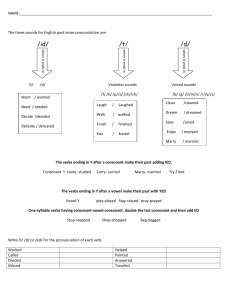
English Phonemic Chart Monophthongs iː bee ɪ sit ʊ book uː food Diphthongs ɪə hear eɪ day e bed ə doctor ɜː bird ɔː law ʊə tour ɔɪ boy əʊ go æ cat ʌ much ɑː car ɒ dog eə hair aɪ why aʊ cow Consonants voiced consonant voiceless consonant p pet b ball t talk d dog tʃ cheap dʒ jam k key g great f fun v van θ think ð this s sell z zoo ʃ shell ʒ vision m man n now ŋ sing j yes l love r run w well h help Other useful symbols ʔ uh oh ɫ fall i happy Are you serious about improving your English pronunciation? Head to www.pronunciationwithemma.com for more resources! Your Handy Phonetics Glossary Allophone A very specific variant of a phoneme, for example [ɫ] is an allophonic variant of /l/ as it's more specific. You also use square brackets to transcribe allophones. Articulation The physical production of sounds. Pitch The degree of highness or lowness of a tone. Prosody The rhythm, stress, and intonation of speech. Segmentals Individual sounds of speech, such as vowels and consonants. Aspiration A puff of air that follows the release of a consonant sound, especially the voiceless plosives like /p/, /t/, and /k/. Diphthong A vowel sound that begins with one vowel sound and transitions smoothly into another within the same syllable. Intonation The variation of pitch while speaking. You use it to emphasise particular words or to express emotion, ask questions, etc. IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) A standardised system of phonetic notation that represents each sound of spoken language. Stress The emphasis placed on certain syllables in words. Primary Stress and Secondary Stress Primary stress is the main stress in a word and is marked with a ˈ symbol, like in /ˈhæp.i/. Secondary stress is not as strong as the primary stress. It is marked with a ˌ symbol and is usually used in much longer words, typically with a prefix, for example /ˌɪn.təˈnæʃ.ən.əl/. Syllable A unit (or ‘section’) of a word, typically comprised of a vowel, such as ‘ed-u-ca-tion’. Tone The use of pitch in a language to distinguish meaning in words and sentences. Monophthong A single vowel sound. Nasal Sounds produced by releasing air through the nose, such as /m/, /n/, and /ŋ/. Voice/Voicing The vibration of your vocal folds to produce sounds. Sounds can be voiced (vocal folds vibrating, as in /z/, /b/ and /g/) or voiceless (vocal folds not vibrating, as in /s/, /p/ and /k/). Phoneme The smallest unit of sound and the most general representation of a sound in transcription. www.pronunciationwithemma.com English Phonemic Chart Monophthongs iː bee ɪ sit ʊ book uː food Diphthongs ɪə hear eɪ day e bed ə doctor ɜː bird ɔː law ʊə tour ɔɪ boy əʊ go æ cat ʌ much ɑː car ɒ dog eə hair aɪ why aʊ cow Consonants voiced consonant voiceless consonant p pet b ball t talk d dog tʃ cheap dʒ jam k key g great f fun v van θ think ð this s sell z zoo ʃ shell ʒ vision m man n now ŋ sing j yes l love r run w well h help Other useful symbols ʔ uh oh ɫ fall i happy Are you serious about improving your English pronunciation? Head to www.pronunciationwithemma.com for more resources! Your Handy Phonetics Glossary Allophone A very specific variant of a phoneme, for example [ɫ] is an allophonic variant of /l/ as it's more specific. You also use square brackets to transcribe allophones. Articulation The physical production of sounds. Pitch The degree of highness or lowness of a tone. Prosody The rhythm, stress, and intonation of speech. Segmentals Individual sounds of speech, such as vowels and consonants. Aspiration A puff of air that follows the release of a consonant sound, especially the voiceless plosives like /p/, /t/, and /k/. Diphthong A vowel sound that begins with one vowel sound and transitions smoothly into another within the same syllable. Intonation The variation of pitch while speaking. You use it to emphasise particular words or to express emotion, ask questions, etc. IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) A standardised system of phonetic notation that represents each sound of spoken language. Stress The emphasis placed on certain syllables in words. Primary Stress and Secondary Stress Primary stress is the main stress in a word and is marked with a ˈ symbol, like in /ˈhæp.i/. Secondary stress is not as strong as the primary stress. It is marked with a ˌ symbol and is usually used in much longer words, typically with a prefix, for example /ˌɪn.təˈnæʃ.ən.əl/. Syllable A unit (or ‘section’) of a word, typically comprised of a vowel, such as ‘ed-u-ca-tion’. Tone The use of pitch in a language to distinguish meaning in words and sentences. Monophthong A single vowel sound. Nasal Sounds produced by releasing air through the nose, such as /m/, /n/, and /ŋ/. Voice/Voicing The vibration of your vocal folds to produce sounds. Sounds can be voiced (vocal folds vibrating, as in /z/, /b/ and /g/) or voiceless (vocal folds not vibrating, as in /s/, /p/ and /k/). Phoneme The smallest unit of sound and the most general representation of a sound. www.pronunciationwithemma.com