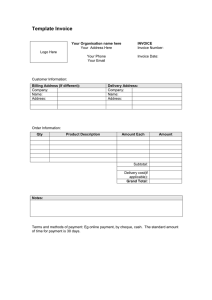
By: Mr Deneshweren ▪ Recognise and understand the following business documents: invoice, debit note, credit note, statement of account, cheque, receipt. ▪ Understand the use of business documents as sources of information. ▪ Complete pro-forma business documents. ▪ Understand trade discount. ▪ Invoices are used by a business at the time of a credit sale (on credit). ▪ The customer (顾客) who receives the original invoice uses it as a record of his/her credit purchases (提供者). The supplier keeps a copy of the invoice as a record of his/her credit sales. ▪ Therefore, the same document can be a sales invoice or a purchases invoice. ▪ A sales invoice is a copy of an invoice retained by a seller when a credit sale is made. ▪ A purchases invoice is the invoice received by a customer for a credit purchase made. LO1&2 LO1&2 LO1 ▪ The list price (牌价) is the price at which the trader usually sells the product. ▪ A trade discount (交易优惠) is given to customers who buy in bulk. It is a deduction on the list price. ▪ A cash discount (现金折扣) is given to customers for paying their debts promptly. LO4 LO1&3 ▪ A debit note is a request from a customer to a supplier to reduce the total amount charged on an invoice. ▪ A customer will issue a debit note if: ▪ The supplier has made a mistake and has overcharged ▪ Goods were not received because they were lost or stolen in transit ▪ The customer has returned unsatisfactory or damaged goods. Page 70 Coursebook LO1&2 LO1 ▪ A debit note can also be issued by a seller (Supplier) instead of an invoice to revise (upwards) the amount of an invoice already issued. ▪ The supplier as well as the customer will make accounting entries to record the debit note in the same way as the original invoice was recorded and the customer’s account will be debited in the books of the seller. LO1&2 ▪ A credit note is a document issued by a supplier if the total price it has charged a customer on an invoice is more the amount that needs to paid. ▪ This can happen because: ▪ The supplier made a mistake and overcharged the customer ▪ The customer did not receive goods because they were lost or stolen in transit ▪ The customer has returned unsatisfactory or damaged goods. Page 71 Coursebook LO1&2 LO1 ▪ At the end of each month, a supplier will usually issue each customer with a statement of account. ▪ A statement of account is a document issued by the (supplier) seller of goods on credit to summarise the transactions for the month. ▪ The purpose of a statement of account is to remind customers of the amount due to their suppliers. ▪ The customer can also use the statement of account to check the statement against their own records to ensure that no errors have been made by either the supplier or themselves. ▪ No need for customer or supplier to record in their book-keeping. Page 72 Coursebook LO1&2 LO1 ▪ A cheque is a written order to a bank to pay a stated sum of money to the person or business named on the order. ▪ The payee (the person to whom the cheque has been issued), lets say supplier, will receive payment in a way that is safe and convenient. ▪ Each cheque has a perforated edge that allows it to be detached from its counterfoil. The counterfoil remains in the cheque book and is used as a source document by the payer (the customer) to record the payment in their accounting records. ▪ When the cheque is deposited in the bank, a paying-in slip is completed. ▪ Page 73 Coursebook LO1&2 ▪ A receipt is a formal written acknowledgement that a business has received money in payment following a sale. ▪ A cash receipt is usually provided to a customer who pays in cash. ▪ Page 74 Coursebook LO1&2 ▪ All documents ▪ Types of Discount ▪ Sales/Purchases uses what document