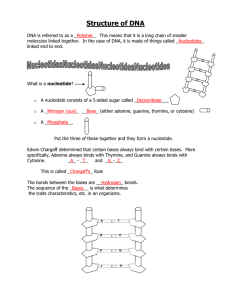
DNA vs. RNA DNA: DNA stands for “deoxyribonucleic acid.” It contains genetic instructions that allow organisms to grow and function. RNA: RNA stands for “ribonucleic acid.” It executes the instructions given by DNA and synthesizes proteins. DNA RNA - A type of nucleic acid - Double-stranded helix - Located in the nucleus of a cell - Contains deoxyribose sugar for its backbone - Contains the following nitrogenous bases: • adenine • guanine • cytosine • thymine - Main type: mostly occurs as B-form DNA - Also a nucleic acid - Single-stranded - Located in the nucleus and cytoplasm - Contains ribose sugar for its backbone - Contains the following nitrogenous bases: • adenine • guanine • cytosine • uracil - Main types: mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA Cytosine Adenine NH₂ NH₂ N C N H C C HC N N N CH C Thymine O O C C N H N H CH CH₃ CH N C C C N H C C N C N N N CH O C NH₂ - Sugar covalently bonds to phosphate groups forming RNA’s backbone with nitrogenous bases binding the two strands - Adenine hydrogen bonds to thymine - Guanine hydrogen bonds to cytosine FACT SHEET HN O C C N H CH N H CH O O NH C C Guanine Uracil HC N H N HC CH O C NH₂ NH₂ Guanine O HN C Cytosine Adenine CH CH N C N H C C HC N NH C NH₂ - Sugar covalently bonds to phosphate groups forming RNA’s backbone with nitrogenous bases formed according to the bases from DNA - Adenine hydrogen bonds to uracil - Guanine hydrogen bonds to cytosine Scan for more resources!