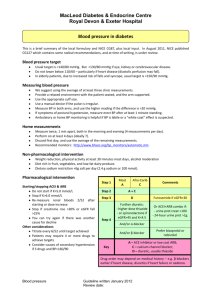
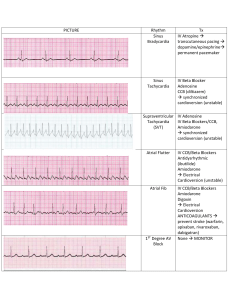
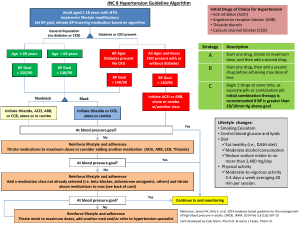
NURS5043 quiz 2 calcium carbonate, aluminium hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate alginate end in tidine end in prazole end in lol antacids neutralise gastric acid combine with antacids, physical barrier H2 receptor agonists, block histamine receptors reduce secretion proton pump inhibitors, inactivate proton pump Beta blockers block receptors for adrenaline, noradrenaline decrease HR, BP, oxygen load AE: hypotension, bradycardia, fatigue, bronchospasm rate limiting CCB Diltiazem or verapamil Digoxin inhibit calcium inflow L channel for contraction reduce vascular resistance and O2 requirements AE: hypotension, bradycardia, flushing, headahce lesser used for physically inactive for rhythm control arrythmia AE: GI, confusion lethargy, bradycardia with exertion Chemical Cardioversion rhythm control Flecainide and Sotalol flecainide - pill in pocket strategy sotalol - beta blocker amiodarone (2) - 1 if structured heart disease anticoagulant Warfarin reduce AF stroke risk by 2/3 only one valvular AF can have limits: increase stroke risk in first week, need a bridging drug, need INR readings weekly Novel oral anticoagulants (NOCAS) end in an no bridging needed, less bleeding risk, less INR readings CI in valvular AF aspirin + clopidogel antiplatlets Thromboembolic risk in AF 1. NOACs or Warfarin 2. aspirin + clopidogrel 3. aspirin monotherapy Rate control AF 1. Beta blockers 2. Rate limiting CCB 3. Digoxin end in pril ACEIs block angiotensin 2 (stop vasoconstriction), reduce Na+ retention AE: dry cough (buildup of bradykinins), hypotension, decr. renal function ARNI - sacubitril + ARB Entresto ARB func (block angiotensin 2) and boost conc. natriuretic peptide, increase conc cGMP inhibit renin and aldosterone release SGLT2i end in gliflozin water follow glucose (dec. BP, inc. CV outcomes AEL: euglycemic (acidosis with reg. gluc. levels loop diuretics furosemide Spironolactone k+ wasting, remove salt and water through urine AE: hyperkalemia, headache, electrolyte imbalance in CHF symptom management of breathlessness and oedema mineralocorticoid receptor agonist (aldosterone) decrease preload (prevent snapping, cardiac output) HFrEF 1. ARNI/ACEI/ARB & SGLT2i (ARNI prefered) 2. beta blockers 3. spironolactone 4. loop diuretics slow acting nitrate contain nitrate prevent angina attack tolerance need 8-12hr free a day (enzyme) AE: hypotension, headache, gastric reflux fast acting nitrate glyceryl trinitrate stable angina (prevention of angina attack) acute angina attack management decrease O2 demand, increase coronary blood supply 1. beta blockers 2. calcium channel blockers (can’t use with beta blockers 2. slow acting nitrate (use with either above) other drugs: antiplatelets, statins, ACEi plase suffix post ACS therapy (fab four) fibrinolysis - dissolve clot in ACS 1. antiplatelets (plural!!!) 2. B blockers (within 24hr) 3. ACEi (after BB stabilization) 4. statin statins end in statin inhibit cholesterol syntehsising enzyme (decrease HDL, increase LDL) primary half max dose, secondary max dose stabilize plaques, anti-inflammatory AE: myopathy, increase creatine kinase, muscle aches fibrates fibra in middle not used as much but good for high triglycerides Ezetimibe cholesterol absorption inhibitor often combined with statin AE: headache, diarrhoea end in ocumab PCSk9 inhibitors reduce liver ability to remove LDL-C (50% reduction) expensive so only for high family risk pts Dyslipidemia high LDL 1. statin 2. add ezetimibe, if statin not tollerated switch to ezetimibe or fibrate monotherapy high TG 1. fibrate +- fish oil 2. add nicotinic acid ARBs end in sartan clinically same as ACEi except for cough block angiotensin 2 & reduce aldosterone AE: hypotension and dec. renal function dihydropyridine CCBs end in dipine uncomplicated hypertension (use rate limiting in complicated hypertension) AE: hypotension, oedema, flushing thiazide or thiazide like duretics hydrochlorothiazide 1st line in >65, 2nd line in <65 lower systolic more than diastolic hypertension 1. ACEi or ARB or CCB or thiazide duretic 1. DHP CCB for uncomplicated, rate limiting CCB for complicated 2. Thiazide for >65 2. ACE/ARB + CCB or Thiazide 3. ACE/ARB + CCB + Thiazide Salbutamol, terbutaline erol suffix ICS - inhaled corticosteroids montelukast Ipratropium Tiotropium SABA - short acting beta agonist bronchodilator LABA - long acting beta agonist bronchodilator & preventer prevetor AE: thrush, clean mouth after use LTRA - leukotriene receptor agonist SAMA - short acting muscarinic antagonist bronchodilator LAMA - Long Acting Muscarinic Antagonist preventor Asthma 1. SABA 2. ICS (low dose) or LTRA (+SABA) 3. ICS (high) or ICS + LABA (low) or ICS + LTRA (low) (+SABA) COPD 1. SABA or SAMA (rarely) 2. LAMA or LABA + SABA 3. LAMA + LABA + SABA 4. ICS + LAMA + LABA + SABA H.pylori with peptic ulcer proton pump inhibitor (prazole) clarithromycin amoxicillin NSAIDs with peptic ulcer stop nsaid if possible proton pump inhibitor (prazole) misoprostol Misoprostol mucosal protective agent prostaglandin analogue NSAIDs inhibit PG synthesis AE: GI severe Sucralfate forms complex gel with mucous not absorbed by body must be taken every 6hr AE: GI severe