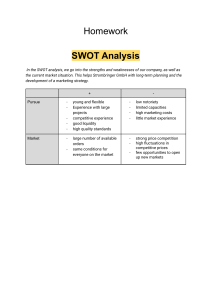
Purposive Communication Exam: Leads, Guiding, SWOT, Reports
advertisement

Final Examination in GEC-PC Purposive Communication First Semester, AY 2024-2025 INSTRUCTIONS: READ THE STATEMENTS AND QUESTIONS CAREFULLY. CHOOSE THE LETTER OF YOUR CHOICE BY SHADING ON THE ANSWER SHEET. 1. What is the primary purpose of a journalistic lead? A. To provide background information. B. To explain the reporter’s opinion. C. To include quotes from sources. D. To grab the reader’s attention and summarize the story. 2. Why should a lead highlight the timeliness of the story? A. To make the story seem more dramatic B. To increase the word count C. To connect the story to current events D. To focus on speculative future events 3. When should attribution be included in a lead? A. When the information is controversial B. When the information is common knowledge C. When the reporter has a strong opinion D. When the story involves public figures 4. Why should clichés be avoided in a lead? A. They are difficult to understand. B. They lack originality C. They make the lead too long. D. They are against journalistic ethics. 5. What is a potential downside of using a question lead? A. It is too formal B. It fails to provide enough detail. C. It may alienate the audience D. It takes too long to develop the story. 6. What should a tour guide do if they cannot answer a tourist's question? A. Make up an answer B. Divert the question to another tourist. C. Ignore the question and move on. D. Admit they don’t know and promise to find the information later. 7. A tour group includes members from diverse cultural backgrounds. When discussing a site with controversial historical significance, the guide should: A. Focus solely on the official narrative B. Present multiple perspectives C. Avoid discussing sensitive topics D. Express their personal views to guide the discussion. 8. A guide is narrating the history of an ancient monument but notices some guests losing interest. The guide’s best approach is to: A. Continue the script B. Shift to an interactive question-and-answer format. C. Add unrelated but entertaining anecdotes D. Focus only on guests who appear interested. 9. How should a guide decide the amount of detail to provide at a specific site? A. Offer as much information as possible B. Share only basic information C. Stick to the same script. D. Adjust the depth of detail based on group interest and time constraints. 10. A guide knows a popular legend about a site is historically inaccurate but highly engaging. The best approach is to: A. Present the legend as historical fact B. Share the legend with a disclaimer about its accuracy. C. Avoid mentioning the legend to maintain historical integrity. D. Mock the legend to discourage misinformation. 11. What is the primary purpose of storytelling in education? A. To simplify complex concepts through relatable narratives. B. To replace traditional teaching methods entirely. C. To entertain students during lectures. D. To eliminate the need for critical thinking. 12. Why is it essential for educators to gather feedback on their storytelling techniques? A. To focus on entertainment over education. B. To maintain the same narrative style regardless of effectiveness. C. To avoid adapting their methods to different classes. D. To ensure the stories align with student learning needs and preferences. 13. Why are metaphors useful in educational storytelling? A. They provide abstract comparisons that clarify complex ideas. B. They replace the need for factual accuracy. C. They confuse students with overly poetic language. D. They ensure the narrative remains vague and open-ended. 14. Why is perspective important in educational storytelling? A. It adds depth by showing different viewpoints B. It simplifies the story to one clear viewpoint. C. It minimizes the need for detailed characters. D. It guarantees agreement from all students. 15. What is the primary advantage of incorporating visuals into storytelling for students? A. It eliminates the need for verbal explanations. B. It aids in memory retention and comprehension of complex ideas. C. It reduces the importance of the narrative’s content. D. It distracts students from the subject matter. 16. What does SWOT analysis primarily assess? A. Company profits and expenses B. Marketing and sales strategies C. Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats D. Product development lifecycle 17. Which of the following is an internal factor in a SWOT analysis? A. Economic trends C. Organizational culture B. Competitors’ strategies D. Technological advancements 18. How does identifying ‘Threats’ in a SWOT analysis benefit an organization? A. It highlights areas for investment. B. It reveals external risks that need mitigation. C. It shows internal weaknesses to address. D. It outlines the company’s competitive edge. 19. What is a key limitation of SWOT analysis? A. It doesn’t allow for qualitative data analysis. Page 2 of 2 B. It focuses only on internal factors. C. It doesn’t prioritize identified elements. D. It requires external consultants to execute. 20. What would a high level of customer loyalty be classified as in a SWOT analysis? A. Opportunity C. Weakness B. Strength D. Threat 21. What kind of factor is a new government regulation that increases compliance costs? A. Strength C. Opportunity B. Weakness D. Threat 22. How can a company leverage its strengths in a competitive market? A. By using them to exploit opportunities B. By diversifying into unrelated markets C. By focusing only on external threats D. By ignoring weaknesses 23. What is the primary goal of identifying weaknesses in a SWOT analysis? A. To highlight areas for investment B. To reduce overall strengths C. To identify external challenges D. To minimize or eliminate vulnerabilities 24. When analyzing opportunities, what factor should be prioritized? A. Alignment with company strengths B. Competitor weaknesses C. Current threats in the market D. Long-term profitability only 25. Which industry is most likely to benefit from regular SWOT analyses? A. Static industries with little change B. Industries with minimal external impact C. Monopoly markets without competition D. Dynamic industries facing rapid technological or market shifts 26. How does a technical report differ from a business report? A. It focuses on personal opinions rather than data. B. It is more persuasive and less factual. C. It emphasizes technical procedures, findings, and solutions. D. It avoids including any graphics or visuals. 27. What is a critical characteristic of a technical report? A. It is highly subjective. B. It avoids using diagrams and tables. C. It uses precise, objective, and technical language. D. It focuses on persuasive storytelling. 28. What is the role of an executive summary in a business report? A. To provide a detailed explanation of all sections. B. To briefly summarize key findings and recommendations C. To include raw data for further analysis. D. To list sources and references. 29. Why is the "Methodology" section crucial in a technical report? A. It outlines the steps taken to achieve results B. It provides a summary of recommendations. C. It lists alternative solutions D. It serves as a concluding summary. 30. What is the primary goal of the "Conclusion" section in a business report? A. To present new data. B. To include detailed appendices. C. To explain the methodology used. D. To summarize findings and reiterate key recommendations. 31. In a business report, what should the introduction include? A. Detailed findings and recommendations. B. Visual aids and appendices. C. Raw data and calculations. D. The purpose, scope, and objectives of the report. 32. Why is active voice preferred in business and technical reports? A. It makes sentences longer and more complex. B. It increases clarity and directness in communication. C. It allows for more creative writing. D. It eliminates the need for formal structure. 33. What tone should be used in a technical report? A. Informal and conversational. B. Persuasive and exaggerated. C. Professional, neutral, and objective. D. Emotional and subjective. 34. How can jargon negatively impact a business or technical report? A. It makes the report more engaging for all audiences. B. It can alienate readers unfamiliar with the terminology. C. It simplifies the communication process. D. It ensures everyone understands the content equally. 35. What should be considered when presenting recommendations in a business report? A. Their feasibility and alignment with the organization's goals. B. Their alignment with personal opinions. C. Their complexity. D. Their entertainment value. 36. Which of the following best defines plagiarism? A. Writing an original paper with help from a peer. B. Paraphrasing without any acknowledgment. C. Using information from a public source with proper citation. D. Copying someone else's work and presenting it as your own without credit. 37. Which action is an example of unintentional plagiarism? A. Failing to properly cite a paraphrased idea from a source. B.Submitting a friend’s paper as your own. C. Copy-pasting large sections from an article without citation. D. Buying a paper online and submitting it as your work. 38. What does self-plagiarism involve? A. Submitting someone else’s work as your own. B. Using your previously submitted work without permission or acknowledgment. C. Rewriting ideas from other authors in your words. D. Properly citing your prior published work. 39. What should you do when in doubt about whether a source needs citation? A. Always err on the side of citing the source. B. Avoid citing it altogether. C. Use it without acknowledgment. D. Depend solely on your memory for facts. 40. How can collaboration with peers sometimes lead to unintentional plagiarism? A. By relying on shared ideas without properly distinguishing contributions. B. By writing separately and then merging the work. C. By avoiding the use of sources altogether. D. By referencing too many sources.