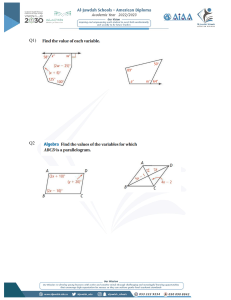
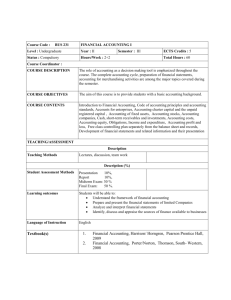
BM2: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT & TQM FIRST SEMESTER: MIDTERM PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN Major Factors in Design Strategy 1. Cost 2. Quality 3. Time-to-Market 4. Customer Satisfaction 5. Competitive Advantage Idea Generation (Sources of Ideas for New or Redesigned Products and Services) 1. Internal Sources a. Research and Development (R&D) Organized efforts to increase scientific knowledge or product innovation. 2. External Sources a. Customers b. Suppliers c. Competitors Reverse engineering o Dismantling and inspecting a competitor’s product to discover product improvements. Design Considerations 1. Product/Service Life Cycle Incubation, growth, maturity, saturation, and decline. 2. Standardization Extent to which there is an absence of variety in a product, service or process. Standardized products are immediately available to customers. Mass Customization o A strategy of producing standardized goods or services but incorporating some degree of customization. o Tactics in Mass Customization a. Delayed Differentiation A postponement tactic, producing but not quite completing a product or service until customer preferences or specifications are known. b. Modular Design A form of standardization in which component parts are subdivided into modules that are easily replaced or interchanged. BM2: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT & TQM FIRST SEMESTER: MIDTERM PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN It allows: (1) easier diagnosis and remedy of failures; (2) easier repair and replacement; (3) simplification of manufacturing and assembly. c. Reliability The ability of a product, part, system to perform its intended function under a prescribed set of condition. Failure is a situation in which a product, part, or system does not perform as intended. Normal Operating Condition is a set of conditions under which an items reliability is specified. d. Robust Design Design results in products or services that can function over a broad range of condition. Designing for Production 1. Concurrent Engineering Bringing together of engineering design and manufacturing personnel early in the design phase. 2. Computer Aided Design (CAD) Designing products using computer graphics. Advantages o Increases productivity of designers, 3 to 10 times. o Creates a database for manufacturing information on product specifications. o Provides possibility of engineering and cost analysis on proposed designs. Designing for Manufacturing 3. Recycling Recovering materials for future use. Reasons for recycling o Cost savings o Environment concerns o Environment regulations 4. Remanufacturing Refurbishing used products by replacing worn-out or defective components. BM2: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT & TQM FIRST SEMESTER: MIDTERM PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN Reliability 1. Independent Events Events whose occurrence or non-occurrence do not influence each other. 2. Redundancy The use of backup components to increase reliability. Rule #1 If two or more events are independent and success is defined as the probability that all these events occur, then the probability of success is equal to the product of the probabilities of the events. Rule #2 If two events are independent and success is defined as the probability that at least one of the events will occur, the probability of success is equal to the probability of either one plus 1.00 minus the probability multiplied by the other probability. Rule #3 If three events are involved and success is defined as the probability that at least one of them occurs, the probability of success is equal to the probability of the first one (any of the events), plus the product of 1.00 minus that probability and the probability of the second event (any of the remaining events), plus the product of 1.00minus each of the first two probabilities and the probability of the third event, and so on. This rule can be expanded to cover more than three events. BM2: OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT & TQM FIRST SEMESTER: MIDTERM PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGN PRACTICE SET Rule #1 .92 x .89 = 0.8188 Rule #2 .92 + (1 - .92) x .80 .92 + 0.08 x .80 .92 + 0.064 = 0.984 Rule #3 1 – [(1 - .90)(1 - .85)(1 - .70)] 1 – [(0.1)(0.15)(0.3)] 1 – 0.0045 = 0.9955 1 – [(1 - .93)(1 - .80)(1 - .79)] 1 – [(0.07)(0.2)(0.21)] 1 – 0.00294 = 0.9970 Total System Reliability 0.8188 x 0.984 x 0.9955 x 0.9970 = 0.7996 Rule #1 .92 x .92 x .89 = 0.7532 Rule #2 .93 + (1 - .93) x .80 .93 + 0.07 x .80 .93 + 0.056 = 0.986 Rule #3 1 – [(1 - .90)(1 - .85)(1 - .70)(1 - .70)] 1 – [(0.1)(0.15)(0.3)(0.3)] 1 – 0.00135 = 0.9986 Total System Reliability 0.7532 x 0.986 x 0.9986 = 0.7416