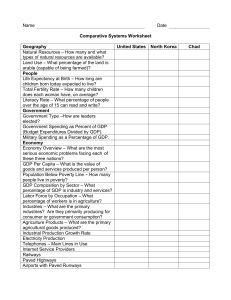
--**Front**: GDP per capita **Back**: GDP divided by total population. --**Front**: Purchasing power parity (PPP) **Back**: Constructs the cost of a representative basket of commodities in each country to compare income across countries. --**Front**: GDP per worker **Back**: GDP divided by the number of people in employment. --**Front**: Productivity **Back**: The value of goods and services a worker generates per hour of work. --**Front**: One dollar a day per person poverty line **Back**: A measure of absolute poverty used to compare poverty levels across countries. --**Front**: Human capital **Back**: Each person’s stock of skills used to produce economic output or value. --**Front**: Physical capital **Back**: Any good, such as machines and buildings, used for production. --**Front**: Physical capital stock **Back**: The value of equipment, structures, and other non-labor inputs used in production. --- **Front**: Technology **Back**: A set of devices and practices that determine how efficiently labor and capital are used in an economy. --**Front**: Aggregate production function **Back**: Describes the relationship between a nation’s aggregate GDP and its factors of production. --**Front**: Total efficiency units of labor **Back**: The product of the total number of workers and the average human capital per worker. --**Front**: Law of Diminishing Marginal Product **Back**: The marginal contribution of a production factor to GDP diminishes as its quantity increases, holding other factors constant. --**Front**: Research and development (R&D) **Back**: Activities aimed at improving knowledge, generating innovations, or applying knowledge in production to enhance technology. --**Front**: Efficiency of production **Back**: The economy's ability to produce the maximum output from given production factors and knowledge.