Grade 7 Biology Test Questions: Reproduction, Cells, Ecology
advertisement

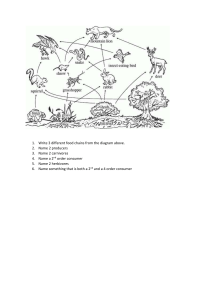
Grade 7 - Quarter 2 SOLO MODEL QUESTIONS COMPETEN CY STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPT SOLO ABLE MODEL ANSWER TAXONOMY RATIONALIZ ATION 7. Differentiate asexual from sexual reproduction in terms of 7.1.number of individuals involved. 7.2.similaritie s of offspring to parents (S7LT-IIg-7) Plants reproduce by sexual or asexual means. Sexually through flowers by pollination and asexually through the different parts of the plant excluding the flower. 1. How many parent/s is/ are required in asexual reproduction? A. One B. Two C. Four D. Six A This is unistructural since it requires only one specific answer UNISTRUCT URAL Source:https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/71 3679872174762954/ TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPT SOLO ABLE MODEL ANSWER TAXONOMY RATIONALIZ ATION 7. Differentiate asexual from sexual reproduction in terms of 7.1.number of individuals involved. 7.2.similaritie s of offspring to parents (S7LT-IIg-7) The flower is the reproductive organ in flowering plants. They have structures that produce the gametes necessary for reproduction which we call as the essential parts. There are also parts for support that help in attracting insects for pollination which we call Sterile/Non-Essential Parts of a Flower. 2.Essential/Reproductive Parts facilitates the union of sperm nucleus with an egg nucleus. Enumerate the essential parts of a flower. A.calyx , corolla, Peduncle & receptacle B. calyx , corolla, Pistil & receptacle C. corolla , pistil, stamen D.Stamen & Pistil D The question requires 2 or more Independent answers Multistructural Source: https://www.careerpower.in/school/biology/fertilization-inplants TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPT SOLO ABLE MODEL ANSWER TAXONOMY RATIONALIZ ATION 7. Differentiate asexual from sexual reproduction in terms of 7.1.number of individuals involved. 7.2.similaritie s of offspring to parents (S7LT-IIg-7) Fertilization in plants involve the fusion of pollen (male gamete) with ovules (female gamete) to form a zygote, and leads in seed development. 1. For fertilization to occur in most flowering plants, insects or other animals must transport the pollen to the pistil. Explain what must happen in order for fertilization to occur in flowering plants? A. The plant must be exposed to sunlight during pollination. . B. There must be water droplets, wind and insects to help facilitate pollination C.The sperm cells in the pollen tube must be able to reach the eggs in the ovule D.The eggs in the ovule must be able to reach the top of the stigma where pollen is trapped. C It requires students to explain the needs in oder for fertilization to occur Source: https://www.careerpower.in/school/biol ogy/fertilization-in-plants Relational TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY 7. Differentiate asexual from sexual reproduction in terms of 7.1.number of individuals involved. 7.2.similaritie s of offspring to parents (S7LT-IIg-7) STEM VENN DIAGRAM ON THE SMILARITIES AND DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SEXUAL AND ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION TEST ITEM Based on the Venn diagram of sexual and asexual reproduction , write a generalization of the concept on sexual and asexual reproduction including the updates of the recent advancements.Your performance will be rated based on the rubrics below. ACCEPT SOLO ABLE MODEL ANSWER TAXONOMY Extended Abstract RATIONALIZ ATION It requires students to draw general conclusion and its applicability in the modern world. COMPETEN CY STEM 1. Describe the different levels of biological organization from cell to biosphere (S7LT-Iic-3) TEST ITEM ACCEPTA BLE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION 10. Make a foldable pyramid on the levels of Biological Organization. C EXTENDED ABSTRACT It extend ideas and applies and transfers ideas to new situation Source: www.libretext.org The highest level of organization for living things is the biosphere; it encompasses all other levels. The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are: cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and biosphere. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY Explain why the cell is considered the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms (S7LT-IIe-5) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPTA BLE ANSWER 1.What is the basic unit A of life? Source: www.thoughout.com Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. It is the structural unit of life because the entire body of an organism is made up of cells which provide structure for the body. The cell is also known as the functional unit of life because it regulates all the functions, like taking in of nutrients from food, converting food into energy and carrying out specialized functions inside an organism. A. B. C. D. Cell Organ Nucleus Tissue SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION UNISTRUCTURAL It needs only one relevant answer TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#5) STEM Explain why the cell is considered the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms (S7LT-IIe-5) Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Cell is the largest structural and conventional unit of all matter. B. Cell is the smallest structural and functional Source: www.thoughout.com unit of all living things. Cell is the basic structural and C. Cell is the largest functional unit of all organisms. It is structural and the structural unit of life because conventional unit of all the entire body of an organism is living things. made up of cells which provide structure for the body. The cell is also D. Cell is the smallest known as the functional unit of life structural and functional because it regulates all the functions, unit of non-living things. like taking in of nutrients from food, converting food into energy and carrying out specialized functions inside an organism. TEST ITEM RATIONALI ZATION ACCEPTA BLE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY B MULTIIt needs STRUCTURAL more than one relevant answer TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#5) STEM Explain why the cell is considered the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms (S7LT-IIe-5) Cancer starts from cells C that start to grow uncontrollably fast. They destroy tissues and organs. What does it say about the effects of diseased cells on organism? A. Cancer cells do not affect Source: www.thoughout.com the other parts of Cell is the basic structural and organism. functional unit of all organisms. It is B. Diseased cells affect only the structural unit of life because the tissues and organs but the entire body of an organism is not the organism. made up of cells which provide C. Diseased cells damage structure for the body. The cell is also the higher level of known as the functional unit of life organization specially the because it regulates all the functions, organism. like taking in of nutrients from food, D. Cancer involves only certain kinds of cell and converting food into energy and does not affect any other carrying out specialized functions kind of cell. inside an organism. TEST ITEM ACCEPTA BLE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION RELATIONAL It is relational since the learners are required to relate the cells to diseases that may affect an organisms TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#5) Explain why the cell is considered the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms (S7LT-IIe-5) STEM Source: www.thoughout.com Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. It is the structural unit of life because the entire body of an organism is made up of cells which provide structure for the body. The cell is also known as the functional unit of life because it regulates all the functions, like taking in of nutrients from food, converting food into energy and carrying out specialized functions inside an organism. TEST ITEM SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION Draw an Animal or Plant cell with its parts and functions and write generalization on why cell is the basic unit of life. EXTENDED ABSTRACT It extend ideas and applies by illustrating animal and plant cell with its parts and functions. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#7) STEM Differentiate asexual from sexual reproduction in terms of 7.1.number of individuals involved. Source: DepEd learners Module 7.2.similaritie s of offspring Based on the Venn diagram of to parents sexual and asexual reproduction , (S7LT-IIg-7) write a generalization of the concept on sexual and asexual reproduction including updates on recent advancement.Your performance will be rated based on the rubrics below. RUBRIC SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION EXTENDED ABSTRACT It extend ideas as to the similarities and differences of sexual and asexual reproducti ons. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#11) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPTAB LE ANSWER Predict the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi-11) Population is a group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area. A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. What is a population? B A) A group of individuals of the same species. B) A group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area. C) A group of individuals of the different species living within a given area. D) A group of individuals of the different species living and interbreeding within a given area. SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION UNISTRUCTU This RAL question is unistructur al because it only requires knowledge of the direct relationshi p between wolves and herbivores in a forest ecosystem. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#11) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPTAB LE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION Predict the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi-11) Population is a group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area. A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. What is an example of predator in the passage? D UNISTRUCTURAL This question is unistructur al because it only requires knowledge of the direct relationshi p between wolves and herbivores in a forest ecosystem. A) Deer B) foxes C) rabbits D) wolves TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#11) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPTAB LE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION Predict the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi-11) Population is a group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area. A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. What population increases rapidly when wolves decline in number of population? A UNISTRUCTURAL This question is unistructur al because it only requires knowledge of the direct relationshi p between wolves and herbivores in a forest ecosystem. A) Deer B) foxes C) rabbits D) Birds of prey TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#11) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPTAB LE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATIONALI ZATION Predict the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi-11) Population is a group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area. A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. What population increases rapidly when wolves decline in number of population? C UNISTRUCTURAL This question is unistructur al because it only requires knowledge of the direct relationshi p between wolves and herbivores in a forest ecosystem. A) Deer B) foxes C) rabbits D) Birds of prey TEAM GRADE 7 RATIONALI ZATION COMPETEN CY (#11) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPTAB LE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY Predict the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi-11) A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. How might the sudden decline in the population of wolves affect the population of herbivores in a forest ecosystem? A UNISTRUCTU This RAL question is unistructur al because it only requires knowledge of the direct relationshi p between wolves and herbivores in a forest ecosystem. A) Increase rapidly B) Decrease rapidly C) Stay the same D) Fluctuate unpredictably TEAM GRADE 7 RATIONALI ZATION COMPETEN CY (#11) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPTAB LE ANSWER SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY Predict the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi-11) A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. Based on the passage, what is the main idea of the statement? A MultiThis STRUCTURAL question is a multistructural because each choices reflects a different main idea from the passage. A) Decreased numbers of wolves can result in an increase in herbivore populations. B) Herbivores such as deer can overgraze vegetation when top predators are absent. C) The decline in rabbit populations can impact the survival of foxes and birds of prey. D) The absence of top predators can lead to an overpopulation of herbivores and potential vegetation damage. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#11) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPT SOLO ABLE MODEL ANSWER TAXONOMY Predict the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi-11) A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. How does the decline in the rabbit population affect animals like foxes and birds of prey? B Source: www.bing.com A) Increase in the fox population B) Scarcity of food for foxes and birds of prey C) Decrease in the fox population D) Increase in the bird of prey population RATIONALIZATIO N RELATIONAL It is a relational type of question because it explores the relationship between the decline in the rabbit population and its influence on other animal populations, specifically foxes and birds of prey. It examines the cause-and-effect relationship between the rabbit population and the populations of these other species. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETE STEM NCY (#11) Predict the effect of changes in one population on other population s in the ecosystem (S7LT-IIi11) A change to a number of one population could have a domino effect on other populations. Suppose there is a sudden decline in the population of a top predator, such as a wolf, in a forest ecosystem. Without the presence of wolves to keep their numbers in check, the population of herbivores like deer may increase rapidly. This surge in herbivores can overgraze the vegetation, leading to a scarcity of food for other herbivores such as rabbits. Consequently, the rabbit population may decline, affecting animals that rely on them as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. Source: www.bing.com RUBRIC ACCEPTABLE ANSWER RATIONALIZATI ON Based on the passage given, write a generalization about the effect of changes in one population on other populations in the ecosystem. (2-3 sentences will do) (Answer may differ) This is an extended abstract since students will give a generalization out of the passage given. The decline in the rabbit population, caused by the scarcity of food, has implications for animals that rely on rabbits as a food source, such as foxes and birds of prey. With fewer rabbits available, the predator populations may also experience a decrease in their numbers. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#4) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPT SOLO ABLE MODEL ANSWER TAXONOMY RATIONALIZATIO N 1.Differentiat e plant cells and animals cells according to presence or absence of organelles; S7LT-IId-4 Plant cells and animal cells exhibit similarities in fundamental structures, such as the cell membrane, nucleus, and mitochondria. Both cell types have a cell membrane that acts as a selective barrier, a nucleus housing genetic material and mitochondria facilitating cellular respiration, as this organelle are essential for energy production through cellular respiration. However, Plant cells feature a rigid cell wall providing structural support and a central vacuole for storage, while animal cells lack a cell wall and have smaller, scattered vacuoles. Chloroplast, crucial for photosynthesis, are exclusive to plant cells. 1.Which part helps plant cells make food from sunlight? B It requires one relevant idea or response. Source: www.bing.com UNISTRUCT URAL A. Nucleus B. Chloroplasts C. Cell Wall D. Mitochondrion TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#4) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEPT SOLO ABLE MODEL ANSWER TAXONOMY RATIONALIZATIO N 1.Differentiat e plant cells and animals cells according to presence or absence of organelles; S7LT-IId-4 Plant cells and animal cells exhibit similarities in fundamental structures, such as the cell membrane, nucleus, and mitochondria. Both cell types have a cell membrane that acts as a selective barrier, a nucleus housing genetic material and mitochondria facilitating cellular respiration, as this organelle are essential for energy production through cellular respiration. However, Plant cells feature a rigid cell wall providing structural support and a central vacuole for storage, while animal cells lack a cell wall and have smaller, scattered vacuoles. Chloroplast, crucial for photosynthesis, are exclusive to plant cells. 6. Which of the following is a correct list of structures found in both plant and animal cells? B MULTISTRUCTURAL It has two or more relevant ideas or response. Source: www.bing.com A. Mitochondria, vacuole, nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall B. Mitochondria, vacuole, nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm C. Mitochondria, vacuole, nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts D. Mitochondria, nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, cell wall, chloroplasts TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#4) STEM TEST ITEM ACCEP TABLE ANSW ER SOLO MODEL TAXONO MY RATION ALIZATI ON 1.Differentiat e plant cells and animals cells according to presence or absence of organelles; S7LT-IId-4 Plant cells and animal cells exhibit similarities in fundamental structures, such as the cell membrane, nucleus, and mitochondria. Both cell types have a cell membrane that acts as a selective barrier, a nucleus housing genetic material and mitochondria facilitating cellular respiration, as this organelle are essential for energy production through cellular respiration. However, Plant cells feature a rigid cell wall providing structural support and a central vacuole for storage, while animal cells lack a cell wall and have smaller, scattered vacuoles. Chloroplast, crucial for photosynthesis, are exclusive to plant cells. 7. Could a plant cell and animal cell survive without its mitochondrion even if all other organelles were present? Explain. D RELATION AL It is relational because the response of the learners requires understandi ng of the topic. Source: www.bing.com A.Yes, both plant and animal cells can survive without mitochondria. While mitochondria are important for energy, some cells have backup ways to produce energy. Not all cells need mitochondria for survival. B.No, plant cells can survive without mitochondria, but animal cells cannot. Plants have other ways to make energy without mitochondria, but animals really need mitochondria for their energy. C.No, animal cells can survive without mitochondria, but plant cells cannot. Animals have a backup plan for energy without mitochondria, but plant rely more on mitochondria for their energy needs. D.No, both plant and animal cells are highly dependent on mitochondria for survival. Both plants and animals really need mitochondria for their energy. Without them, it’s tough for cells to do their jobs and stay alive. TEAM GRADE 7 COMPETEN CY (#4) STEM TEST ITEM SOLO MODEL TAXONOMY RATION ALIZATI ON 1.Differentiat e plant cells and animals cells according to presence or absence of organelles; S7LT-IId-4 Plant cells and animal cells exhibit similarities in fundamental structures, such as the cell membrane, nucleus, and mitochondria. Both cell types have a cell membrane that acts as a selective barrier, a nucleus housing genetic material and mitochondria facilitating cellular respiration, as this organelle are essential for energy production through cellular respiration. However, Plant cells feature a rigid cell wall providing structural support and a central vacuole for storage, while animal cells lack a cell wall and have smaller, scattered vacuoles. Chloroplast, crucial for photosynthesis, are exclusive to plant cells. Task: Form a group of 6. Three groups will create a 3D model of plant cell and the other 3 groups will make a 3D model of animal cell. Let each group present their output in class. EXTENDED ABSTRACT It requires the students to create a 3D model. Source: www.bing.com Rubric: TEAM GRADE 7 THANK YOU!