOMICS________________________ SUBJECT: ECONOMICS TOTAL MARKS: ______________40_________________ INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer All QUESTIONS in Section A,B and C 2. Write your ID. Number, and Surname & initials on the Cover Page of the Answer Book. DO NOT OPEN THIS PAPER UNTIL YOU HAVE BEEN TOLD TO DO SO BY THE SUPERVISOR/INVIGILATOR No. of Pages Excluding Cover 1 SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (1 Mark Each = 20 Marks) Answer ALL Questions using CAPITAL LETTERS for your Answers 1.The fundamental problem of economics is: A) to establish a democratic political framework for the provision of social goods and services. B) the establishment of prices that accurately reflect the relative scarcities of products and resources. C) the scarcity of productive resources relative to economic wants. D) to achieve a more equitable distribution of money income in order to mitigate poverty. 2. According to economists, economic self-interest: A) is a reality that underlies economic behavior. B) is more characteristic of men than of women. C) has the same meaning as selfishness. D) is usually self-defeating. 3. Because of their scarcity, the efficient use of resources is: A) an important issue in all economies. B) an important issue only in centrally planned economies. C) an important issue only in market economies. D) not an important issue. 4. The term "ceteris paribus" means: A) that if event A precedes event B, A has caused B. B) that economics deals with facts, not values. C) other things equal. D) prosperity inevitably follows recession. 5. Which of the following statements is true? A) The process of deriving economic theories and principles is known as policy economics. B) Full employment, price-level stability, and economic growth are widely accepted macroeconomics goals in Botswana. C) Normative economics deals with "what is," whereas positive economics deals with "what ought to be." D) There can be too little of a good thing, but never too much of a good 2 thing. 6. The production possibilities curve illustrates the basic principle that: A) the production of more of any one good will in time require smaller and smaller sacrifices of other goods. B) an economy will automatically obtain full employment of its resources. C) if all the resources of an economy are in use, more of one good can be produced only if less of another good is produced. D) an economy's capacity to produce increases in proportion to its population size. 7. When an economy is operating under conditions of full employment, the production of more of commodity A will mean the production of less of commodity B because: A) of the law of increasing opportunity costs. B) economic wants are insatiable. C) resources are limited. D) resources are specialized and only imperfectly substitutable. 8. Any point inside the production possibilities curve indicates: A) the presence of technological change. B) that resources are imperfectly substitutable among alternative uses. C) the presence of inflationary pressures. D) that more output could be produced with available resources. 9. The law of increasing opportunity costs states that: A) if society wants to produce more of a particular good, it must sacrifice larger and larger amounts of other goods to do so. B) the sum of the costs of producing a particular good cannot rise above the current market price of that good. C) if the sum of the costs of producing a particular good rises by a specified percent, the price of that good must rise by a greater relative amount. D) if the prices of all the resources used to produce goods increase, the cost of producing any particular good will increase at the same rate. Use the following diagram to answer questions 10-11: 3 10. Refer to the above diagram. Flow (1) represents: A) wage, rent, interest, and profit income. B) land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability. C) goods and services. D) consumer expenditures. 11.Refer to the above diagram. Flow (4) represents: A) wage, rent, interest, and profit income. B) land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability. C) goods and services. D) consumer expenditures. 12. The law of demand states that: A) price and quantity demanded are inversely related. B) the larger the number of buyers in a market, the lower will be product price. C) price and quantity demanded are directly related. D) consumers will buy more of a product at high prices than at low prices. 13. The relationship between quantity supplied and price is _____ and the relationship between quantity demanded and price is _____. A) direct, inverse B) inverse, direct C) inverse, inverse D) direct, direct 4 14. In 2003 the price of oil increased, which in turn caused the price of natural gas to rise. This can best be explained by saying that oil and natural gas are: A) complementary goods and the higher price for oil increased the demand for natural gas. B) substitute goods and the higher price for oil increased the demand for natural gas. C) complementary goods and the higher price for oil decreased the supply of natural gas. D) substitute goods and the higher price for oil decreased the supply of natural gas. Use the following to answer questions 15-16: (1) Qd 50 60 80 90 100 (2) Qd 40 50 60 70 80 (3) Price $10 9 8 7 6 (4) Qs 70 60 50 40 30 (5) Qs 80 70 60 50 40 15. Refer to the above table. If demand is represented by columns (3) and (2) and supply is represented by columns (3) and (5), equilibrium price and quantity will be: A) $10 and 60 units. B) $9 and 50 units. C) $8 and 60 units. D) $7 and 50 units 16. Refer to the above table. If demand is represented by columns (3) and (1) and supply is represented by columns (3) and (4), equilibrium price and quantity will be: A) $10 and 60 units. B) $9 and 60 units. C) $8 and 80 units. D) $7 and 30 un Use the following to answer questions 17-18: 5 17. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $60 in this market will result in: A) equilibrium. B) a shortage of 50 units. C) a surplus of 50 units. D) a surplus of 100 uni 18. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A) a shortage of 50 units. B) a surplus of 50 units. C) a surplus of 100 units. D) a shortage of 100 units. 19. Given the equations for demand and supply: Qd = 48 - 4P and Qs = 4P - 16, respectively, the market is in equilibrium when the quantity bought and sold is: A) 8. B) 16. C) 24. D) 32 20. Which of the following statements is true about a downward-sloping demand curve that is a straight line? A) The slope and the elasticity are the same at all points. B) The slope remains the same, but elasticity rises as you move down the demand curve. C) The slope remains the same, but elasticity falls as you move down the demand curve. D) The slope and the elasticity fall as you move down the demand curve. SECTION B: True or False Question (1 Mark Each = 10 Marks) 6 Answer ALL Questions in this section. Write 'True in full' if the statement is true and 'False in full’' if the statement is false. 1) Economics is the social science concerned with the best use of scarce resources to achieve maximum satisfaction of economic wants. 2) Economic theory involves the logical development of hypotheses which are then tested against actual outcomes. 3) The concave, or bowed-out, shape of the production possibilities curve illustrates the law of increasing opportunity costs. 4) Because economic generalizations are simplifications from reality, they are impractical and useless. 5) Positive statements are expressions of value judgments. 6) If A is the dependent variable and B is the independent variable, then a change in A results in a change in B. 7) In the circular flow model, households’ function on the selling side of the resource market and the buying side of product markets. 8) Surpluses drive market prices up; shortages drive them down. 9) If demand increases and supply simultaneously decreases, equilibrium price will rise. 10) The law of supply states that, ceteris paribus, there is an inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied of the good. SECTION C Answer ALL Questions (10 Marks) 1, In 2022 the consumer price index in country X was 127 in 2023 it stands at 153. Calculate the rate of inflation between 2022 and 2023 for country ( 4 marks) 2 Given : q = 100 – 0.95P Calculate the price elasticity of demand when the price is P100 and interpret the coefficient of elasticity (6 marks) 7