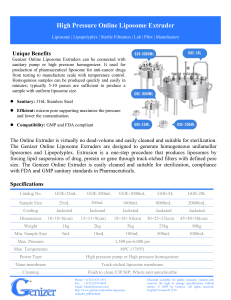
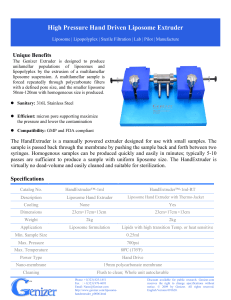
Liposome Extruder: What it is, How does it work, Advantages, Applications and Types Liposome Processing: Liposome Extruders Instrument: Genizer Liposome Extruders AKA: Exosomes Extruders, Artificial Cell Membrane Extruders; Liposomes Preparation devices by extrusion Advantages: Liposome extruders are mainly used for the liposome formulation and achieving uniform size distributions. It is an ideal instrument to generate nanoscale liposome formulations, and to prepare exosomes and artificial cell membranes. By utilizing the tracked-etched filter membranes, the liposome extruders are capable of capturing large particles, precipitation and achieving sterile filtration. Application: Research and Development for the liposomal drug delivery system, vaccine, gene delivery, and cosmetics Working Principles: A liposome is a spherical-shaped vesicle composed of phospholipid bilayers. Phospholipid bilayers are critical components of cell membranes, with hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. In an aqueous solution, the hydrophobic ends tend to bind to each other, and spontaneously form small sphericalliposomes. The liposome extruder is designed for the preparation of liposomes. It is easy to use, and has high precision particle size control ability with narrow distributions and satisfactory repeatability. So far it has been widely used in the preparations of complex injectable liposome products. Figure 1 Gene delivery liposome with phospholipid bilayers Liposome extrusion technology is employing the structural and performance characteristics of liposomal phospholipid bilayers. When the operational temperature is slightly above the phase transition temperature of phospholipids, the large vesicles of liposomes will pass through polycarbonate membranes with specific pore sizes by a certain external extrusion force. The large particle size liposome or multiple compartments liposomes are rapidly repolymerized into smaller-size liposomes after being ruptured by the shear of membrane pores. Since the pore size of polycarbonate membrane is fixed (e.g., 50nm, 100nm, 200nm, 400nm, 1um, etc.), and the polycarbonate extrusion membrane features vertical and uniform nano pore distributions on the membrane surface, when the large vesicles pass through the membrane with a specific nano pore size several times, the sample is extruded to the uniform size decided by the pore. Figure 2 Schematic diagram depicting the liposome extrusion 1. Common Types of Liposome Extruders Liposome extruders can be classified into three categories: hand drivenliposome extruders, jacketed liposome extruders, and online liposome extruders. Each category is based on its different power sources. 1.1 Hand DrivenLiposome Extruders The hand driven liposome extruders are capable of processing the sample volume from 0.25mL to 2.5mL, which is suitable for mini sample volume applications during the experimental phase. It is operated by simply pushing the plunger manually. There are two types of hand driven extruders: extruders under ambient temperature, and extruders with jacketed option. The hand driven liposome extruders with cooling jacket are designed for those extrusion conditions to control the sample temperature. Figure 3 Hand Driven Liposome Extruders 1.2 Jacketed Liposome Extruders The jacketed liposome extruders have a wide range of processing capacities, from sample volume 2mL to 3L depending on the models. It is suitable for lab scale and pilot scale applications. It is driven by compressed nitrogen cylinder. Most of the jacketed liposome extruders are designed with jacketed barrel to achieve the temperature control of the sample. Figure 4 Jacketed Liposome Extruders 1.3 Online Liposome Extruders Online liposome extruders are available for the processing capacity from 2mL to 20L depending on the different models. These extruders are more suitable for pilot scale applications. It is powered by a high-pressure pump unit or other production equipment. Figure 5 Online Liposome Extruders 1.4 Multiple Liposome Extruders System The multiple liposome extruders system is able to process the volume from 1L to 200L. It features both the temperature and pressure sensors in the product line, and a control panel to control the production for liposomes. Figure 6 Multiple Liposome Extruders systems with liposome extruding control panel 2. Track-Etched Polycarbonate Extrusion Membranes The operations of liposome extruders have high requirements for the extrusion membranes. The nucleus track-etched polycarbonate membranes should have uniform distributions of filter pores. In an ideal membrane, all nano pores should be of the same size. Furthermore, the extrusion membrane with vertical pore distribution is more conducive to the preparation of liposome extrusion. Figure 7 Microscopic Representation for Track-Etched Polycarbonate Membranes In general, selecting right size of the polycarbonate membranes will ensure successful extrusion. It is strongly recommended to know the initial particle size of the processing sample before the extrusion. Another factor to consider for selecting the membrane is the desired particle size for your end product. For example, if the initial particle size of the sample is 1μm, and the target is to achieve the particle size below 100 nm, here are two options available: 1) Extrusion Multiple Times via the Target Pore Size Membranes For example, the user can extrude the sample through a 100 nm polycarbonate membrane using a liposome extruder several times. But the problems that may arise are: 1) The difficulties in extrusion process; 2) The large vesicles may block the surface of the polycarbonate membrane, and request a replacement of a new membrane, etc. 2) Extrusion via the Different Pore Size Membranes This procedure is to use different pore size membranes to extrude step by step. For example, the sample is extruded through a 400nm polycarbonate membrane first, and observe the extrusion process. If it is hard to extrude the sample through the 400nm membranes, then replace a new membrane with a larger pore size, such as 800nm for extrusion 3~5 times. It can be optimized during the process. After the first-round extrusion, select a smaller pore size polycarbonate membrane, such as 100 nm or 80 nm to extrude again. 200 nm polycarbonate membranes can be used as a transition if the extrusion is difficult to go through the 100 nm membranes. 3) High Pressure Homogenization-Extrusion Method The sample can be high pressure homogenized first, and extruded through a 100nm or 80nm polycarbonate membrane after homogenization.(Figure 8) Figure 8 High Pressure Homogenizer combines with online liposome extruder