Organic Molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
advertisement

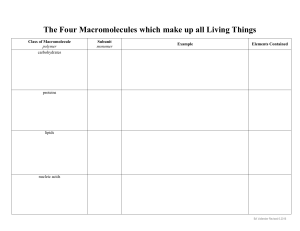
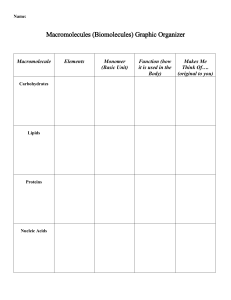
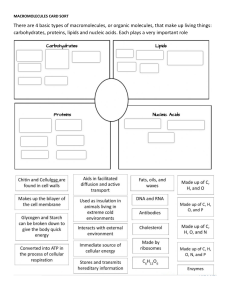
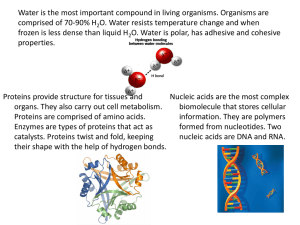
2.3 Molecules of life What organic molecules are found in living organisms? 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic acids Summary of the macromolecules Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Organic molecules Examples Monomers Functions CH2OH Monosaccharides, Carbohydrates disaccharides, polysaccharides O H OH Immediate energy and stored energy; structural molecules H H HO OH H OH Glucose H Lipids Fats, oils, phospholipids, steroids H H H H H C C C C C C H H H H H O H C OH H C OH HO H C OH R Fatty acid H Glycerol Proteins Structural, enzymatic, carrier, hormonal, contractile amino group H2N H C acid group COOH R group Long-term energy storage; membrane components Support, metabolic, transport, regulation, motion Amino acid phosphate P Nucleic acids DNA, RNA base C O S Nucleotide Storage of genetic information 2.4 Carbohydrates 1. What are carbohydrates? • Made of subunits called monosaccharides • Made of C, H and O in which the H and O atoms are in a 2:1 ratio • Function as short and long-term energy storage • Found as simple and complex forms 2.4 Carbohydrates What are simple carbohydrates? • Monosaccharide – 1 carbon ring as found in glucose Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 6 CH2OH 5C CH2OH O O O H H H H H 4 C C 1 OH OH H OH HO C H HO HO C 2 3 OH H H OH C6H12O6 • Disaccharide – 2 carbon rings as found in maltose Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH2OH CH2OH O O O maltose C12H22O11 2.4 Carbohydrates What are complex carbohydrates? • Polysaccharides are made of many carbon rings • Glycogen is the storage form in animals • Starch is the storage form in plants Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CH2OH H O CH2OH O H OH H H OH H H O CH2OH O H OH H H OH H H O CH2OH O H OH H H OH H O H O H OH H H OH H O branched nonbranched starch granule cell wall potato cells © Jeremy Burgess/SPL/ Photo Researchers, Inc. 2.5 Lipids 2. What are lipids? • Molecules that do not dissolve in water • Used as energy molecules • Found in cell membranes • Found as fats and oils, phospholipids and steroids 2.5 Lipids How are fats and oils different? • Fats • Usually animal origin • Solid at room temperature • Function as long-term energy storage, insulation from heat loss and cushion for organs • Oils • Usually plant origin • Liquid at room temperature 2.5 Lipids What is the structure of fats and oils? • A glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid tails Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. H H C H C O OH OH HO + O HO O H C OH HO H H H H C C C C C H H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C H H H H H H H H H H H H C C C C C C H H H H C O H H H dehydration reaction H C O O H H H H C C C C C H H H H O H H H H H H C C C C C C C H H H H H H O H H H H H C C C C C H H hydrolysis reaction H C O H C H H H + 3 H2O H H glycerol 3 fatty acids fat molecule 3 water molecules 2.5 Lipids Understanding fats when reading a nutrition label Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. • Recommendation for total amount of fat for a 2,000 calorie diet is 65g Start here • Be sure to know how many servings there are • A % DV of 5% or less is Limit these low and 20% or more is nutrients high • Try to stay away from Get enough trans fats these • Would you eat the food of nutrients on the right? Why or why not? Nutrition Facts Serving Size 1 cup (228g) Servings Per Container 2 Amount Per Serving Calories 250 Calories from Fat 110 % Daily Value Total Fat 12g Saturated Fat 3g Trans Fat 1.5g Cholesterol 30mg Sodium 470mg Total Carbohydrate 31g Dietary Fiber 0g Sugars 5g Protein 5g 18% 15% Vitamin A Vitamin C Calcium Iron 4% 2% 20% 4% 10% 20% 10% 0% 2.5 Lipids What are steroids? Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. H 3C • A lipid CH3 CH3 H 3C CH3 • Structure is four fused HO a. Cholesterol carbon rings • Examples are cholesterol and sex hormones OH CH3 OH CH3 CH3 HO O b. Testosterone c. Estrogen b: © Warren Toda/epa/Corbis; c: © Tony Marsh/Reuters/Corbis 2.6 Proteins 3. What are proteins? • Made of subunits called amino acids • Important for diverse functions in the body including hormones, enzymes, antibodies and transport • Can denature, change in shape, that causes loss of function 2.6 Proteins What do amino acids look like? Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. H C H O CH2 C O C C CH H3C C O C H O CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 valine (val) (nonpolar) glutamic acid (glu) (ionized, polar) H C lysine (lys) (ionized, polar) O C CH2 H O C C NH C CH2 O C CH2 C O tryptophan (trp) (nonpolar) H aspartic acid (asp) (ionized, polar) SH cysteine (cys) (polar) O 2.6 Proteins What are the four levels of protein organization? • Primary – the linear order of amino acids • Secondary – localized folding into pleated sheets and helices • Tertiary – the 3-D shape of the entire protein in space • Quaternary – combination of more than one polypeptide • All proteins have primary, secondary and tertiary structure, while only a few have quaternary structure 2.6 Proteins What do the levels of organization look like? Primary Structure: sequence of amino acids amino acid COO– peptide bond Secondary Structure: alpha helix or a pleated sheet hydrogen bond C CH CH CH C N R C N R R CH C N R CH C N N R C hydrogen bond C CH C N R CH CH N R (alpha) helix Tertiary Structure: final shape of polypeptide Quaternary Structure: two or more associated polypeptides (beta) sheet = pleated sheet disulfide bond 2.7 Nucleic acids 4. What are nucleic acids? • Made of nucleotide subunits • Function in the cell to make proteins • Includes RNA and DNA 2.7 Nucleic acids What are the 3 parts of a nucleotide? Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. phosphate C P 5' Nucleotide O S 4' 1' 2' 3' sugar nitrogencontaining base 2.7 Nucleic acids What are the five bases found in nucleotides? • Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are double-ringed purines • Cytosine (C), thymine (T) and uracil (U) are single-ringed pyrimidines • In DNA A pairs with T and G pairs with C Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Hydrogen bond H N N H CH2 O C N N H P bases N N O Thymine (T) (DNA only) Adenine (A) A C S N HN C P O S T backbone H C C A N H O P N S G N N H N N P N N H Guanine (G) a. DNA structure with base pairs: A with T and G with C H O CH N H Uracil (U) (RN only) A G T CH U S Cytosine (C) b. RNA structure with bases G, U, A, C 2.7 Nucleic acids Summary of DNA and RNA structural differences? • DNA – Sugar is deoxyribose – Bases include A, T, C and G – Double stranded • RNA – Sugar is ribose – Bases include A, U, C and G – Single stranded