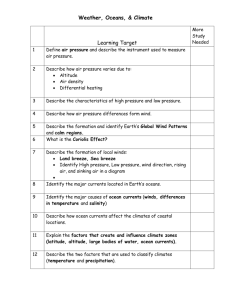
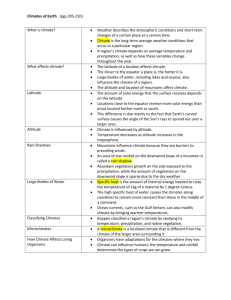
9 Science 9 Quarter 3 – Module 4: Factors Affecting Climate Introductory Message This Self-Learning Module (SLM) is prepared so that you, our dear learners, can continue your studies and learn while at home. Activities, questions, directions, exercises, and discussions are carefully stated for you to understand each lesson. Each SLM is composed of different parts. Each part shall guide you to a stepby-step as you discover and understand the lesson prepared for you. Pre-tests are provided to measure your prior knowledge on lessons in each SLM. This will tell you if you need to proceed on completing this module or if you need to ask your facilitator or your teacher’s assistance for better understanding of the lesson. At the end of each module, you need to answer the post-test to self-check your learning. Answer keys are provided for each activity and test. We trust that you will be honest in using these. In addition to the material in the main text, Notes to the Teacher are also provided to our facilitators and parents for strategies and reminders on how they can best help you on your home-based learning. Please use this module with care. Do not put unnecessary marks on any part of this SLM. Use a separate sheet of paper in answering the exercises and tests. And read the instructions carefully before performing each task. If you have any questions in using this SLM or any difficulty in answering the tasks in this module, do not hesitate to consult your teacher or facilitator. Thank you. ii What I Need to Know In Grade 7 Earth and Space, you have learned about weather and the different factors affecting weather. These factors which you have discussed helped to determine the weather on a day-to-day basis. Description of what a weather is, was emphasized as the condition of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. In this module, you will look into the distinction between weather and climate. You will also be tasked to identify the factors that affect climate as well as its effect on the climate of an area. As you go through this module, you are expected to: 1. Describe climate 2. Identify the factors that affect climate 3. Explain how each factor affects climate What I Know Choose the letter of the correct answer. Write your answers on your answer sheets. 1. It refers to the atmospheric condition over a long period of time? a. Weather c. Monsoon b. Climate d. Typhoon 2. How much is the tilt of the earth’s axis? a. 13.5 c.33.5 b. 23.5 d.43.5 3. It is the distance of a place North or South of the equator. a. Altitude c. Latitude b. Topography d. Ocean currents 4. Which part of the earth receives most of the sun rays? a. Equator c. Northern Hemisphere b. Arctic Zone d. Southern Hemisphere 5. What happens to air temperature when altitude increases? a. Decreases c. remains the same b. increases d. changes 6. What determines the earth’s major climatic zones? a. Winds c. Altitude b. Ocean Currents d. Latitude 7. What causes wind formation? a. Differences in air pressure b. Differences in air temperature c. Equal in air pressure d. Equal in air temperature 8. Coldest places on earth are found near the a. Equator c. Tropics b. Outer space d. Poles 9. Cold current brings water, while warm current takes along water a. cold ,warm c. cold, cold b. warm, cold d. warm, warm 10. which of the following does not influenced climate? a. Altitude c. Magnitude b. Latitude d. Ocean current 11. What will happen when the rates of evaporation and condensation is equal? a. Cloud form b. The dew point is reached c. The humidity increases d. Precipitation occurs 12. How does the windward side differ from the leeward side of a high land? a. The windward receives more precipitation than leeward b. The leeward side has more vegetation than the windward side c. The windward side receives more heat than the leeward side d. The leeward side receives more precipitation than the windward side 13. Why are the coldest places on earth found at the poles? a. Great amount of gaseous particles trap heat from the surface b. Great amount of the thermal radiation is received by these areas c. Less amount of the thermal radiation is received by these areas d. Less amount of gaseous particles trap heat from the surface 14. What happens to water vapor as it rises over the mountain? a. It rises up to the atmosphere b. It moves down at the back of the mountain c. It will result in precipitation on the windward side d. It condenses to form clouds 15. Which cools and heats faster? a. Water c. water and soil b. Soil d. can’t be determined Lesson 5 Factors Affecting Climate What’s In From your discussions of the weather, you were able to learn that weather generally refers to the day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity in the atmosphere particularly in the troposphere. It also describes the interactions of air, water and solar energy in a specific period of time. It’s thought of in terms temperature, humidity, precipitation, brightness visibility and wind on a particular day or hour. To check how well you understood the discussion in weather, you have to go over the following activity. Activity 1 The Weather Taxonomy Objective: To widen one’s vocabulary in weather Task#1: To write down a word for each letter of the alphabet that is related to weather. Write down your answers on the table (copy and fill up the table by writing down a word for each letter of the alphabet that is related to weather A N B O C P D Q E R F S G T H U I V J W K X L Y M Z What’s New This section introduces you to climate. You have to encircle the group of letters which are related to climate. The words can be read vertically, Horizontally, diagonally and backwards. Sixteen words are hidden. Write your answers on your answer sheet. Activity 2 Word Grid – Climate O Q S E A B R E E Z E W E C R T L W I N D W A R D L E Q U A T O R Y W U I O E A P A T S D C L I M A T E N F G I H J O K N L L Z W C R X T W C L V T B T N A U E M U A Q D W E E I R R R M T D R Y U I R O T P D R M T E M P E R A T U R E E U A S D F G H J K D L Z N S X L A N D B R E E Z E T O P O G R A P H Y C V B P R E C I P I T A T I O N What is It Climate describes the average weather condition of a region over a long period of time. It includes the average temperature and amount of precipitation of an area. What factors affect climate? There are several factors that affect climate around the world. The varying influence of this factors lead to the different climate that is experienced around the world. The factors include the following’ 1. Latitude 2. Ocean Currents 3. Wind & Air Masses 4. Elevation (altitude) 5. Relief (topography) 6. Nearness to the bodies of water (continentality) 1. Latitude • Refers to the distance of a place north or south of the equator. Distance from the equator is measured in degrees. The equator is at 0 degree latitude. South or North pole Is at 90 degrees latitude. It dictates the intensity and duration of sun exposure to the earth. • Places at low latitudes (close to the equator) receive greater sunlight than places located at high latitude (far from the equator) • The equator is the portion of the earth which receives the greatest solar energy; thus, it is the warmest or hottest. As a point moves away from the equator, the solar energy it receives decreases. Thus, places in higher latitudes are much colder. • With respect to the latitude, there are three general climate zones which includes: a. Tropic or tropical climate (at tropical latitude) • The amount of solar heating between summer and winter do not differ much, so the average monthly temperature is almost the same throughout the year. b. Temperate climate (in the middle latitude) • From the tropics (23.5 degrees North or South) to the arctic and Antarctic circles (about 60 degrees North or South), solar heating is greater in summer than in winter. In these latitudes, summers are therefore warmer than in winter. c. Arctic climate (in high latitudes) • From mid -latitudes and upward close to the poles, the sun never rises during the large portions of the year. Summers are cool to mild and winters are extremely cold. 2. Ocean currents • Acts as a conveyor belts of warm and cold water, sending heat towards the polar regions and helping tropical areas cool off • Regulate global climate, helping to counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching the earth’s surface. Without currents in the ocean, regional temperatures would be more extreme-super hot at the equator and frigid towards the poles (https://ocean explorer.hoaa.gov) How does ocean currents affect climate? Caused by the global winds blowing across the ocean surface and the differences in water temperature and water salinity • Warm ocean currents that flow towards toward the poles result in warm air masses that move over land causing the climate of the land to be warmer • Cold ocean currents that flow towards the equator results in cold air masses causing the climate of the nearby land to be cooler. 3. Winds and air masses • Earth’s moisture and heat is distributed globally through the global movement of air masses. • Forms when air moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. • Affects climate because they move solar energy from one place to another, causing the temperature in one place to decrease and the temperature in another place to increase. • The humidity and temperature of an air mass depend on the earth’s surface over which it moves. Air masses that originate from high latitudes are colder than air masses that form over low latitudes and the tropics, and those that form over the oceans are relatively humid than those, that form over the continents are relatively dry 4. Elevation (altitudes) • Refers to the height above sea level • The altitude of a place depends on its terrain or the presence of highland and lowland features. • As elevation (altitude) increases, temperature tends to decrease. For every 1000 meter (1 kilometer) rise in the altitude, air temperature decreases by 6.5 degrees Celsius 5. Relief (topography) • Refers to the shape of the land’s surface. • Includes some of the topographical features of the earth (mountains, hills, valleys, mountain ranges, lakes. • As air is forced to rise over the mountain (wind ward side), the temperature decreases and condensation increases. As it condenses, water droplets get bigger and heavier and are forced to fall. Once the air mass goes over the mountain (leeward side), the temperature and evaporation increase but condensation decreases, thus precipitation does not happen; thus creating a rain shadow (dry area on the leeward side of a mountain range). 6. Nearness to bodies of water • Bodies of water such as oceans, rivers, and lakes can affect an area’s climate. It absorbs and releases heat more slowly than land. This quality helps regulates the air temperature over the land nearby • During day time, land heats up faster than water so the air over the land becomes warmer and less dense. It rises and is replaced by a cooler denser air flowing from over the water (sea breeze) • During nighttime, land cools faster than water as does the corresponding air ;thus creating land breeze. It is where the warm air • over the water rises and is replaced by the cooler and denser air from the land. What’s More Activity 3 The Factors Affecting Climate Copy and fill up the table by writing down the ways in which each of the following factors affect climate in your activity notebook. Factors EFFECT ON CLIMATE Latitude Ocean currents Winds and air masses Elevation (altitude) Relief (topography) Nearness to bodies of water What I Have Learned Copy and fill up the Climate Frames with the concepts that you have learned in climate in your answer sheet. Activity 4 CLIMATE FRAMES My chosen word is climate . I know that I know First, I know In addition, I know Finally, I know Now you know something I know . . . . . What I Can Do Activity 5 The Why’s of Climate Answer the following questions. Write your answer in your answer sheet. 1. Why do mountain climbers wear jackets and thick clothes when they go up the mountain? 2. Why do clouds form as air moves over a mountain? 3. Why do some areas that are far from bodies of water have extreme climate? 4. Why do cool surface currents caused the air above them to become cooler? 5. Poland lies at 52-degrees north latitude. Nigeria lies at 9 degrees north latitude. Which country receives more sunlight? Why? Assessment Choose the letter of the correct answer and write it in your activity note book 1. Climate is different from weather in that: a. Climate involves a longer period of time b. Weather lasted for three months c. Climate changes frequently and rapidly d. None of the above 2. During summer, many people visit Baguio because of the cold weather what do you think makes Baguio cold? a. Topography b. Distance from the ocean c. Altitude d. All of the above 3. What happens to air temperature as the altitude increases? a. Remains the same b. Varies c. Increases d. Decreases 4. City A is surrounded by bodies of water and has a moderate climate it is located near the equator. What will most likely affect the climate of the city? a. Altitude b. Latitude c. Topography d. All of the above 5. There are three general climatic zones with respect to latitude, which one is not? a. Polar b. Tropic c. Temperate d. Equatorial 6. As latitude increases, the intensity of solar energy; a. decreases b. increases c. stays the same d. varies 7. As you move away from the equator towards the north and south poles, temperature becomes; a. varies b. stays the same c. cooler d. hotter 8. Mountains are cooler than low lands because; a. Low lands are closer to the oceans b. There are fewer mountains near the oceans c. Air temperature decreases 6.5 degree Celsius for every 1km rise in the ocean d. None of the above 9. Which side of a mountains receives the most precipitation? a. Leeward side b. Windward side c. Rain shadow d. Peak 10. Why do places at the same latitude but different altitudes have different climates? a. The amount of heat received varies. b. The amount of precipitation varies c. The higher altitudes have lower temperature d. The higher altitudes have higher temperature 11. Why does cloud formation disappears the air moves slowly towards the leeward side of the mountain? a. The air condenses as it moves to the leeward side b. The amount of water vapor is not enough c. The temperature becomes lower d. There is too much water vapor 12. How do oceans currents affect climate? a. Ocean currents either warm or cool the air above them b. Ocean currents just warms the air above c. Ocean currents just cools the air above d. Ocean currents changes the climate of a certain area 13. How does body of water regulate the temperature of a certain region or country? a. Body water warms the air of a certain region or country b. Body of water cools the air of a certain region or country c. Body of water circulates the warm air and cold air of a certain region or country d. Body of water moderates the temperature 14. What is the relationship between altitude and temperature of a place? a. As the altitude increases, temperature decreases b. As the altitude decreases, temperature decreases c. As the altitude increases, temperature increases d. As the altitude increases, temperature remains the same 15. Which or the following best describes climate? a. The weather that occurs in the atmosphere within a day b. The pattern of weather that occurs in a region over a long period of time c. The pattern of weather that occurs in a region over a short period of time d. The disturbance in the atmosphere that happens in a long period of time Additional Activities Complete each the statement below by providing answers in the blanks. Write your answers on your answer sheet. A. Latitude 1. When the area is farther from the equator, the air temperature is . 2. When the area is to the equator the air temperature is higher. 3. The sun’s rays strike vertically in places near the . B. Ocean currents 4. The current flows in a clockwise direction in the . 5. The current flows in a direction in the southern hemisphere . 6. The clockwise and counter clockwise direction of these ocean currents are caused by the . C. Winds and air masses 7. Air masses that originate from high latitudes are . 8. Air masses that form over and warmer. 9. Earth’s and is distributed globally through the global movement of air masses. D. Elevation (altitude) 10. Air temperature as the altitude increases 11. For every rise in the altitude, air temperature decreases by 6.5 degree Celsius 12. As the altitude , air temperature increases E. Relief/ topography 13. The dry region on the leeward side is called the . 14. The side of the mountain facing the wind and has low temperature is the . 15. The side of the mountain which experiences high temperature is the . F. Nearness to bodies of water 16. Bodies of water can affect an areas . 17. absorbs and releases heat more slowly than land. 18. Places that are the oceans have moderate climate as the body of water regulates temperature . References Abistado,j.,andM.Valdoz.2014.Science Links. Work text in science and technology. Manila ,Philippines.Rex Book Store,inc. Alvarez,L.et.al.2014.Science 9 Learners Module. Philippines . FEP Printing Corporation. https://education.seattlepi-com.what are the four factors that influence weather https://www.birdsvilleschools.net https://en.m.wikipedia.org.LOWERN https://mountainstudiesinstitute.squarespace.com.Factors that affect climate worksheet