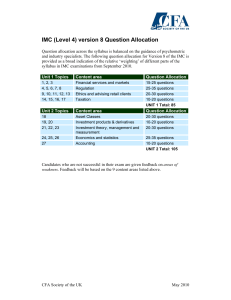
Bus 120 Final Exam W2024 Course Review This exam is written at the Abbotsford campus for all sections including online sections. You must report to the room assigned to your section. Notes Introduction to Marketing Final Exam: Date: December 16, 2024 Time: 2:00 pm to 5:00 pm, PST Place: AB2: B132 AB4: B132 Exam Rules: This is NOT an open book exam. By selecting to start this exam you are agreeing to the following: • I will not give or receive aid on this examination. This includes, but is not limited to, viewing the exams of others, sharing answers with others, making unauthorized use of books, notes, or electronic devices while taking the exam, discussing the exam with students who have not yet taken it, or have taken it. Anybody found doing so will be subject to UFV Policy 70 on Academic Misconduct. • I understand that anybody who is found to cheat on the exam, or have a cell phone, or have another unauthorized electronic device accessible during the exam will be subject to UFV Policy 70 on Academic Misconduct. • I understand that if I am aware of any cheating on this examination, I have an obligation to inform my professor. I also understand that my professor will follow UFV Policy 70 if they witness any acts of academic misconduct. Exam Rules: • This exam is written in person, on campus. • Late arrivers WILL NOT be given extra time. You have 1.5 hours (90 minutes) in total to write this exam. At the end of the 1.5 hours you will be asked to stop writing. • Anybody who is found to be talking to a neighbour during the exam will IMMEDIATELY BE REMOVED from the exam without warning. Your exam will be over. If you have a question, do not ask your neighbour, ask your instructor. Introduction to Marketing Exam Total Score: 70 marks Exam Exam Coverage: • Chapters 9, 10, 11, 12&13, 2&15 (75%) • All other course concepts included in the CRNs (25%) Exam Composition: Not confirmed • 50 MCQs (50 marks): • 4 Mini Case Questions (20 marks) Course Review Notes: All concepts tested in the Final Exam are found in these Course Review Notes (CRNs). If the concept is not in these slides, it will NOT be tested on your exam. Students are encouraged to read these notes using NOTE VIEW. Important information is often included at the bottom of every slide. You can only see this information if you are looking at the slide in NOTE VIEW. Where there are no notes at the bottom of a slide, students are expected to consult their class notes, Student Lecture Notes, Concept Videos and textbook. You must be able to IDENTIFY and EXPLAIN to the level of detail as discussed in class and described in the textbook. Chapters 1&14 Introduction to Marketing Defining Marketing | Philosophies | Value | Marketing Mix | CRM| The Marketing Mix: 7Ps ?????? Product ?????? online no contract price $449.99 1 yr contcract $399.99 2 yr contract $349.99 3 yr contract** $99.99 ?????? offline Chapters 2&15 Introduction to Marketing Planning Process | Strategic Planning | Marketing Planning |Managing Marketing Strategizing the Marketing Mix: Segmentation People Targetin g Differentiation Product Positioning Price Place Promotion Profit Chapters 1&14 Introduction to Marketing Defining Marketing | Philosophies | Value | Marketing Mix | CRM| Marketing Business Function: 🞈 Define the buyer and seller (Ch 7) 🞈 Understand the consumer needs (Ch 6) 🞈 Create wants to satisfy needs (Ch 8) 🞈 Building a competitive advantage Marketers are in the business of creating unique wants to satisfy needs. Chapters 1&14 Introduction to Marketing Data Types / Research Process / Research Types / Interpretation Customer Satisfaction: Expectations = What buyer believes the company Delivered > What company promised brand experience will be Perceive Performance Chapters 1&14 Introduction to Marketing Data Types / Research Process / Research Types / Interpretation Why Focus on Satisfaction? ❑ Greater customer loyalty ❑ Repeat purchasing ❑ Brand evangelist ❑ Increased share of wallet BUS 120 _Midterm #1 – Chapters 1&14 Introduction to Marketing Defining Marketing | Philosophies | Value | Marketing Mix | CRM| Customer Relationship Types: Potential Profitability Goodness of Fit Butterflies Best Friends Projected Loyalty Strangers Barnicles Chapter 1 & 14 Introduction to Marketing Defining Marketing | Philosophies | Value | Marketing Mix | CRM| Customer Relationship Activities: Customer Acquisition: The cost of the incentives companies use to attract customers. Customer Development: Activities companies use to get you to buy more, more often. Activities include often include upselling, multi-items purchase (add-on selling) Customer Retention: Activities companies do to get you to continue to buy from them. Often include loyalty programs and club membership with special benefits. Chapter 4 Introduction to Marketing Data Types / Research Process / Research Types / Interpretation Applying 5Ws to Research Design: Who - are we going to survey (target population)? What – behaviour/characteristic are we observing or measuring? E.g. beer drinking preferences When – time of measurement; would results differ if selected different time of day, time of year? E.g. evening telemarketing calls Where – do we conduct the field study? Would the results change if we changed the location? E.g. in bar, at hockey game Why – what is the deliverable; what question is being answered (hypothesis being tested). Why do you care? What will you do with the info? How – what survey format will we use? E.g. Questionnaire, observation, telephone, in-person, or mail. Chapter 4 Introduction to Marketing Data Types / Research Process / Research Types / Interpretation Types of Exploratory Designs: ⮲ Literature Search ⮲Depth Interviews ⮲ Experience Surveys ⮲Projective Techniques ⮲ Focus Groups ⮲Ethnography ⮲ Analysis of selected cases Projective Techniques only one to capture emotional data. Exploratory Research method are generally qualitative in nature. Chapter 4 Types of Research Methodologies: Exploration - designed to discover ideas and insight Descriptive - designed to determine the frequency of an occurrence or relationship between two variables Causal - designed experiment to determine cause and effect relationships between two or more variables There is no one best research methodologies (method) Introduction to Marketing Consumer Participation: Chapters 3&5 Data Types / Research Process / Research Types / Interpretation Simple Random Convenience Sample Types Stratified Random Quota Introduction to Marketing Applying 5Ws to Buyer Profiles: Chapters 3&5 Data Types / Research Process / Research Types / Interpretation Who - are they (demos, psychos, behavs)? What – do they want (features & benefits being sought)? Why – do they seek it (needs being met)? When – do they use or buy product? Where – do they use/ buy product? How – do they use product / pay for product / learn about the product? Chapter Six Introduction to Marketing Identification | Segmentation | Positioning | Ethics & Globalization Positioning Map: AMA the various products are plotted onto maps, using product attributes as dimensions. Attribute A American Marketing Association A product’s position is the space it occupies in the mind of a consumer. A product positioning is the strategy of comparing your product features benefits to your competitors to create an advantage. Repositioning- updating the existing positioning strategy to reflect the current marketplace. Attribute B Chapter Six Demographics:Behaviouristics: 🞈 Age 🞈 Income 🞈 Ethnicity 🞈 Geography 🞈 Life-stage 🞈 Benefits segmentation 🞈 Usage segmentation 🞈 Occasion segmentation 🞈 User status Chapter Six Psychographics: 🞈 VALs Firmographics: B2B only 🞈 Size of firm in terms of employees 🞈 AIOs 🞈 Size of firm in terms of sales 🞈 Personality 🞈 Status in industry 🞈 Prizms 🞈 Geographic location / number of locations 🞈 Behaviouristics Chapter 7 Introduction to Marketing Strategy | Management | Communication | Equity Brand Equity: $$$$$ + Our Product $1069.00 - Their Product $ 499.00 Price Premium x Average # buyers Brand Equity Chapter Seven Introduction to Marketing Strategy | Management | Communication | Equity Brand Architecture: ❖ Individual brands ❖ Family (Umbrella) brands ❖ Co-branding ❖ National vs. Private Label brands ❖ Brand Licensing ❖ Multibrands ❖ Brand Extension Chapt er 8 Introduction to Marketing Products | Product Line | Product Mix | PLC Product Types (Forms) : Good Person Service Product Types Idea Place Experience Introduction to Marketing Chapt er 8 The Service Concept: erishability P I nseparability V ariability I ntangibility Chapters 2&15 Introduction to Marketing Planning Process | Strategic Planning | Marketing Planning |Managing Marketing The Planning Process: 🞈 Strategic Planning 🞈 Operational Planning 🞈 Individual Action Plans 🞈 Evaluation and Control Chapters 2&15 Introduction to Marketing Planning Process | Strategic Planning | Marketing Planning |Managing Marketing Market Analysis: Internal External SWOT Chapters 2&15 Introduction to Marketing Planning Process | Strategic Planning | Marketing Planning |Managing Marketing P: Political E: Economical S: Social T: Technical E: Environmental L: Legal P: People Chapter 6 Planning Process | Strategic Planning | Marketing Planning |Managing Marketing Porter’s Six Forces: Suppliers Direct Competitors Us Buyers Complementors Chapters 2&15 Introduction to Marketing BCG Model: Chapters 2&15 Introduction to Marketing Planning Process | Strategic Planning | Marketing Planning |Managing Marketing Ansoff’s Grow a Business Grid Current Products New Products Current Markets New Markets Market Penetration: entice consumers to buy more products. Market Development: geographically develop new markets Product Development: develop new line of products aimed at existing market. Diversification: expand into new consumer market segment More of the cart Value | PEof Demand | Profit | Market Share | Competitive | Tactics Chapter 9 Calculation of Value: + utilitarian benefits (faster, safer, better) + emotional benefits (image, status, prestige) - operating costs (training, maintenance, etc.) - opportunity cost (benefits- cost forgone) - switching costs ( cost to relearn) = Value Received Chapter 9 Value | PEof Demand | Profit | Market Share | Competitive | Tactics Consumer Reference Price: ❑ Buyer Pricing Expectations ❑ Internal Reference Price ❑ Price-Quality Inference Chapter 9 Introduction to Marketing Value | Cost | Competitive | Strategic | Adjustments | Online | Globalization Strategic Pricing Decisions: New Products 1. Price Skimming Pricing Setting prices based on willingness to pay 2. Penetration Pricing Low introductory price to create widespread rapid adoption Chapter 9 Introduction to Marketing Value | Cost | Competitive | Strategic | Adjustments | Online | Globalization Strategic Pricing Decisions: New Products 3. Trial Pricing – Initially set the price below the regular price for a fixed period of time, to attract buyers. If you keep the price low for too long (more than 3 months), buyers will believe it is the regular price and you will have a hard time increasing the price. Chapter 9 Introduction to Marketing Value | Cost | Competitive | Strategic | Adjustments | Online | Globalization International Pricing: ❖ Exchange rates ❖ Transportation costs ❖ Affordability ❖ Convenience Chapter 9 Introduction to Marketing Value | Cost | Competitive | Strategic | Adjustments | Online | Globalization On-line Pricing: ❖ Auction Pricing – E-bay ❖ Dynamic Pricing – price easily changed to meet changes in marketplace ❖ Price Discrimination - easier to do and less likely to be caught ❖ On-line Price Advantages – intense competition driving down price Introduction to Marketing Consumer Channel Types: Chapter 10 Channels | Functions | Supply Chain | Value Chain | Logistics Direct Indirect Chapter 10 Managing the Channels: ⮚ Managing channel partners (Channel coverage) Introduction to Marketing Channels | Functions | Retailing | Non-retailing Intensive Selective Exclusive Single ⮚Distribution Channel Strategy Dual Omni ⮚ Managing movement of goods Sea freight Truck freight Train freight Air freight Chapter 10 Supply Chain: Introduction to Marketing Channels | Functions | Retailing | Non-retailing Chapter 10 Vertical/Horizontal Marketing System: Introduction to Marketing Channels | Functions | Retailing | Non-retailing Corporate: Single company owns all the firms in the chain Vertical: Cooperate from top to bottom Contractual: formal contract governs relationship Horizontal: Administered: No formal contractindustry leader dictates rules Cooperate across level Chapter 10 Introduction to Marketing Channels | Functions | Supply Chain | Value Chain | Logistics Value Chain: R&D Marketing and Sales Customer Service Chapter 10 Introduction to Marketing Channels | Functions | Retailing | Non-retailing Logistics Management: Logistics: Freight line Trains Sea line Air Freight JIT MIS ❖Time ❖Cost ❖Safety ❖Outsource Reverse Logistics: ❖Who pays ❖Cost ❖Safety ❖Outsource Chapter 11 Retailing | E-tailing | Other Types of Retailers and product types: Convenience Warehouse Superstore Factory Outlet Supermarket Specialty General Merchandise Discount Chapter 11 Introduction to Marketing Channels | Functions | Retailing | Non-retailing Retailing Strategy Choices: Experience Assortment Selection Buyer Group Image Availability Price Points Service Mix Chapter 11 Retailing | E-tailing | Other Retailer Selection: Product Mix Breadth Low High Narrow assortment/ Broad assortment/ Shallow selection Shallow selection High Brand Offering Depth Low Narrow assortment/ Broad assortment/ Deep selection Deep selection Chapter 11 Retail Store Image: ⮚ Furnishings and merchandise density ⮚ Store layout ⮚ Music, colour, and lighting ⮚ Store personnel ⮚ Pricing Retailing | E-tailing | Other Introduction to Marketing Chapter 11 Channels | Functions | Retailing | Non-retailing Purchase Process: Showrooming Prepurchase Purchase Webrooming PostPurchase Introduction to Marketing Chapter 11 Offline Types | Strategy | Image | Online Textbook: Why Customers Shop online Convenience Choice Cost Customization Control Communication Click Why customers shop offline: Fun (experience, social factor) Fit Feel Fast (no wait, want it now) You will not find this 4F model online, I have made it up. However, you will find the data to support it online. vs Advantages: Choice Cost (Price) Convenience Disadvantages: Returns Wait Distrust Brick Advantages: Fast (Now) Fit Feel Fun Disadvantages: Price Less choice Chapter 11 Retailing | E-tailing | Other Marketing Message Strategy: PULL PUSH Advertising Channel Partners Introduction to Marketing Chapter 12/13/14 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Promotion Mix: 1. Advertising 2. Personal Selling 3. Sales Promotion 4. Public Relations 5. Direct Response Marketing 6. Internet 7. Alternative Introduction to Marketing Chapter 12/13 Promotion Mix | Budgeting Promotion Mix: Advertising Broadcast Print TV Newspaper Radio Magazines Internet Out-door Personal Selling Direct Selling Public Relations Sales Promotion Internet Other Salesforce Traditional Mail Publicity B2B Website Vending Telemarketing Email Employee Relations B2C Social Networking Guerrilla Mobile Mail Community Relations WOM Investor Relations User Generated Crisis Management Public Policy Chapter 12/13/14 Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Advertising: Broadcast TV: Cable, Network and Satellite (Linear); Streaming TV content (Connected TV-CTV) RADIO: AM, FM, Satellite Internet: All the places online we pay to place our digital banner (display) ads. Chapter 12&13 Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Broadcast: Mobile Marketing Introduction to Marketing Broadcast-Internet: Social Media Marketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Agreed upon nowadays, nobody looks at FB or YT ads. Introduction to Marketing Advertising: Broadcast- Internet Ad styles Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Banner / skyscraper / button Floater / Takeover Interstitial Pop up / in / downs Introduction to Marketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Marketing Lifecycle Objectives: Inform Persuade Resonate Build Remind Introduction to Marketing Personal Selling: Telemarketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Follow-up after the sale Introduction to Marketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Global Marketing: Product • Tailor or not • Change in consumer tastes Pricing • Economic affordability • Consistency Place • Build • Befriend Promotion • Brand ownership • Tailor or not Chapter 12&13 Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Table 12.1 Profiles of Major Media Types Media Selection: Medium Advantages Limitations where and when you say it as important as what you say Size ($US) Newspaper (digital/print) Flexibility; timeliness; broad coverage; credibility, older audience, video ads (digital) Short life; poor quality (print), where in scroll (digital) $ 42.8 Bn Magazines (digital/print) Selectivity; pass along (print); quality; warm audience Cost, lead time, positioning $ 10.4 Bn Television Mass/Selectivity; multi-media High cost production and placement; public abhorrence $267 Bn Radio Selectivity; low cost Audio; noise $ 37 Bn Out-of-home Flexibility; repeat exposure (static/digital) Creative restrictions $ 10.4 Bn Direct Mktg Selectivity; flexibility; personalization Low response rate $ 66.84 Bn Online Selectivity; low cost; immediacy; personalization Low impact; audience controls exposure $833.9 Bn Alternative High impact Must go viral to max audience ???? Introduction to B2C Sales Promotion: Marketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Sweepstakes / Contests Sampling Bonus Packs Cents off Rebates Frequent Buyer Premiums Introduction to Marketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting B2B Sales Promotion: Merchandis e Allowances Event Marketing Volume Discounts Promo Products Gifts Incentive s Sweepstakes / Contests Sampling Chapter 12&13 Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Traditional Direct Response Marketing: 1. Catalogues 2. Telephone 3. Mailers 4. 1-800 numbers Introduction to Marketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting e-mail Marketing: Message personalization Low response rates- Spam List driven distribution Permission - CASL Introduction to Marketing Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Promotion Mix #6: Internet Marketing Company FB Page Company LinkedIn Company website Company TikTok Company Instagram Company You-Tube Channel Company Blog Company Pintrest Company X (Twitter) Chapter 12&13 Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Digital / Interactive Marketing: Digital Signage Website Marketing Mobile Marketing e-commerce Podcasts: On-line Advertising: e-mail Marketing Blogging and Marketing: Social Media Marketing: Chapter 12&13 Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Guerrilla – generally out of home designed to have viewers interact with the campaign. The audience is comparatively small - the hope is that it will go viral and EARN advertising. Chapter 12&13 Marketing Lifecycle • New brand driven • New brands always start at the beginning. Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Product Lifecycle • New product category driven • A new brand can be in the maturity stage of the product lifecycle. E.g. SMEG brand of small electronics (toasters, coffee makers, etc.) all products are in the mature stage of PLC but SMEG is a new brand. Chapter 12&13 Introduction to Marketing Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Media Budget: ⮚ What can we afford (Top down)? ⮚ Percent of Sales? ⮚ What are promotion are we planning to do (Bottom up)? ⮚ What are our competitors spending? Chapter 12&13 Defining IMC | Message Design | Promotion Mix | Budgeting Media Selection Drivers: ⮚ GI, Frequency, Reach ⮚ CPM ⮚ Budget Introduction to Marketing Introduction to Marketing CMA Professional Ethics: • • • • • • • • Individually accountable Respect the law Act with integrity Act with competency Respect confidentiality Avoid conflict of interest Act with professionalism Adhere to CMA Code of Ethics Introduction to Marketing Chapters 3&5 Data Types / Research Process / Research Types / Interpretation Regulations: Pipeda (collection) The 10 Privacy Principles of PIPEDA 1.Accountability 2.Identifying Purposes 3.Consent 4.Limiting Collection 5.Limiting Use, Disclosure, and Retention 6.Accuracy 7.Safeguards 8.Openness 9.Individual Access 10.Challenging Compliance ; CASL (use) • Include your business name, postal address and either a telephone number or email address in your emails • Only sending to those who’ve agreed to receive email from you • You keep records of your consents (implicit or explicit) including the date and time of the consent. • You must remove people from list as soon as their consent expires. • Emails contain a working unsubscribe link and removing them from list cannot take more than 10 business days. Chapter 11 Introduction to Marketing Offline Types | Strategy | Image | Online Ethics and Retail: Selective Hiring – hiring based on brand image Exchange Policies – defective goods; time limits; packaging Wages Scales – minimum wage jobs Working Conditions – hours; overtime; stat holidays Chapter 10 Introduction to Marketing Channels | Functions | Supply Chain | Value Chain | Logistics Ethics and Distribution: Outsourcing – loss of blue collar and now WHITE collar jobs Environmental Concerns – overall carbon footprint of goods Quality Management – who is responsible; who should be? Wages Scales – below poverty line pay scales! Chapter 2 & 15 Introduction to Marketing Planning Process | Strategic Planning | Marketing Planning | Managing Marketing International Marketing Tactics: 🞈 Cultural differences 🞈 Standard of Living 🞈 Market channel differences 🞈 Political Differences