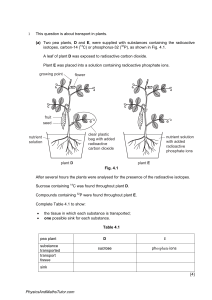
1 In tulip plants, the petals can have markings called flecks. There are two alleles for flecks in tulip plants: with flecks F; and without flecks f. (a) Explain the meaning of the term dominant allele. ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................. [1] (b) A tulip grower crosses two tulip plants. He finds that 76 of the offspring have petals with flecks and 23 of the offspring have petals without flecks. (i) Complete the genetic diagram to explain this result. parental genotypes ………………… X ………………… parental phenotypes ………………… X ………………… gametes .... .... X .... .... offspring genotypes …………………………… …………………………… offspring phenotypes petals with flecks present petals without flecks [5] (ii) The tulip grower wants to produce a pure-breeding variety of tulips with petals without flecks. State the genotypes of the parent plants he should use to produce tulip plants without flecks. Explain your answer. parental genotypes ………………… X ………………… explanation ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [2] [Total: 8] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 2 (a) Sickle cell anaemia is an inherited disease. The gene for haemoglobin exists in two forms, HbN and HbS. People who are HbSHbS have the disease and experience symptoms including fatigue and extreme pain in their joints. People who are HbNHbS are carriers of the disease and may have mild symptoms, if any at all. (i) Table 2.1 shows four genetic terms. Complete Table 2.1 by stating a specific example, used in the paragraph above, of each genetic term. Table 2.1 genetic term example used in the passage an allele a heterozygous genotype a homozygous genotype phenotype [4] (ii) Sickle cell anaemia is not found throughout the whole world. Most cases of the disease occur in sub-Saharan Africa and in parts of Asia. The distribution is similar to that for the infectious disease malaria. Explain why the distribution of sickle cell anaemia and malaria are similar. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[5] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (b) Down’s syndrome is an example of a characteristic that shows discontinuous variation. State the cause of Down’s syndrome. ................................................................................................................................................... ...............................................................................................................................................[1] (c) Explain how discontinuous variation differs from continuous variation, in its expression and cause. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ...............................................................................................................................................[3] [Total: 13] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 3 (a) Sickle cell anaemia is a genetic disorder that is found among people in certain parts of the world. A sample of blood was taken from a person with sickle cell anaemia and examined with an electron microscope. Fig. 4.1 shows some of the red blood cells in the sample. Fig. 4.1 Explain the problems that may occur as these cells circulate in the blood system. [4] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (b) The gene for haemoglobin exists in two alternative forms: HA HS codes for the normal form of haemoglobin; codes for the abnormal form of haemoglobin. (i) State the name for the alternative forms of a gene. [1] (ii) A child has sickle cell anaemia. The parents do not have this disorder. Complete the genetic diagram to show how the child inherited the disorder. Use the symbols HA and HS in your answer. parental phenotypes normal × normal parental genotypes HAHS × HAHS + gametes child’s genotype ................... child’s phenotype sickle cell anaemia [2] (iii) The parents are about to have another child. What is the probability that this child will have sickle cell anaemia? [1] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (c) The maps in Fig. 4.2 show the distribution of sickle cell anaemia and malaria in some parts of the world. distribution of malaria Indonesia and the Philippines key malaria distribution of sickle cell anaemia key sickle cell anaemia Fig. 4.2 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com northern Australia (i) Explain why sickle cell anaemia is common in people who live in areas where malaria occurs. [4] (ii) Suggest why sickle cell anaemia is very rare among people who live in Indonesia and northern Australia. [2] [Total: 14] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 4 (a) The production of human gametes involves the type of nuclear division known as meiosis. State two reasons why meiosis is suitable for gamete production. 1 2 [2] (b) The sex of a human fetus is determined by the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Fig. 5.1 shows the determination of sex in four different examples. Examples 3 and 4 show sex determination in twins. example gametes zygote cell from a fetus 1 X + X XX XX 2 X + Y XY XY XX 3 X + X XX XX X + X XX XX X + X XX XX 4 Fig. 5.1 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (i) Use 5.1 to explain how the sex of a fetus is determined. [2] (ii) Examples 3 and 4 show two ways in which twins are formed. The twins in example 3 are identical. Use Fig. 5.1 to explain why. [2] (c) During the development of a fetus, different genes are expressed at different times. Explain what is meant by the term development. [2] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (d) One of the genes that controls the ability of blood to clot is found only on the X chromosome. XH represents an X chromosome with the dominant allele for normal blood clotting. Xh represents an X chromosome with the recessive allele which causes the blood to clot slowly. The Y chromosome is small and does not have the gene for blood clotting. Here is a list of four genotypes. XHXH, XHXh, XHY, XhY Choose the genotype from the list that matches each of the following: ● gives a phenotype of long clotting time; ● is heterozygous; ● is homozygous. [3] (e) Haemophilia is a rare genetic condition in which the blood clots very slowly. In the USA, haemophilia affects 1 in 5000 male births each year. In some cases these births occur in families where the condition has not occurred before. Explain how boys can have haemophilia when the condition has not previously existed in their family. [2] [Total: 13] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 The four o’clock plant, Mirabilis jalapa, can have flowers of three different colours as shown in Fig. 4.1. yellow flower crimson flower orange-red flower Fig. 4.1 (a) A student crossed some crimson-flowered plants with some yellow-flowered plants (cross 1). She collected the seeds and grew them. All of the plants that grew from these seeds had orange-red flowers. Complete the genetic diagram to explain the result of cross 1. parental phenotypes crimson flowers × yellow flowers parental genotypes A CA C × AYAY .............. + .............. gametes offspring genotype ................ offspring phenotype ........................ [3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (b) The student then carried out three further crosses as shown in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 cross ross 2 offspring of cross 1 × offspring of cross 3 offspring of cross 1 × crimson-flowered plant 4 offspring of cross 1 × yellow-flowered plant geno of offspring Complete Table 4.1 by writing the genotypes of the offspring of crosses 2, 3 and 4, using the same symbols as in the genetic diagram in (a). Write the genotypes in Table 4.1. You may use the space below for any working. [3] (c) Flower colour in M. jalapa is not an example of the inheritance of dominant and recessive alleles. Explain how the results of the crosses show that these alleles for flower colour are not dominant or recessive. [3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Flowers from M. jalapa were cross-pollinated. (d) Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination. [2] (e) Some species of plants are self-pollinated. Discuss the long-term effects of self-pollination on the evolution of these plants. [4] [Total: 15] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 2 Haemoglobin is a large protein molecule. The structure of each haemoglobin molecule is controlled by a gene that has two alleles: • HbA codes for the normal form of haemoglobin, • HbS codes for an abnormal form of haemoglobin. Red blood cells containing only the abnormal form of haemoglobin become a stiff, sickle shape in conditions of low oxygen concentration. This gives rise to sickle cell anaemia. (a) Describe the harmful effects on the body of having red blood cells which become sickle-shaped. [5] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com People who are heterozygous for the gene for haemoglobin produce both the normal and abnormal forms of haemoglobin. These people show no symptoms or have very mild symptoms known as sickle cell trait. (b) (i) Complete the genetic diagram to show how a couple who are both heterozygous may have a child with sickle cell anaemia. parental phenotypes sickle cell trait × sickle cell trait parental genotypes ................ × ................ gametes .............. .............. offspring genotypes ................ ................ offspring phenotypes ........................ ........................ + .............. .............. ................ ................ ........................ ........................ [3] (ii) What is the chance of a child born to this couple having sickle cell anaemia? [1] In some parts of the world, up to 25% of the population have sickle cell trait. (c) State the advantage of having sickle cell trait. [1] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (d) Discuss whether sickle cell trait is an example of codominance. [2] [Total: 12] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 3 Two species of beetle, Tribolium castaneum and T. confusum, can infest and eat stored flour. In an investigation these two species were kept together in containers of flour under different environmental conditions. Many identical containers were set up, each with the same mass of flour. Equal numbers of male and female flour beetles of the two species were put into each container at the start. The numbers of beetles were counted regularly. The containers were left until only one species survived. Table 5.1 shows the percentage of containers in which T. castaneum or T. confusum were the only survivors. Table 5.1 environmental conditions percentage of containers in percentage of containers in which only T. confusum which only T. castaneum survived / % survived / % A hot and wet 100 0 B hot and dry 10 90 C warm and wet 86 14 D warm and dry 13 87 E cold and wet 29 71 F cold and dry 0 100 (a) Compare the survival of the two species of flour beetle in different temperatures and humidities. Use data from Table 5.1 to illustrate your answer. [4] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (b) Suggest why only one species survived in each container. [2] There is a gene in T. confusum which controls body colour. A represents the dominant allele for red-brown body colour. a represents the recessive allele for black body colour. (c) Complete the genetic diagram below to show the colour of beetles produced when heterozygous beetles are crossed with beetles that are homozygous recessive for this gene. parental phenotypes ............................ × ............................ parental genotypes ............................ × ............................ gametes ............. ............. + ............. ............. offspring genotypes ........................................................ offspring phenotypes ........................................................ ratio of phenotypes ........................................................ [4] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com The eyes of Tribolium species are usually black. A very small number of flour beetles have white eyes. (d) Explain how this happens and why they are so rare. [2] (e) Insect pests, such as flour beetles, eat the flour and deposit nitrogenous waste in urine and faeces into the flour. This leads to the growth of bacteria and fungi in the flour. Suggest and explain what happens to the nitrogenous waste and the faeces released by the flour beetles. [4] [Total: 16] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Fig. 2.1 shows the root systems of two species of desert plant, A and B. A B soil level 20 m Fig. 2.1 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (a) Describe the two root systems shown in Fig. 2.1 and explain how each is an adaptation for survival in a desert ecosystem. [4] (b) Describe and explain two ways in which the leaves of desert plants reduce water loss in transpiration. 1. 2. [4] (c) Xylem and phloem are transport tissues in plants. They transport substances from organs that are known as sources to organs known as sinks. Complete the table to show: • • • two substances being transported in each tissue an organ that is a source for substances being transported in each tissue an organ that is a sink for substances being transported in each tissue. tissue substances being transported source of substances in the plant sink for substances in the plant 1 ………………… xylem 2 …………………. 1 ………………… phloem 2 …………………. [6] [Total: 14] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 2 (a) Define the term self-pollination. [2] Snapdragon plants have flowers with three colours: red, pink and white. Some students investigated the inheritance of flower colour in snapdragons. In cross 1 they cross-pollinated plants that were homozygous for red flowers with plants that were homozygous for white flowers. They collected and planted the seeds from cross 1. All of the resulting plants had pink flowers. In cross 2 they self-pollinated all the pink-flowered plants and found that in the next generation there were red-flowered plants, white-flowered plants and pink-flowered plants. (b) Complete the genetic diagrams to show how flower colour is inherited in snapdragon plants. Use the symbol IR for the allele for red flowers and IW for the allele for white flowers. cross 1 parental phenotypes red flowers × white flowers parental genotypes ........... × ........... gametes ........... ........... offspring genotypes ................... offspring phenotypes pink flowers PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com cross 2 parental phenotypes pink flowers × pink flowers parental genotypes ........... × ........... gametes offspring genotypes ........... ........... …………………………………………………………………………………………. ratio of offspring phenotypes ……………………………………………………………………………………… [4] (c) Another student cross-pollinated pink-flowered plants with white-flowered plants. Complete the genetic diagram to show the results that the student would expect. phenotypes pink flowers × white flowers genotypes ........... × ........... gametes offspring genotypes ........... ........... …………………………………………………………………………………………. ratio of offspring phenotypes ……………………………………………………………………………………… [3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (d) Explain the advantages of sexual reproduction to a species of flowering plant, such as the snapdragon. [4] [Total: 13] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 3 (a Define the term gene. [1] The medical condition sickle cell anaemia is widely distributed in Africa, parts of Asia and the Americas. People with sickle cell anaemia have red blood cells with an abnormal form of haemoglobin. The gene for haemoglobin exists in two forms: HN = allele for normal haemoglobin HS = allele for abnormal haemoglobin (b) Complete the genetic diagram below to show how two people who are heterozygous for this gene may have a child who has sickle cell anaemia. Use the symbols HN and HS in your answer. parental phenotypes normal x normal parental genotypes ……… x ………. gametes ……… + ………. child’s genotype ………… child’s phenotype sickle cell anaemia [3] (c) Describe the effects of sickle cell anaemia on the body. [4] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (d) Fig. 5.1 is a map that shows the distribution of the allele for the abnormal form of haemoglobin (HS) and malaria in Africa. sickle cell allele malaria Fig. 5.1 Explain how natural selection is responsible for the distribution of the allele for the abnormal form of haemoglobin (HS). [5] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (e) Sickle cell anaemia is an example of the variation that exists in the human population. It is a form of discontinuous variation. Explain why sickle cell anaemia is a form of discontinuous variation. [3] [Total: 16] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 4 Transpiration and translocation are processes responsible for transporting materials around a plant. (i) Complete the table by stating the materials moved by these processes, their sources and their sinks. process materials moved source of materials in the plant sink for materials in the plant 1 transpiration 2 1 translocation 2 [6] (ii) State two reasons why the source and sink for translocation in a plant may change at different stages in the growth of a plant. [2] [Total: 8] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 One variety of the moth, Biston betularia, has pale, speckled wings. A second variety of the same species has black wings. There are no intermediate forms. Equal numbers of both varieties were released into a wood made up of trees with pale bark. Examples of these are shown in Fig. 5.1. Fig. 5.1 After two weeks as many of the moths were caught as possible. The results are shown in Table 5.1. Table 5.1 wing colour of moth number released number caught pale, speckled 100 82 black lac 36 (a) (i) Suggest and explain one reason, related to the colour of the bark, for the difference in numbers of the varieties of moth caught. [1] (ii) Suggest and explain how the results may have been different if the moths had been released in a wood where the trees were blackened with carbon dust from air pollution. [2] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com Table 5.2 shows the appearance and genetic make-up of the different varieties of this species. Table 5.2 wing colour genetic make-up pale, speckled GG; Gg black la (b) (i) State the appropriate genetic terms for the table headings. wing colour genetic make-up [2] (ii) State and explain which wing colour is dominant. dominant wing colour explanation [2] (c) State the type of genetic variation shown by these moths. Explain how this variation is inherited. [3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (d) Heterozygous moths were interbred. Use a genetic diagram to predict the proportion of black winged moths present in the next generation. proportion of black winged moths = [5] (e) (i) Name the process that can give rise to different alleles for wing colour in a population of moths. [1] (ii) Suggest one factor which might increase the rate of this process. [1] [Total: 17] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 2 Fig. 1.1 shows seven lizards that are at risk of becoming extinct. C A B E D F G PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (a) (i) Name the vertebrate group that contains lizards. .......................................................................................................................................[1] (ii) Use the key to identify each species. Write the letter of each species (A to G) in the correct box beside the key. One has been done for you. key 1 2 3 4 5 6 (a) feet with three toes go to 2 (b) feet with five toes go to 3 (a) has a collar or crest on head go to 4 (b) has no collar or crest on head Chalcides minutus (a) spikes along back go to 5 (b) no spikes along back go to 6 (a) ridges extend along back and tail Brookesia perarmata (b) no ridges along back or tail Calumma parsonii (a) blunt, rounded head Amblyrhynchus cristatus (b) elongated head Cyclura lewisi (a) large raised scales on skin Abronia graminea (b) scales on skin are not large or raised Varanus komodoensis D [3] (b) The effect of humans on the environment has caused the populations of the lizard species in Fig. 1.1 to decrease. Explain why conserving lizards is important. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ...............................................................................................................................................[3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (c) Zookeepers report that isolated female Komodo dragons, Varanus komodoensis, have produced offspring asexually. This is very unusual in vertebrates. (i) State two disadvantages of asexual reproduction. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[2] (ii) State two disadvantages of sexual reproduction. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[2] (d) Sexual reproduction requires meiosis to occur. (i) Define the term meiosis. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[2] (ii) Explain the significance of meiosis to the survival of endangered species of lizards. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[3] [Total: 16] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 3 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows a section through the anther of a lily flower. The cells in the centre are dividing by meiosis. Fig. 4.1 (i) Name the product of meiosis that is formed in anthers. .......................................................................................................................................[1] (ii) Explain the importance of meiosis in sexual reproduction. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[2] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (b) Fig. 4.2 shows a flower of Lilium polyphyllum, a lily that grows in the Himalayan mountains. This species is cross-pollinated by insects. Fig. 4.2 (i) Explain what is meant by cross-pollination. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[2] (ii) Name one feature visible in Fig. 4.2 that helps to attract insects. .......................................................................................................................................[1] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (c) Plants of this species that grow at low altitudes produce flowers 60 days before the plants of the same species that grow at high altitudes. (i) Suggest one environmental reason why lilies that grow at lower altitudes flower earlier than the lilies at higher altitudes. .......................................................................................................................................[1] (ii) Explain why flowering time is an example of continuous variation. ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................................[2] (d) Scientists think that plants of L. polyphyllum growing at high altitudes may evolve into a new species. Explain how natural selection could lead to the evolution of a new species of lily. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ...............................................................................................................................................[5] [Total: 14] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 A healthy kidney controls the excretion of urea and other waste products of metabolism from the blood. After kidney failure there are two possible treatments: dialysis or a kidney transplant. Fig. 4.1 shows how blood and dialysis fluid move through a dialysis machine. A blood flow dialysis fluid B bubble trap pump blood patient’s arm Fig. 4.1 (a) Describe the changes that occur to the blood as it flows through the dialysis machine from A to B. [2] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (b) Discuss the advantages of kidney transplants compared with dialysis. [3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (c) Two brothers have to make a difficult decision. One brother, with blood group AB, has kidney failure and is on dialysis. The healthy brother has agreed to donate one of his kidneys to his brother. He has to have a blood test. Their father has blood group A and their mother has blood group B. The brothers have a sister who has blood group O. (i) Explain how this girl has blood group O when her parents have different blood groups. You must use the space below for a genetic diagram to help your answer. Use the symbols IA, IB and IO to represent the alleles involved in the inheritance of blood groups. parental phenotypes blood group A × blood group B parental genotypes ................... × ................... ................... ................... + ................... ................... gametes girl’s genotype ................... girl’s phenotype ................... [4] (ii) The healthy brother can only donate the kidney to his brother if they both have the same blood group. What is the probability that the healthy brother also has blood group AB? [1] [Total: 10] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 2 Fig. 1.1 shows a vertical section through a flower of soybean, Glycine max, following self-pollination. Fig. 1.2 shows part of the section at a higher magnification. stigma A Fig. 1.1 A B C Fig. 1.2 (a) a) Name the parts labelled A to C shown in Figs. 1.1 and 1.2. A B C PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com [3] (ii) Describe what happens to the structures shown in Figs. 1.1 and 1.2 to bring about fertilisation. You may refer to the structures labelled A to C by their letters if you wish. [3] (iii) Explain the advantages and disadvantages of self-pollination for flowering plants, such as soybean. advantages disadvantages [4] (b) Soybean is a dicotyledonous plant. (i) Name the genus to which the soybean belongs. [1] (ii) State two features which are only found in dicotyledonous plants. 1. 2. [2] [Total: 13] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 3 Fig. 4.1 is a photograph of a root of radish covered in many root hairs. Fig. 4.1 (a) Using the term water potential, explain how water is absorbed into root hairs from the soil. [3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com A potometer is a piece of apparatus that is used to measure water uptake by plants. Most of the water taken up by plants replaces water lost in transpiration. A student used a potometer to investigate the effect of wind speed on the rate of water uptake by a leafy shoot. As the shoot absorbs water the air bubble moves upwards. The student’s apparatus is shown in Fig. 4.2. capillary tube coloured water air bubble beaker of water Fig. 4.2 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com The student used a fan with five different settings and measured the wind speed. The results are shown in Table 4.1. Table 4.1 wind speed / metres per second distance travelled by the air bubble / mm time / minutes rate of water uptake / mm per minute 0 4 10 0.4 2 12 5 2.4 4 20 5 4.0 6 35 5 7.0 8 40 2 ………… (b) Calculate the rate of water uptake at the highest wind speed and write your answer in the table. [1] (c) Describe the effect of increasing wind speed on the rate of water uptake. You may use figures from Table 4.1 to support your answer. [2] (d) State two environmental factors, other than wind speed, that the student should keep constant during the investigation. 1. 2. PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com [2] (e) Some of the water absorbed by the plants is not lost in transpiration. State two other ways in which water is used. 1. 2. [2] (f) Water moves through the xylem to the tops of very tall trees, such as giant redwoods of North America. The movement of water in the xylem is caused by transpiration. Explain how transpiration is responsible for the movement of water in the xylem. [4] (g) Plants that live in hot, dry environments show adaptations for survival. State three structural adaptations of these plants. 1. 2. 3. [3] [Total: 17] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 4 (a Four definitions of terms used in genetics are shown in Table 5.1. Table 5.1 definitions efini the outward appearance of an organism …………………….. a length of DNA that codes for a protein …………………….. having one set of chromosomes …………………….. type of nuclear division which gives daughter nuclei that are genetically identical ……………………. For each of the definitions, select an appropriate term from the list and write it in the box provided. chromosome genotype mitosis diploid haploid mutation dominant heterozygous phenotype gene homozygous recessive [4] (b) A couple who have blood groups A and B have four children. Each child has a different blood group. Use the space below to draw a genetic diagram to show how this is possible. Use the symbols, IA , IB and Io, for the alleles. parental blood groups parental genotypes A × B × gamete genotypes children’s genotypes children’s blood groups [4] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (c) Explain what is meant by codominance. You may refer to the genetic diagram in (b) to help you with your answer. [3] (d) Insulin produced by genetically engineered bacteria first became available in 1982. Before 1982, insulin had been prepared from dead animal tissues. Explain the advantages of using insulin produced by genetically engineered bacteria rather than insulin from dead animal tissues. [3] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com (e) Fig. 5.1 shows some of the steps involved in the genetic engineering of bacteria. human cell bacterium chromosomes in nucleus R S T geneticallyengineered bacterium reproduction of bacteria production of insulin Fig. 5.1 (i) Name structure R and state what it is made from. [2] (ii) State what is added at stages S and T. [1] [Total: 17] PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com