Intermolecular Forces: States of Matter & Dispersion Forces
advertisement

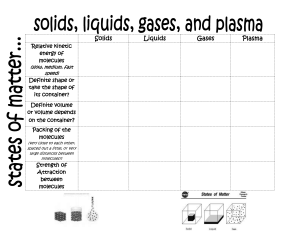
Intermolecular Forces (Chapter 12) Solids, Liquids, Gases ● Density affects freedom of movement, this is why liquids take up the shape of their containers and why gasses can be compressed easily, whereas liquids cannot. ○ Solid (definite shape, definite volume), liquid (indefinite shape, definite volume), gas (indefinite shape, indefinite volume) ● Solids can be either crystalline (composing atoms or molecules are arranged in a well ordered three-dimensional order) or amorphous ● Changes between states ○ Solids have most IMF (keeping the molecules close together), while gasses have less (the molecules are more spread out) Intermolecular Forces ● Intermolecular forces are attractive forces that hold condensed states together ○ At room temperature: ■ Strong IMF forces tend to result in solids and liquids ■ Weak IMF forces tend to result in gasses ● Dispersion Force ○ Present in all molecules and atoms ○ Result of electron presence/distribution ○ Factors that affect dispersion force ■ Molar mass ■ Surface area and molecular shape