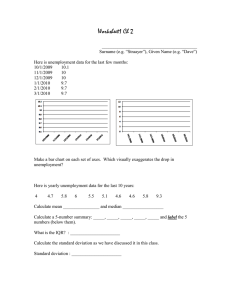
Effectiveness of Supply-side Policies Market based supply side policy • Direct tax cuts, reductions in unemployment benefits, labor market reforms, deregulation, and privatization are examples of market-based supply-side policies. • The goal of these policies is to boost aggregate supply and market forces. They might also hinder rather than boost economic growth, which would go against the goals of income redistribution and unemployment reduction. Effects of Reduced Unemployment Benefits and Income Tax • Reductions in unemployment insurance and income taxes could shift wealth from those with low incomes to those with higher incomes. • As a result of privatization, affluent people and organizations now hold state-owned businesses. • Some privatized businesses raise the cost of their goods, which lowers lowincome people's income. • Deregulation and labor market reforms can lower low-income people's relative wages. • Due to a lack of job openings, a lack of skills, or variances in job locations, cuts may not always result in an increase in employment and growth. • Employees keeping their disposable income and spending more time relaxing are examples of unintended outcomes. • Due to a lack of competition, privatization might not improve productivity or reduce manufacturing costs. • As monopolies, state-owned businesses might be auctioned off, which could result in mergers. Interventionist Supply-side Policy Overview • Involves government's larger role in the economy. • Policy tools include government spending on education, training, infrastructure, and technological improvement. • Potential benefits include increased economic growth, reduced inflation, improved balance of payments, reduced unemployment, increased development, and reduced income inequality. • Risks include potential ineffectiveness of education and training in areas not in demand, and potential structural unemployment from technological advancements.