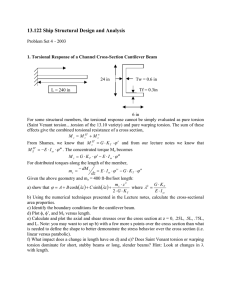
Torsion in 3D Printing: Enhancing Design and Performance Torsion principles play a crucial role in 3D printing, improving material selection, design optimization, and component validation. This cohesion advances modern engineering solutions across various industries. Material Properties and Torsion 1 3 Shear Modulus 2 Shear Stress Determines material Critical for components behavior under twisting experiencing torsional forces. loads. Shear Strain Indicates material deformation under torsional stress. Optimizing 3D-Printed Designs 1 Analyze Geometry Consider polar moment of inertia for cross-section design. 2 Adjust Parameters Increase diameter or create different infill pattern/ structures for enhanced resistance. 3 Reduce Material Create lightweight yet strong components for various applications. Torsion Testing for 3D-Printed Components Specimen Preparation Create standardized 3D-printed test samples. Apply Controlled Forces Subject specimens to precise twisting loads. Analyze Results Assess mechanical performance and validate component integrity. Elastic and Plastic Deformation Elastic Behavior Materials exhibit elasticity up to their yield point. Plastic Deformation Occurs beyond yield point, affecting dimensional stability. Material Selection Choose materials with high elasticity for critical applications. Bambu Lab X1-Carbon: Advanced 3D Printing High-Speed Printing Achieves rapid production without compromising quality. Precision Engineering Delivers accurate prints for complex torsion-resistant designs. Multi-Material Capability Supports various filaments for diverse mechanical properties. Applications in Aerospace and Automotive Turbine Blades Engine Components Withstand high torsional Maintain structural integrity loads during operation. under twisting forces. Safety Assurance Prevent failures that could lead to catastrophic outcomes. Addressing Nominal Stress Assumptions Layer-by-Layer Construction Material Property Variations Anisotropy Real-World Conditions Stress Distribution Performance Reliability Future of Torsion in 3D Printing Infrastructure Medical Implants Robotics 3D-printed structures optimized for Customized implants with enhanced Advanced components with superior torsional loads. torsional properties. torsional resistance. Conclusion: Advancing Engineering Solutions 1 3 Interdisciplinary Approach 2 Enhanced Performance Combining torsion Creating components mechanics with 3D that withstand complex printing technology. loading conditions. Innovation Driver Pushing boundaries in material science and manufacturing techniques.