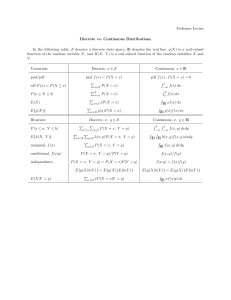
ADM2303 formula sheet: 2023 Random variables (RV) Discrete and continuous distributions Expected value of discrete RV X : The Binomial probability distribution: Probability theory E(X) = µ = Rule of sum of probabilities: n X xi P(X = xi ) i=1 P(S) = 1 P(A) = 1 − P(Ac ) = n X (xi − µ)2 P(X = xi ) i=1 = n X 2 x2i P(X = xi ) − µ2 i=1 Addition rule for two mutually exclusive events (where ∪ connotes “or” aka union): Standard deviation of discrete RV X: p SD(X) = σ = V ar(X) P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) Coefficient of variation of discrete RV X: Addition rule for two not mutually exclusive events: CV (X) = SD(X) E(X) P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∩ B) Multiplication rule for two independent events (where ∩ connotes “and” aka intersection): Correlation of two discrete RV X and Y : ρx,y Pn i=1 (xi − µx )(yi − µy ))P(X = xi ∩ Y = yj ) = sx sy Combining random variables P(A1 ∩ A2 ∩ ...An ) = P(A1 ) × P(A2 ) × ... × P(An ) Multiplication rule for dependent events: P(A ∩ B) = P(B|A)P(A) = P(A|B)P(B) Partition rule: for a partition B1 , B2 , ..., Bk : P(A) = k X P(A ∩ Bi ) = i=1 k X The Poisson probability distribution (if approx’n of binomial, λ = np): e−λ λx for x = 0, 1, 2, ... x! E(X) = λ, V ar(X) = λ, e = 2.718 P(X = x) = The Geometric probability distribution: P(X = x) = (1 − p)x−1 p for x = 1, 2, ... 1−p 1 E(X) = , V ar(X) = p p2 The Normal distribution: P(A ∩ B) = P(A) × P(B) Multiplication rule for n independent events: n! px (1 − p)n−x for x = 0, 1, ..., n (n − x)!x! E(X) = np, V ar(X) = np(1 − p) Variance of discrete RV X: Var(X) = σ Complement rule (Let Ac be complement of A, i.e., Not A): P(X = x) = Adding a constant c to random variable X: E(X ± c) = E(X) ± c 1 1 x−µ 2 X ∼ N (µ, σ) ⇒ f (x) = √ exp − ( ) 2 σ σ 2π X −µ Z= ∼ N (0, 1) ⇒ P(Z<z) = using normal table σ 2 V ar(X ± c) = V ar(X) = σX Multiplying random variable X by a constant a : E(aX) = aE(X) The Exponential distribution : X ∼ Expo(λ) ⇒ f (x) = λe−λx P(X ≤ a) = 1 − e−aλ 1 1 E(X) = , V ar(X) = ( )2 λ λ 2 V ar(aX) = a2 σX P(A|Bi )P(Bi ) i=1 Expected value of linear combination of RVs:1 Bayes’ formula: E(aX + bY + c) = aE(X) + bE(Y ) + c P(A|Bi )P(Bi ) P(A|Bi )P(Bi ) = Pk P(Bi |A) = P(A) i=1 P(A|Bi )P(Bi ) Events A and B are independent if: P(A|B) = P(A) and P(B|A) = P(B) or:P(A ∩ B) = P(A) × P(B) 1 For cases like 2X − 3Y The Uniform distribution: Variance of linear combination of RVs(1) : 2 2 V ar(aX + bY + c) = a σX + b2 σY2 + 2 a b Cov(X, Y ) where Cov(X, Y ) = ρx,y σX σY . If X and Y independent then ρx,y = 0 and covariance component drops out. 1 for a ≤ x ≤ b b−a x2 − x1 P(x1 <X<x2 ) = b−a (b − a)2 a+b E(X) = , V ar(X) = 2 12 X ∼ Uniform(a, b) ⇒ f (x) = the coefficient on Y is (−3), thus treat accordingly; want to subtract a constant rather than add — put minus sign on c. Sampling distributions for proportion Descriptive statistics Sample mean: x̄ = n 1X n i=1 X n If n is large i.e. np ≥ 10 and n(1 − p) ≥ 10 ! r p(1 − p) ⇒ p̂ ∼ N p, n X ∼ Binomial(n, p), and p̂ = xi Sample variance: n 1 X 1 (xi − x̄)2 = n − 1 i=1 n−1 s2x = n X ! x2i − nx̄2 Sampling distributions for mean i=1 σ If X ∼ N (µ, σ) ⇒ X̄ ∼ N (µ, √ ) n Sample coefficient of variation: CV = s If X ∼ N (µ, unknown) ⇒ X̄ ∼ tdf =n−1 (µ, √ ) n σ If n is Large If X ∼ unknown(µ, σ) ========⇒ X̄ ∼ N (µ, √ ) CLT n s x̄ Sample covariance: n 1 X 1 Cov(x,y) = (xi − x̄)(yi − ȳ) = n − 1 i=1 n−1 n X ! xi yi − nx̄ȳ i=1 Sample correlation: s If n is Large If X ∼ unknown(µ, unknown) ========⇒ X̄ ∼ tdf =n−1 (µ, √ ) CLT n Finite population correction factor n > 10% use : In case of a finite population where N r= Cov(x, y) = sx sy Pn i=1 (xi − x̄)(yi − ȳ) (n − 1)sx sy Percentile: - sort your data first kth percentile index : i = ( k )(n + 1) 100 - if i is integer, kth percentile is the ith value - if i is not integer, kth percentile is mean of the observations on either side of i Boxplot elements: IQR = Q3 − Q1 U pperLimit = Q3 + 1.5(IQR) LowerLimit = Q1 − 1.5(IQR) Normal approximation to Binomial If X ∼ Binomial(n, p) If n is large i.e. np ≥ 10 and n(1 − p) ≥ 10 p ⇒ X ∼ N µx = np, σx = np(1 − p) r standard deviation × N −n N −1