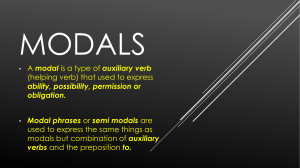
II Modals Modals & Types Verbs Main Action State Bare Infinitive Infinitive ‘to’ Usage: imperative/infinitive Auxiliary Be Perfective Modals Modals: are they always one word? Modals Phrasal Modals He must eat his food. He has to eat his food. Modals: Some Facts Can modals change their base form? He mays come soon. Modals are single words that always have the same form. What is the issue of these sentences? I can waiting for him./ You must to leave. We use modals before the base forms of other verbs. What about ought to? Modals: Some Facts Which is correct? Can you speak Arabic? OR Do you can speak Arabic? I couldn’t swim fast. OR I didn’t could swim fast. We do not use do with modals in Qs and negation. Why? What is the difference between the two? We’ll leave at 8a.m. / We will leave at 8a.m. ‘Shall’, ‘will’, and ‘would’ are contracted. Modals: Some Facts Which is correct? 1a) She didn’t know she can speak English. 1b) She didn’t know she could speak English. 2a) I was hoping you may give me some advice. 2b) I was hoping you might give me some advice. We usually use ‘could’, ‘might’, and ‘would’ in embedded clauses after past tense verbs, especially in indirect speech. What is the issue here: We will can win this game. Phrasal Modals: Some Facts can (ability) be able to will be going to can / may (permission) be allowed to should be supposed to must have to Phrasal Modals are verb phrases beginning with be or have which can be used instead of modals. Are they similar then? No. ‘must’ is different than ‘have to’ Can we put phrasal modals together? I’m going to have to go to the shop for more bread. When do we use phrasal modals instead of modals? We may be going to increase the salary. 1) after a modal He seems to be able to do everything. 2) where an infinitive form is needed I love being able to sit outside in the sun. 3) where a gerund form is needed They have had to wait for hours. 4) where the perfective form is needed She is having to pay extra money. 5) where a continuous form is needed Modals’ Types Modals Phrasal Modals He must eat his food. He has to eat his food. Complex Modals Complex Modals Prediction Will Would Be going to Shall Prediction: Will ‘Will’ is used for many reasons: Predictions. What we think is most likely. Do not call them! They will be sleeping. It will rain tomorrow. Prediction: Will vs. Would Compare between the two sentences: You will look better without that blue tie. You would look better without that blue tie. ‘Will’ is used for predictable situations whilst ‘Would’ is used for hypothetical situations. Prediction: Will vs. Would (with the perfective tense) Compare between the two sentences: It’s not good phoning at midnight. Everyone will have gone to bed. Life in the Middle Ages was harsh. You would have hated it. ‘will’ = prediction about an event that has already have happened at some future time (future perfect) / ‘would’ = prediction about an imaginary past event. Prediction: Going to (vs. would) Look at the sentences: I am going to visit my grandmother. Be careful! You’re going to drop it! ‘Going to’ = decision already made (before moment of speech). ‘Going to’ = When something is starting to happen. Do we use ‘was going to’ or ‘would’ for past actions? I was going to do law but changed my mind. I would go to law but changed my mind. How can we use ‘would’ & still make it correct? Prediction: Will vs. Going to Compare between the two sentences: Too much coffee will give you a headache. He’s going to get a headache from drinking all that coffee. ‘will’ = predictions based on past experience & knowledge. / ‘going to’ = predictions based on what we feel & think now. Prediction: ‘Shall’ We already talked about ‘Shall’ 1) We make offers & suggestions or ask for suggestions. 2) Express determination. Shall I close the door? Let’s try again, shall we? We lost a battle, but we shall never give up. Willingness Habits Preferences Will Would Willingness: Will vs. Would I will give you one more chance. Most people would pay more for better healthcare. ‘Will’ = We are definitely willing now. / ‘Would’ = willingness in the future. Can you help me carry these books? Oh, I would help you, but I’ve injured my back. ‘Would’ = ‘willing but not able to’