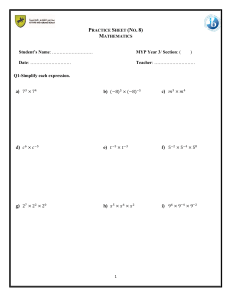
MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Grade 6 (MYP 1) Unit Timeline 29 August 2023 – 19 January 2024 22 January 2024 – 21 June 2024 Unit Title Desktop Solutions (Product Design) Scratch Education Games Development (Digital Design) Key concept Creativity Systems, Creativity Related Concept Function, Form Collaboration, Function Global Context Scientific and Technical Innovation Scientific and Technical Innovation Modern desks require innovative solutions in order to satisfy their function with creative form Educating younger students in adaptive and innovative ways, beyond the school curriculum, allows the expression of ideas and differentiation at a more meaningful level. Statement of Inquiry Content Factual Questions Conceptual Questions In this hands - on project, Grade 6 students will design and create a desk organiser for PYP students. They will research and explore different design opportunities while considering size, functionality, safety and aesthetics. Using hand tools, students will manufacture their desk organisers, developing skills in measuring, cutting, drilling, sanding and assembling. They will evaluate their products for functionality and durability, seeking feedback from the target audience. Through this project, students will gain practical experience in product design, woodworking and problem - solving while understanding the importance of user-centred design for a specific audience Students will enhance their coding skills through the creation of an Educational Video Game. This project will encourage active communication, research and creative thinking using the Design Cycle. Throughout this Design Cycle students will research and investigate different design opportunities, develop key success criteria to generate ideas and present their chosen designs. They will acquire computational thinking skills using Scratch to create their digital projects. Students will evaluate their products by designing and conducting relevant testing methods and discuss the impact of their solution on the target audience. What are the characteristics of a functional product? What technology can we use to aid our learning? What is the best point when starting an evaluation? Is Scratch used for block-based coding? Where can we evaluate a product? What factors make an educational game successful? Why would we adapt a functional product? Do we all learn the same way? How might we start an evaluation? To what extent can games aid our learning? Why do we need to develop a product? Debatable Questions Is a functional product a successful one? Is technology always useful for learning? Who should determine if a product is functional are needs to be adapted? Is a computer always needed for the best Design outcome? Why would we develop a functional product? Could creating more screen-time for students be detrimental to their health? What age groups would most benefit from using an educational game? ATL Communication: Communication: Social: Research: Self-management: Thinking: Thinking: MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Risk takers: Students will be encouraged to experiment and take risks with their design ideas to create innovative solutions. Students will demonstrate risk taking in the presentation of assessments, using a wide variety of media to do so. Learner Profile Focus Commnicators: Students need to communicate with their client in order to satisfy their needs. Students will use a variety of media to do this including sketches, presentations, and evaluation surveys. Balanced: Students will need to balance form and function when creating their solutions. Their designs will need to be innovative and aesthetically pleasing yet functional for the intended user. Assessment Criteria A-D Inquirers: Researching existing products to inform with own product designs. Investigate and experiment with ideas. Investigate software options for producing own games. Researching how to complete various software related tasks through tutorials and online learning tools. Communicators: Students will need to communicate with their intended target audience for their game (PYP students). They will interview and survey PYP students to gain insight into their educational needs and survey them to evaluate the success of their games. Risk takers Students will be encouraged to experiment and take risks with their design ideas to create innovative solutions. Students will demonstrate risk taking in the presentation of assessments, using a wide variety of media to do so. A-D MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Grade 7 (MYP 3) Unit Timeline 29 August 2023 – 19 January 2024 22 January 2024 – 21 June 2024 Unit Title Sustainable Timepiece (Product Design) Sustainable House Design (Digital Design) Key concept Global Interactions Creativity Global Interactions Related Concept Adaptation, Innovation, Resources, Sustainability Function, Innovation, Sustainability. Global Context Globalization and sustainability Globalization and sustainability Global interactions have shown that the world has a finite amount of resources, by being innovative we can reduce waste and adapt products to give them a sustainable life cycle beyond the original use. Students will design and manufacture an up-cycled clock for one of three potential clients. They will further develop their hand tool skills and have the option to incorporate laser cutting into their designs. Research and investigation will guide their understanding of client preferences and the importance of sustainability in Design. Students will develop key design specifications, learn to communicate effectively through the medium of sketching and apply practical workshop skills to re-purpose materials and create the clock. A final evaluation and reflection on functionality, aesthetics and user experience will complete the project, fostering design thinking and creativity. Modern homes require creative and innovative solutions to ensure limited consumption of increasingly scarce natural resources which depend on creating sustainable and divergent designs. Statement of Inquiry Students will enhance their knowledge of sustainability through the creation of an Eco - Friendly Home. This project will encourage active communication, research and creative thinking using the Design Cycle. Throughout this Design Cycle students will research and investigate different design opportunities, develop key success criteria to generate ideas and present their chosen designs. They will develop their 3D Modelling skills to create their digital projects. Students will evaluate their products by designing and conducting relevant testing methods and discuss the impact of their solution on the target audience Definition of 6 R's - students will need to define the 6Rs and upcycling, including the similarities and differences to aid them when discussing ideas. Content Using empathy in a design context - students will need to take empathy skills and relate them to a design context when looking at a problem and justifying it. Types of research sources - students will need to know if their research is from a primary or secondary sources and how to recognize specific materials; Developing designs around an established item - the students designs will be based around an existing component, they will need to be shown how to design around this. Use of a range of hand tools and machinery - for use when developing the practical work Factual Questions Types of data found when testing - students should know the difference between qualitative or quantitive data Which finite resources do humans use every day? What materials are used in traditional home design? Where do we dispose of all the waste produced by the finite resources? What impact does traditional home design have on the environment? What sector is the largest contributor to waste of resources What 3D modeling software can be used to model an eco home? MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Conceptual Questions Debatable Questions ATL How can we sustain the lifecycle of products beyond their original form? How can modern homes adapt to become more sustainable? If we are not sustainable, who will the waste we produce impact the most? How does eco design impact our environment? Why would we reuse material to adapt products beyond their original use Who would benefit from having an eco home? Would global interactions always help to reduce the human impact on the environment? What makes an eco home aesthetically pleasing? Why should we be innovative in our designs? Where in the world is most suitable for eco homes? Who should adapt the products to allow for a sustained lifecycle? Which is the best software to create an innovative 3d model? Communication: Communication: Social: Self-management: Self-management: Research: Research: Thinking: Thinking: Communicators: Working alongside peers to problem solve issues that arise using Google Sketch-up software. Caring: Learner Profile Focus Supportive of peers throughout all lessons, particularly when presenting individual Dream House tours. Students will consider the impact sustainable design on the environment and how it effects people, globally. They will design houses that provide solutions to existing problems such as climate change. Risk takers: Students will be encouraged to experiment and take risks with their design ideas to create innovative solutions. Students will demonstrate risk taking in the presentation of assessments, using a wide variety of media to do so. Assessment Criteria A-D A-D MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Grade 8 (MYP 3) Unit Timeline 29 August 2023 – 19 January 2024 22 January 2024 – 21 June 2024 Unit Title Formula One Car Design (Product Design) Well-Being Mobile Application (Digital Design) Key concept Creativity, Form, Development. Development Related Concept Evaluation, Function, Innovation Innovation, Ergonomics, Function Global Context Scientific and Technical Innovation. Scientific and Technical Innovation Statement of Inquiry An understanding of the balance of form and function is required to develop innovative and aerodynamic formula one cars The development of innovative and ergonomic mobile apps can provide functionality for systems that improve lives Content Students will learn and apply Computer Aided Design skills through the creation of a 3D visual model of an F1 model Car. These projects will encourage active communication, research and creative thinking using the Design Cycle. Throughout this Design Cycle students will research and investigate different design ideas, develop key success criteria to generate ideas and present their chosen cars. They will acquire product development knowledge using 3D Computer Aided Design software. Students will evaluate their products by designing and conducting relevant testing methods and discuss the impact of their solution on the target audience. Students will enhance their App Development skills through the creation of a Mobile App designed to improve student well - being. This project will encourage active communication, research and creative thinking using the Design Cycle. Throughout this Design Cycle students will research and investigate different design opportunities, develop key success criteria to generate ideas and present their chosen designs. They will acquire app development knowledge using dedicated app design software to create their projects. Students will evaluate their products by designing and conducting relevant testing methods and discuss the impact of their solution on the target audience What is 3D modelling and how can it help us when designing an F1 Car? What are the key principles of user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design, and how do they influence the overall effectiveness of a website's design and functionality? What is aerodynamics and how does it effect F1 racing? What is the significance of web accessibility in web design, and how can designers ensure that websites are accessible to individuals with disabilities? Factual Questions Describe the concept of visual hierarchy in web design. How does it impact the aesthetics of a website, and what techniques can be employed to establish an effective visual hierarchy on a web page? Why would F1 teams employ 3D modelling to design F1 cars? Why is it important for an F1 car to be aesthetically pleasing? Conceptual Questions Accessibility and Inclusivity: How can web designers ensure that their websites are accessible to individuals with disabilities, and what are the ethical implications of neglecting accessibility in web design? User-Centered Design: What is the significance of user-centered design principles in the creation of effective and user-friendly websites, and how can designers balance user preferences with business goals? Responsive Design and Cross-Browser Compatibility: How does responsive web design contribute to a positive user experience, and what strategies can be employed to ensure that a website functions consistently across various browsers and devices? MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Should F1 teams be required to make more environmentally sustainable vehicles? Between Form, and Function, which plays a bigger role in the design of an effective F1 car? Is minimalist web design more effective than visually complex designs in terms of user engagement and conversion rates? Should web designers prioritize mobile-first design strategies over desktop-first approaches, considering the growing prevalence of mobile device usage? Debatable Questions To what extent should web designers prioritize accessibility features, such as alt text for images and keyboard navigation, in their designs, even if it potentially compromises aesthetics or functionality for some users? Communication: Communication: 1.2c Make inferences and draw conclusions 9c. Design new and improved machines, media and technologies Research: 1.1c Use a variety of media to communicate with a range of audiences Interpret and use effectively modes of non-verbal communication Social: Thinking: 8d. Draw and test conclusions and generalizations ATL Self-management: Problem Solve Plan short- and long-term assignments; meet deadlines Research: 6a. Search effectively, collect and record information 6e. Identify primary and secondary sources Learner Profile Focus Inquirers: Inquirers: Students inquire how 3D modelling softwares can enhance the aerodynamics of an F1 car. Students explore real-life applications of these softwares, such as wind tunnel simulations and discover how to apply these softwares in other capacities. Students will carry out research and learn to find reliable sources of information to help them identify key principles in app design. Risk takers: Students are encouraged to take risks with their designs and think more concept based rather than a recreation of existing F1 car designs. This unit involves Primary and Secondary research to gather data and learn about various app design techniques. The knowledge they gain from their research will promote a deeper understanding of the course they could possibly be studying themselves in the near future. Students will also learn to use dedicated design software as part of the app creating process. Reflective: Students critically evaluate the success of their solutions in Criterion D, to determine the impact of their F1 Car designs on their chosen target audience. Knowledgeable: Communicators: Students will communicate to a target audience and provide content about their chosen area of wellbeing. Reflective: MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Students will evaluate the app that they create and suggest improvements. They will evaluate their learning throughout the unit. Assessment Criteria A-D A-D MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Grade 9 (MYP 5) Unit Timeline 29 August 2023 – 19 January 2024 22 January 2024 – 21 June 2024 Unit Title Flat Pack Farm (Product Design) Web Design (Digital Design) Key concept Communities Aesthetics, Creativity Related Concept Innovation, Resources, Sustainability Form, Function, Innovation. Global Context Globalisation and sustainability Scientific and Technical Innovation Statement of Inquiry For Communities to be truly Sustainable, they must find a balance between consumption and production. To help achieve UN SDG’s #11 and #12, we need to be Innovative with the Resources available to us. Content In grade 9 product design, students will complete the 'Flat Pack Farm' unit, addressing UN Sustainable Development Goals 11 and 12. They will gain a deeper understanding of globalization and sustainability, focusing on human impact, consumption, and urban planning. Students will develop critical thinking and communication skills while designing their own sustainable flat-pack farms and utilizing CAD/CAM for laser-cutting parts. This engaging experience will empower them to be globally aware citizens, making a positive difference. Factual Questions A successful website requires creative aesthetics to innovatively provide an attractive function, as well as, satisfying a modern and unique form. What does it mean to have a balance between consumption and production? Students will enhance their Web Design skills through the creation of a personal interest website, designed for a teen UAE audience. This project will encourage active communication, research and creative thinking using the Design Cycle. Throughout this Design Cycle students will research and investigate different design opportunities, develop key success criteria to generate ideas and present their chosen designs. They will acquire website development knowledge using dedicated design software to create their projects. Students will evaluate their products by designing and conducting relevant testing methods and discuss the impact of their solution on the target audience. What is the most suitable, open source web-design software? Where does your food come from? Can evaluating existing products enhance the technical knowledge of the web-designer? What resources are available to us? What do we mean by virtual environment? What foods can we grow in our climate? What are the benefits to growing plants at home? Conceptual Questions How can you make your community more sustainable? How can we evaluate the reliability of a source of information? What are the challenges to growing crops in urban areas like cities? Can the developer rely only on web-based applications to reach an advanced level of creativity? To what extent is creativity an essential skill in today's information age? Do you think we should be concerned about food supply in the UAE? Debatable Questions As individuals, how big of an impact can we make a difference to sustainability in our communities? Are people beginning to depend only on the World Wide Web as a resource to find reliable information? What is creativity? Which impacts the user experience more, form or function? MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Communication: Communication Social: ATL Social Self-management: Research: Self-management Thinking: Research Communicators: Students need to communicate with their client in order to satisfy their needs. Students will use a variety of media to do this including sketches, presentations, and evaluation surveys. Learner Profile Focus Risk-takers: Students will be encouraged to experiment and take risks with their design ideas to create innovative solutions. They will need to balance form and function while creating unique mobile technology organisers. Students will also demonstrate risk taking in the presentation of assessments, using a wide variety of media to do so. Reflective: Students will consider the impact of their final product on their client/target audience overall. They will use evaluation tools such as surveys, interviews, expert appraisal, and user trial to reflect on how successful they were in meeting their clients design specifications. Inquirers: Students will carry out research and learn to find reliable sources of information. They will create external hyperlinks to source websites using recognised conventions. Knowledgeable: This unit involves Primary and Secondary research to gather data and learn about various programming techniques. The knowledge they gain from their research will promote a deeper understanding of the course they could possibly be studying themselves in the near future. Students will also learn to write code in HTML and apply this knowledge to implement an online support guide. Communicators: Students will communicate to a target audience and provide content about a chosen product/topic. Reflective: Students will evaluate the website that they create and suggest improvements. They will evaluate their learning throughout the unit. Assessment Criteria A-D A-D MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Grade 10 (MYP 5) Product Design 4 December 2023 – 21 June 2024 Unit Timeline 29 August 2023 – 1 December 2023 Unit Title Decorative Lasercut Project Key concept Communication, Creativity, Systems Related Concept Invention, Markets and trends, Sustainability Function, Innovation, Invention Personal and cultural expression: Craft, Creation, Products Personal and cultural expression: Craft, Creation, Products Scientific and technical innovation: Adaptation, Products Scientific and technical innovation: Adaptation, Products Through their engagement with this unit, students will construct a contextualized conceptual understanding of how creativity, craftsmanship, and technology intersect in the realm of product design, specifically in the context of decorative lasercut projects. They will develop an appreciation for the importance of effective communication in design processes and recognize the role of systems thinking in creating aesthetically pleasing and functional decorative pieces. The Decorative Lasercut Project is a hands-on unit designed to introduce Grade 10 students to the world of product design through the creative exploration of decorative lasercutting techniques. Students will delve into the process of designing and fabricating intricate and visually appealing decorative items using a laser cutter machine. This unit encourages students to unleash their imagination, develop problem-solving skills, and refine their craftsmanship while gaining a deeper understanding of design principles and materials. Creativity is an essential element in the invention and innovation of products that meet the needs of a specific community. What are the different types of materials that can be used for decorative lasercut projects, and what are their unique properties and characteristics? What is an open-ended brief? Global Context Statement of Inquiry Content Factual Questions Conceptual Questions Open Design Project Communities, Creativity Students will enhance their computational thinking skills through the creation of a physical product to meet the needs of a Client/Target Audience through an Open Design Brief. These projects will foster active communication, research, and creative thinking, while utilizing the Design Cycle. Throughout this process, students will explore various design opportunities, establish essential success criteria, and showcase their chosen designs. They will acquire knowledge of product development using a range of Computer Aided Design software and Manufacturing. Moreover, students will evaluate their products by designing and implementing appropriate testing methods, as well as analyze the impact of their solution on the target audience. What are the drivers for invention? What is User Centered Design? How do different finishing techniques, such as painting, staining, or surface treatments, impact the overall aesthetics and durability of lasercut decorative pieces? How does the integration of creativity and technology enhance the design process in the context of decorative lasercut projects? How do you design an innovative product, that solves a problem and has a sustainable life cycle? How can users be included in the design of products that meet their specific needs and wants? MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 How can products be designed to reflect the users beliefs and values? How does an understanding of systems thinking help designers consider the interdependencies and interactions between various design elements in a decorative lasercut piece? Should students be encouraged to prioritize functionality or aesthetics when designing and creating decorative lasercut pieces? Which aspect holds more significance in the context of product design? Which of Rogers characteristics of innovation and consumers have the biggest impact on the creation of new products? Should their be a responsibility on designers to create sustainable products? Debatable Questions To what extent does the use of laser cutting technology in decorative projects enhance or diminish the value of traditional craftsmanship and handmade artistic expression? Communication: Communication: Social: 1.1a: Students give an receive peer feedback and assessment before the end of each assignment. Self-management: 1.1d: Students use a variety of sketching, images and writing to communicate their product to their audience. 3Research: 6a: Students are required to gather data in Criterion A in order to best research their target audience. Also, in Criterion D students are required to gather feedback through interviews, surveys etc. regarding their product in order to reflect effectively and progress their skills further for the following year. ATL 1.1g: Students must negotiate project ideas with peers and the teacher in order to create an effective solution to the educational toy topic. 1.1j: Students use a variety of mediums such as Onenote and Forms to share ideas with peers and their audiences. 6n: Students are required in Criterion A to effectively identify primary and secondary resources and use them to better analyse the market they are targeting. 1.2c: Students must understand their audiences to the best extent in order to draw a successful conclusion to their product. Thinking: 1.2l: Students must use information provided by both Math and Design in order to create a successful product and to create an innovative assignment. 8o: Students must study and identify a variety of solutions and continue to analyses each for their effectiveness toward the problem. Social: 8p: Regular challenges and obstacles will face the students, which they must learn to overcome and foresee in future. 2e: All students must Design and create a unique product, whereby, they use tools responsibly and safely. 8r: Students are required to use innovative 3D modeling programmes to create areas of their design with lasercutting and 3d printing and try to explore these programmes to the fullest extent. 2i: Students must be open to change and reflect on their project continuously in order to create a successful product. Self-management: 9a: Students are encouraged to create visual diagrams to help create successful assignments rather than text based. 9i: Students are required to ensure their work is original and unique, however, also solves the problem effectively. 3a: Students must manage their time effectively and create mini deadlines in order to successfully meet the larger summative deadlines. 3d: Each students is creating their own product which allows all students to create challenging goals toward their own needs. MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 10b: Students are encouraged to inquire and use their knowledge within Design to help solve unfamiliar problems. This is done in Criterion B whereby they must create a variety of ideas rather than one conclusion. 10g: Within Grade 8-9, students learnt the basis of 3D modeling. In Grade 10 students must use this knowledge and put it into physical practice. 4.5d: Students are constantly introduced to new programmes and methods of creating a product. They must embrace change in order to make an innovative product for their audience. 5a: Students are encouraged to become reflective learners and develop new skills in the workshop and online to effectively increase their attitude toward learning the subject. 5f(ii): Gifted and talented students are encouraged to peer teach others around them to help increase their skills and also help weaker students meet their goals effectively. Research: 6a: Students are required to gather data in Criterion A in order to best research their target audience. Also, in Criterion D students are required to gather feedback through interviews, surveys etc. regarding their product in order to reflect effectively and progress their skills further for the following year. 6n: Students are required in Criterion A to effectively identify primary and secondary resources and use them to better analyse the market they are targeting. Thinking: 8o: Students must study and identify a variety of solutions and continue to analyses each for their effectiveness toward the problem. 8p: Regular challenges and obstacles will face the students, which they must learn to overcome and foresee in future. 8r: Students are required to use innovative 3D modeling programmes to create areas of their design with lasercutting and 3d printing and try to explore these programmes to the fullest extent. 9a: Students are encouraged to create visual diagrams to help create successful assignments rather than text based. 9i: Students are required to ensure their work is original and unique, however, also solves the problem effectively. 10b: Students are encouraged to inquire and use their knowledge within Design to help solve unfamiliar problems. This is done in Criterion B whereby they must create a variety of ideas rather than one conclusion. 10g: Within Grade 8-9, students learnt the basis of 3D modeling. In Grade 10 students must use this knowledge and put it into physical practice Learner Profile Focus Inquirers: Inquirers: Students will be encouraged to explore and investigate different materials, design techniques, and cultural influences related to decorative lasercut projects. During each class discussion is promoted and encouraged to ask questions about these new technologies. Students are introduced to the real-life examples of the programmes that they use and how it will apply to them later in life if they choose this route. They will develop essential inquiry skills by asking questions, conducting research, and seeking answers to design-related challenges. Thinkers: Through iterative design processes, students will embrace a sense of curiosity and openmindedness, continuously refining their ideas and seeking innovative solutions. During the use of these complex programmes, students are required to think creatively and use their concrete knowledge of the subject. The need to think uniquely to create an innovative product. Knowledgeable: Caring: Students will acquire a solid foundation of knowledge regarding design principles, materials, laser cutting technology, and digital design software. The students must show empathy toward the children who will use their product. This will enhance a sense of duty toward the child's learning and will help them to make it unique and successful. MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 They will engage in research and analysis to understand the characteristics and properties of various materials suitable for laser cutting, considering aspects such as durability, aesthetics, and sustainability. Reflective: Students are encouraged in Criterion D to gather feedback and reflect on their project. They are recommended to use this newfound knowledge to help build their skills toward the following year. By examining existing decorative designs and studying different cultural influences, students will develop a broader understanding of the historical, cultural, and social contexts of design. Communicators: Throughout the unit, students will practice effective communication skills by presenting their design concepts, sharing their design thinking process, and providing constructive feedback to peers. They will develop skills in visual communication by creating design sketches, digital renderings, and prototypes to articulate their ideas and convey their intended aesthetic. Collaborative activities, such as group projects or peer critiques, will encourage students to express their thoughts, actively listen, and engage in meaningful dialogue, fostering effective communication and teamwork. Assessment Criteria A-D A-D MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Grade 10 (MYP 5) Digital Design Unit Timeline 27 August 2023 – 10th January 2024 Unit Title Marketing in a Digital World Key concept Communities Related Concept Adaptation, Form Global Context Scientific and Technical Innovation Statement of Inquiry Content Factual Questions Conceptual Questions 11 January 2024 – 15th June 2024 Designing for Success: Business Digital Solutions Communication, Creativity, Systems To successfully market a company to a specific community, the form of a website must be adapted to appeal to the consumer’s tastes, values and aspirations. Students will enhance their computational thinking skills through the creation of a digital product and an Open Design Brief. These projects will foster active communication, research and creative thinking, while utilising the Design Cycle. Throughout this process, students will explore various design opportunities, establish essential success criteria and showcase their chosen designs. They will acquire knowledge in product development using a range of software and programming languages. Moreover, students will evaluate their products by designing and implementing appropriate testing methods, as well as analyse the impact of their solution on the target audience. How can copyright laws and fair use guidelines be applied when using third-party content in videos? Collaboration, Function, Invention Scientific and technical innovation The successful design of a digital product for a local business requires an understanding of the target audience's needs, effective communication with the client, and the application of design principles and techniques. In this unit, students will explore the field of digital design by creating a practical product for a local business. Students will develop their skills in website development, app creation, or database design while considering the needs and requirements of a real-world client. By engaging with the design cycle, students will work collaboratively and demonstrate their understanding of the subject's key concepts, global contexts, and skills. What are the best practices and principles of user-centered design that can be applied in creating a digital product for a local business? What are some commonly used video editing software or tools? What are the specific technological tools and programming languages commonly used in website/app development or database design for local businesses? How does the medium of video differ from other forms of communication in terms of its impact and effectiveness? How does the design of a digital product for a local business reflect and convey its brand identity and values to the target audience? How does the creation of videos support the development of critical thinking and creativity skills? What impact can sustainable design practices have on the development and implementation of a digital product for a local business, both in terms of environmental considerations and long-term viability? How does video production contribute to the cultivation of digital literacy and media fluency? What are the essential elements of effective visual communication in videos? Debatable Questions To what extent does the production quality of a video affect its ability to effectively communicate a message? Should there be guidelines or regulations regarding the use of videos for promotional purposes within the school community? To what extent should the design of a digital product prioritize aesthetics over functionality in order to attract and engage the target audience for a local business? MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 Should students be involved in the decision-making process for video content creation within the school? What ethical considerations should be taken into account when collecting and utilizing user data in the development of a digital product for a local business, and how can these considerations be balanced with the need for personalized experiences? 1. Communication Skills: ATL: Communication - How: Students will be explicitly taught and practiced communication skills through various activities such as video scriptwriting workshops, peer feedback sessions on video content, and group discussions on effective verbal and non-verbal communication techniques. Skill Indicator: Effectively communicating design ideas, project updates, and feedback to peers, clients, and stakeholders. - Where: These skills can be explicitly taught and practiced during language arts classes, media studies classes, and dedicated video production workshops. 1. Teaching and Practice Approach: - When: Communication skills will be continuously reinforced throughout the unit, especially during video planning, scripting, recording, and editing stages. - How: Students will be explicitly taught effective communication strategies and techniques through class discussions, modeling, and examples. They will learn how to articulate their design ideas clearly, provide constructive feedback, and present project updates professionally. 2. Research Skills: - Where: Communication skills will be practiced during collaborative group work, client meetings, peer feedback sessions, and formal presentations. - How: Students will be explicitly taught and practiced research skills by guiding them on how to conduct thorough research on their video topics, evaluate sources for credibility, and integrate information effectively into their video content. - Where: These skills can be explicitly taught and practiced in dedicated research sessions within the school library, computer labs, or through online research platforms. - When: Research skills will be explicitly taught and practiced during the pre-production phase of the video creation process when students gather information and develop a strong understanding of their chosen topics. 3. Critical Thinking Skills: ATL - How: Students will be explicitly taught and practiced critical thinking skills through activities such as analyzing and evaluating the effectiveness of existing videos, engaging in debates on ethical considerations related to video production, and reflecting on the impact and implications of their own video creations. - When: Communication skills will be continuously developed throughout the unit, with specific focus given during group work sessions, client interactions, and formal presentation preparations. Regular feedback and reflection opportunities will allow students to refine their communication skills. 2. Self-Management Skill Indicator: Planning and organizing tasks effectively, meeting project deadlines, and managing time and resources efficiently. Teaching and Practice Approach: - How: Students will be explicitly taught strategies for effective planning, organization, and time management. They will learn techniques for setting goals, breaking tasks into manageable steps, prioritizing, and creating timelines. - Where: These skills can be explicitly taught and practiced in classroom discussions, reflection sessions, and structured analysis of video examples. - Where: Self-management skills will be practiced during individual and group work sessions, project planning stages, and throughout the design process. - When: Critical thinking skills will be continuously developed and reinforced throughout the unit, especially during the analysis and reflection stages of video production. - When: Self-management skills will be emphasized from the beginning of the unit and reinforced throughout. Students will have dedicated time to plan and organize their work, and regular checkpoints will be set to ensure progress and timely completion of tasks. 4. Self-Management Skills: - How: Students will be explicitly taught and practiced self-management skills through activities that promote organization and time management, such as creating production timelines, setting individual and group goals, and monitoring progress throughout the video production process. 3. Thinking - Where: These skills can be explicitly taught and practiced during dedicated project management sessions or incorporated into regular classroom routines. Teaching and Practice Approach: - When: Self-management skills will be emphasized from the beginning of the unit to ensure students effectively plan, allocate resources, and meet deadlines during the video creation process. 5. Social Skills: - How: Students will be explicitly taught and practiced social skills through collaborative video production tasks, such as working in teams to plan, film, and edit videos, giving and receiving constructive feedback, and resolving conflicts that may arise during the creative process. Skill Indicator: Applying critical thinking skills to analyze design challenges, generate innovative ideas, and make informed decisions. 1. How: Students will be explicitly taught critical thinking strategies and techniques, such as brainstorming, problem-solving frameworks, and analytical thinking. They will learn to identify design challenges, consider multiple perspectives, and evaluate potential solutions. 2. Where: Thinking skills will be practiced during individual and group brainstorming sessions, design critiques, and reflection activities. 3. When: Thinking skills will be fostered throughout the unit, with a particular emphasis during the initial research and ideation phases. Students will engage in discussions, collaborative problem-solving, and reflection activities to develop their critical thinking abilities. MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025 - Where: These skills can be explicitly taught and practiced during group work sessions, peer review activities, and structured team-building exercises. - When: Social skills will be continuously developed and practiced throughout the unit, especially during the collaborative stages of video production. 5. Research Skill Indicator: Conducting research to gather relevant information, analyzing data, and using credible sources to inform design decisions. Teaching and Practice Approach: - How: Students will be explicitly taught research methodologies, information literacy skills, and techniques for gathering and analyzing data. They will learn how to identify reliable sources, evaluate information critically, and extract relevant data for their design process. - Where: Research skills will be practiced during the initial client and target audience research, competitive analysis, and gathering user feedback during usability testing. - When: Research skills will be developed and practiced throughout the unit, with specific emphasis during the early stages of the design process. Students will engage in research activities, cite credible sources, and critically analyze data to inform their design decisions. Communicator: Students will be encouraged to effectively express their ideas, thoughts, and messages through videos, using appropriate visual and verbal communication techniques. They will also develop active listening skills to understand and respond to feedback from peers and teachers. Inquirer: Students will demonstrate curiosity and enthusiasm as they explore different video production techniques, research various topics, and investigate the power of videos as a communication medium. They will ask questions, seek information, and deepen their understanding of the role and impact of videos. Learner Profile Focus Reflective: Students will engage in reflective practices throughout the video creation process. They will reflect on the purpose and intended message of their videos, evaluate their own strengths and areas for improvement, and consider the impact and implications of their creations on the school community. Caring: Students will demonstrate empathy and concern for the needs and interests of their target audience when creating videos. They will strive to create content that promotes inclusivity, diversity, and a sense of belonging within the school community. Reflective: Students will engage in reflection on their learning, growth, and achievements throughout the unit. They will critically analyze their video creations, identify areas of improvement, and set goals for future video projects. Assessment Criteria Inquirers: Students will be encouraged to ask questions, explore local businesses, and conduct research to gather information about the client's needs and target audience. They will develop their inquiry skills by investigating design challenges and seeking innovative solutions. Knowledgeable: Students will deepen their understanding of design principles, user-centered design, and the use of appropriate technologies and tools for creating digital products. They will acquire knowledge about different programming languages, UX design principles, and ethical considerations in digital design. Thinkers: Students will engage in critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making throughout the design process. They will analyze design challenges, generate creative ideas, and make informed decisions based on their research and reflection. Communicators: Effective communication is crucial in this unit. Students will practice articulating their design ideas, providing feedback, and presenting their work to clients, peers, and stakeholders. They will develop their communication skills in written, oral, and visual forms. Principled: Ethical considerations are important in digital design. Students will explore the ethical implications of data privacy, security, and consent in their design choices. They will develop a principled approach by considering the impact of their designs on the local business, its audience, and the wider community. A-D A-D MYP Design Unit Planning Overview 2024-2025