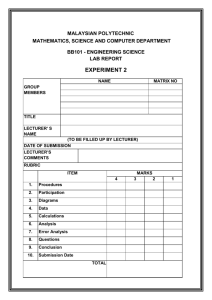
IGCSE TERM 1 PHYSICS ASSESSMENT • Complete the following assessment in the spaces provided below. • Answer all of the questions (Section A and Section B). • Where it does not stipulate, round answers to two (2) decimal points. • REMEMBER: provide all your workings for section B. • Once this assessment has been completed, please scan and submit it to your submission’s portal (located on the left-hand side of your dashboard) as one PDF document. • Remember to include your name, surname, grade and date. Student full name: __________________________ Grade: __________________________ Date: ___________________________ Total: _____ /50 Page 1 of 10 SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE [__________/20] 1.1 A long-distance runner wishes to calculate her average speed for a race. Which calculation should she use? a) 𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 b) 𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 × 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 c) 𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 d) 𝑎𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑠𝑝𝑒𝑒𝑑 = 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑖𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 + 𝑡𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 1.2 A digital stop-clock measure time in minutes and seconds. The stop-clock reads 00:50 when it is started (i.e. 00 minutes 50 seconds). It reads 02:10 when it is stopped. What is the shortest possible time that has elapsed between starting and stopping the stopclock? a) 1 minute 20 seconds b) 2 minutes 00 seconds c) 2 minutes 10 seconds d) 3 minutes 00 seconds 1.3 Which quantity is measured in newtons? a) Density b) Energy c) Pressure d) Weight 1.4 The diagram shows an experiment to find the density of a liquid. What is the density of the liquid? a) 0.5g/cm3 b) 2.0g/cm3 c) 8.0g/cm3 d) 10.0g/cm3 Page 2 of 10 1.5 The graph shows how the distance travelled by a vehicle change with time. Which row describes the speed of the vehicle in each section of the graph? 1.6 Two runners take part in a race. The graph shows how the speed of each runner changes with time. What does the graph show about the runners at time t? a) Both runners are moving at the same speed. b) Runner 1 has zero acceleration. c) Runner 1 runs ahead of runner 2. d) Runner 2 is slowing down. Page 3 of 10 1.7 The diagrams show four solid blocks with their dimensions and masses. Which block has the greatest density? 1.8 Four identical submarines P, Q, R and S are lowered from one depth to another in water of constant density. The initial and final depths of each submarine are shown in the diagram. Which row is correct for the difference in pressure form the initial to final depth of each submarine? Page 4 of 10 1.9 Why can a gas be compressed easily into a smaller volume? a) The molecules are far apart. b) The molecules do not attract each other. c) The molecules move randomly. d) The volume of each molecule can be reduced. 1.10 The graph below shows the motion of an airplane that is flying at constant altitude (height). What is the speed of the airplane when it is traveling at a constant speed? a) 45 m/s b) 42.5 m/s c) 40 m/s d) 45km/h Page 5 of 10 SECTION B: LONG ANSWERS AND CALCULATIONS [ 1. /30] The figure below shows an oil tank that has a rectangular base of dimensions 2.4m by 1.5m. The tank is filled with oil of density 850kg/m3 to a depth of 1.5m. 1.1 Calculate the pressure exerted by the oil on the base of the tank. (2) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 1.2 Calculate the force exerted by the oil on the base of the tank. (2) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 1.3 The force calculated in 1.1 is the weight of the oil. Calculate the mass of the oil in the tank. (1) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Page 6 of 10 1.4 When he is checking the level of oil in the tank, a man drops a brass key into the oil, and it sinks to the bottom of the oil. a) State what this shows about the density of brass. (1) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ b) Explain how attaching the key to a piece of wood could prevent the key from sinking. (1) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2. The figure below shows part of the speed-time graphs for a cyclist and for a runner. 2.1 Compare the motion of the cyclist and the runner during the first 6 seconds. Explain your answer. (3) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Page 7 of 10 2.2 Describe the motion of the cyclist between time t= 6.0s and time t = 12.0 s (1) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2.3 Calculate the total distance travelled by the cyclist between t=0s and t = 12.0s (4) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 2.4 After the first 6.0 seconds, the runner moves at constant speed for 4.0 seconds. He then slows down uniformly and stops in a further 2.0 seconds. On the graph below complete the graph for the runner’s motion. (2) Page 8 of 10 3. One way of analysing motion in a physics lab is to use ticker tape. A long tape is attached to a moving trolley and threaded through a device that places a tick upon the tape at regular intervals of time. The movement of a trolley down a slope was investigated using ticker tape with a frequency of 50 Hz. The ticker tape produced 50 dots per second. The 14 cm length of the ticker tape was cut into four strips. It was cut through the middle of the first and then the sixth hole 3.1 What is meant by acceleration? (1) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3.2 How would the appearance of ticker tape be different if the trolley moved at constant velocity? (1) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 3.3 Calculate the time that it took for each strip to form and hence show that mean velocity of the trolley in the strip marked A was 20cm/s. (2) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Page 9 of 10 3.4 The mean velocity of the trolley in strip B was 30cm/s. Recall a suitable equation to calculate the acceleration of the trolley in cm/s2. (3) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4. A boy steps off a high board into a swimming pool. The figure below shows the forces acting on the boy at one point in his fall. 4.1 The 540N force is caused by gravitational attraction. State the cause of the 100N force. (1) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4.2 Calculate the mass of the boy. (2) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ 4.3 Calculate the resultant force on the boy. State its direction. (3) ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Page 10 of 10