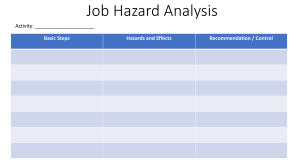
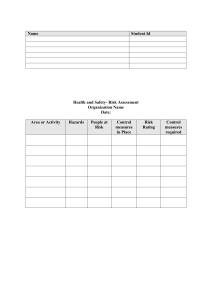
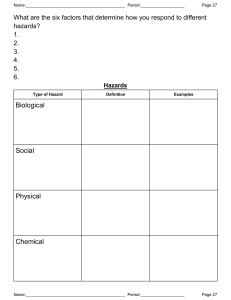
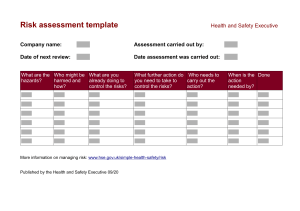
Electrical Safety Importance of Electricity Electricity powers our modern world and daily devices, but mishandling can lead to serious risks. Hazards Awareness Raise awareness of the risks of mishandling electricity to prevent injury and accidents. Safety Guidance Provide guidance on working with electricity safely to avoid potential dangers. Consequences of Unsafe Electrical Practices 🔌⚠️ 1 3 Electrical Shock ⚡️ 2 Electrical Fires 🔥 Improper grounding and lack of insulation can Overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, and lack of lead to dangerous electrical shocks, causing maintenance can spark electrical fires, putting injury or even death. lives and property at risk. Equipment Damage 💸 4 Legal Liabilities 🚨 Neglecting electrical safety can result in Failure to comply with electrical safety damage to valuable equipment and machinery, regulations can result in fines, lawsuits, and leading to costly repairs or replacements. potential legal consequences for the organization. Understanding Electrical Hazards 1 Shock Hazards Electrical shocks can occur when the body becomes part of an electrical circuit, allowing current to flow through the body. This can result in burns, muscle spasms, and even cardiac arrest, depending on the voltage and current involved. 2 Arc Flash Hazards An arc flash is an explosive release of electrical energy that can occur when there is a fault or short circuit in an electrical system. This can lead to severe burns, eye damage, and even fatalities if the appropriate safety precautions are not in place. 3 Fire Hazards Electrical faults, overloaded circuits, and faulty wiring can all lead to the ignition of flammable materials, resulting in devastating fires. Proper electrical safety measures are critical to preventing these hazards. Identifying Electrical Risks Workplace Risks Residential Risks Environmental Risks Common electrical risks in the Electrical risks in the home can Environmental factors such as workplace include exposed live include outdated or faulty wiring, water, humidity, and extreme parts, damaged or worn wiring, overloaded outlets, the use of temperatures can increase the overloaded circuits, and the use damaged electrical cords, and risk of electrical hazards. Proper of improper tools or equipment. the improper installation or insulation, grounding, and the Identifying these risks is the first maintenance of electrical use of weatherproof equipment step in implementing effective appliances and devices. Regular are essential for ensuring safety measures. inspections and updates to electrical safety in challenging electrical systems are crucial for environments. home safety. Proper Grounding and Bonding Error uploading image. Grounding Bonding Grounding is the process of connecting an electrical Bonding is the process of connecting metal parts of system or equipment to the earth, providing a safe an electrical system to ensure they are at the same path for excess current to flow in the event of a fault. electrical potential. This helps prevent the formation of Proper grounding helps prevent the buildup of unintended paths for current flow, which can lead to dangerous electrical charges and reduces the risk of shocks, fires, and other hazards. shocks and fires. Electrical Shock Prevention Eliminate Exposure Implement Safe Work Practices Provide PPE electrical shocks is to eliminate Safe work practices, such as (PPE), such as insulated exposure to live electrical parts. de-energizing equipment, using gloves, face shields, and This can be achieved through proper tools, and following protective clothing, can help the use of insulation, guarding, lockout/tagout procedures, are mitigate the impact of an and other engineering controls. essential for reducing the risk of electrical shock and prevent electrical shocks. serious injuries. The first step in preventing Personal protective equipment Electrical Fire Safety Identify Fire Hazards Common electrical fire hazards include overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, damaged cords, and the improper use of electrical equipment. Regularly inspecting and maintaining electrical systems is crucial for fire prevention. Use Proper Equipment Ensure that all electrical equipment, including wiring, outlets, and switches, are designed and rated for their intended use. Avoid using makeshift or improvised solutions, as these can increase the risk of electrical fires. Install Fire Alarms and Extinguishers Having working smoke detectors and fire extinguishers readily available can help detect and contain electrical fires before they become uncontrollable. Regular maintenance and testing of these safety devices is critical. Train Employees Provide comprehensive training to employees on electrical fire safety, including how to recognize and report potential fire hazards, as well as how to properly use fire extinguishers and other safety equipment. Lockout/Tagout Procedures 1 Preparation Identify all energy sources that need to be controlled, gather the necessary lockout/tagout devices, and ensure that all affected employees are aware of the procedure. 2 Isolation Disconnect the equipment from its energy sources, such as electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic power, and apply locks and tags to the isolation devices to prevent accidental re-energization. 3 Verification Ensure that the equipment is properly isolated by attempting to start or activate it, and check that all energy sources have been effectively controlled. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Insulated Gloves Protect hands from electrical shocks and burns by wearing properly rated insulated gloves when working with live electrical equipment. Face Shields Safeguard the face from the intense heat and bright light generated by arc flashes by using a face shield designed for electrical work. Flame-Resistant Clothing Wear clothing made of flame-resistant materials to protect the body from the thermal effects of an electrical arc flash or fire. Safety Glasses Electrical Safety Training Basic Electrical Safety specialized Electrical Work Refresher Training All employees who may For employees who are required Electrical safety training should encounter electrical hazards to perform specialized electrical be an ongoing process, with should receive training on the work, such as maintenance, regular refresher courses to fundamentals of electrical safety, repair, or installation, more ensure that employees stay up- including how to identify and comprehensive training is to-date with the latest safety avoid common electrical risks, essential. This should cover protocols and are able to apply the importance of proper topics like lockout/tagout them effectively in their day-to- grounding and bonding, and the procedures, arc flash and shock day work. use of personal protective hazard analysis, and the proper equipment. use of specialized tools and equipment. s Maintaining Electrical Equipment Regular Inspections Regularly inspecting electrical equipment, including wiring, outlets, and circuit breakers, can help identify and address potential issues before they become serious hazards. Proper Maintenance Ensuring that electrical equipment is properly maintained, repaired, and replaced as needed can help extend its lifespan and reduce the risk of failures or malfunctions. Upgrades and Replacements Upgrading or replacing outdated or obsolete electrical equipment with modern, code-compliant alternatives can significantly improve safety and reduce the risk of electrical hazards. Documentation and Record-Keeping Maintaining detailed records of electrical inspections, maintenance, and repairs can help Thank you By: Aarav Parekh