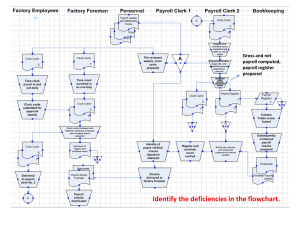
HR Generalist Handbook A Complete Guide to HR Generalist Roles Prepared By: Vijayakumar R Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com vijay@maxprohrtraining.com Table of Contents 1. Introduction to HR Generalist Roles What is an HR Generalist? Key Responsibilities and Skillsets Career Path of an HR Generalist 2. Employee Relations Building Positive Employee Relations Conflict Resolution Strategies Managing Employee Grievances and Complaints Communication and Engagement Best Practices 3. Policy Development Importance of Clear HR Policies Step-by-Step Guide to Policy Development Examples of Common HR Policies Ensuring Legal Compliance in Policies Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com 4. Payroll Administration Introduction to Payroll Processing Key Payroll Components (Basic Pay, Overtime, Deductions, etc.) Compliance with Payroll Regulations Payroll Software Overview and Best Practices 5. Benefits Administration Overview of Employee Benefits Health Insurance, Retirement Plans, and Paid Leave Managing Employee Benefits Enrollment Legal and Compliance Considerations for Benefits 6. HR Compliance Understanding Labor Laws and Regulations Compliance with ESI, EPF, and Other Statutory Requirements Managing HR Audits and Reporting Compliance Best Practices for HR Generalists Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com 7. Performance Management Basics of Performance Appraisal Systems Setting and Managing Performance Goals Conducting Performance Reviews and Feedback Sessions Legal Considerations in Performance Management 8. Talent Acquisition and Recruitment Understanding the Recruitment Process Strategies for Attracting Talent Screening, Interviewing, and Selecting Candidates Onboarding Best Practices 9. HR Technology and Analytics Introduction to HR Software and Tools Basics of HR Analytics for Decision Making Managing Employee Data Integrating Technology into HR Functions Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com 10. Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Importance of DEI in the Workplace Implementing DEI Strategies as an HR Generalist Creating Inclusive Policies and Practices Measuring the Success of DEI Initiatives 11. Learning and Development (L&D) Identifying Training Needs Designing Effective Training Programs Managing Employee Development Initiatives Measuring Training Outcomes and ROI 12. Employee Engagement and Retention Understanding Employee Engagement Metrics Strategies to Improve Retention Creating a Positive Work Culture Employee Recognition and Motivation Programs Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 1: Introduction to HR Generalist Roles What is an HR Generalist? An HR Generalist is a versatile role within the Human Resources field that requires a broad understanding of various HR functions. Unlike specialists who focus on one particular area, HR Generalists are involved in several facets of HR, including recruitment, employee relations, payroll, benefits administration, compliance, and more. This role is crucial for ensuring that HR processes run smoothly, and it often serves as a bridge between the company and its employees. Key Responsibilities and Skillsets HR Generalists typically handle the following: Employee Relations: Managing employee grievances and fostering positive relationships. Policy Development: Creating, implementing, and updating company policies. Payroll and Benefits Administration: Ensuring employees are paid correctly and receive their benefits on time. Compliance: Ensuring the company complies with labor laws and regulations. Skills needed for success in an HR Generalist role include strong communication, problem-solving, organizational, and time management abilities. Career Path of an HR Generalist Starting as an HR Generalist opens numerous career opportunities. After gaining experience, HR Generalists can advance into specialized roles such as HR Manager, HR Director, or even CHRO (Chief Human Resources Officer). Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 2: Employee Relations Building Positive Employee Relations A key aspect of being an HR Generalist is maintaining positive employee relations. This involves ensuring open lines of communication between employees and management and creating a supportive work environment. HR Generalists play a critical role in mediating conflicts, resolving grievances, and promoting a culture of trust. Conflict Resolution Strategies Active Listening: Understand the issues from both sides. Empathy: Show understanding and respect for employees' feelings. Neutral Mediation: Act as an unbiased mediator to resolve conflicts fairly. Managing Employee Grievances and Complaints Handling employee grievances in a timely and efficient manner is vital to maintaining morale and preventing larger issues from arising. Establishing a clear grievance process ensures that employees feel heard and valued. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 3: Policy Development Importance of Clear HR Policies HR policies serve as the foundation of the organization’s relationship with its employees. Clear policies help prevent misunderstandings and ensure that all employees are treated consistently. Step-by-Step Guide to Policy Development 1. Identify the Need for a Policy 2. Draft the Policy: Ensure clarity and alignment with legal requirements. 3. Review and Revise: Involve key stakeholders. 4. Communicate and Implement: Ensure all employees are aware of the new policy. 5. Monitor and Update: Regularly review policies for relevance. Examples of Common HR Policies Attendance Policy Code of Conduct Anti-Harassment Policy Remote Work Policy Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 4: Payroll Administration Introduction to Payroll Processing Payroll involves calculating employee wages and managing deductions, taxes, and benefits. Ensuring accuracy and compliance with local regulations is crucial in payroll management. Key Payroll Components Employee Information: Collect and maintain accurate employee data, Salary Structure: Payroll administration involves calculating salaries based on the company’s salary structure, Time and Attendance: Accurate time and attendance tracking is essential for determining wages Overtime Pay: In many jurisdictions, overtime pay is regulated by law. Leave Management: Payroll must reflect employee leave, Compliance: Payroll must comply with a variety of local, state, and federal laws regarding wages, taxes, and benefits. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Key Payroll Process : Data Collection: Gather all necessary information, Payroll Calculation: Calculate employee earnings based on their salary structure, Tax Calculation and Withholding: Determine the amount of tax to be withheld based on employee income and applicable tax laws. Payment Processing: After calculations, process payroll by issuing payments to employees. Payslip Distribution: Provide employees with payslips detailing their earnings, deductions, and net pay.. Reporting: Generate payroll reports for management and compliance purposes. Post-Payroll Activities: These include filing tax returns, making tax payments, and depositing contributions to provident funds or insurance schemes. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Compliance and Legal Considerations for the Payroll Process : Income Tax Act: HR Generalists must ensure that payroll adheres to the provisions of the Income Tax Act, Minimum Wages Act: Payroll must comply with the Minimum Wages Act, ensuring that no employee is paid below the prescribed minimum wage for their role or industry. Provident Fund (PF) Compliance: HR Generalists are responsible for ensuring that both employer and employee contributions to the provident fund are deducted and deposited correctly, Employee State Insurance (ESI): Payroll must reflect ESI deductions and ensure compliance with the Employees’ State Insurance Act. Professional Tax: Depending on the state, employees may be subject to professional tax. Payroll must calculate and deduct this tax appropriately. Labour Law Compliance: Payroll administration must also adhere to labor laws, such as payment of gratuity, bonuses, and other statutory benefits. Audit Readiness: Maintaining accurate and detailed records of all payroll activities is crucial for audit purposes. Payroll data should be organized and readily available in case of internal or external audits. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 5: Benefits Administration Overview of Employee Benefits Employee benefits go beyond just salary—they encompass a range of perks like health insurance, retirement savings plans, paid leave, and more. Offering competitive benefits is a key factor in attracting and retaining top talent. Types of Employee Benefits 1. Health Insurance: Medical, dental, and vision coverage. 2. Retirement Plans: Provident fund (PF), pension schemes, 3. Paid Time Off (PTO): Vacation, sick leave, and maternity/paternity leave. 4. Wellness Programs: Mental health support, wellness initiatives. 5. Flexible Working Arrangements: Work-from-home, flexible hours, etc. Managing Employee Benefits Enrollment Effective administration ensures that employees are aware of the benefits available and are able to take full advantage of them. Legal and Compliance Considerations for Benefits It’s crucial to ensure that employee benefits comply with labor laws and regulations. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 6: HR Compliance Understanding Labor Laws and Regulations Compliance with labor laws is one of the most critical areas for HR Generalists. Missteps can result in fines, legal action, or reputational damage to the organization. Key Labor Laws to Consider 1. Minimum Wages Act: Ensures that employees are paid a fair wage. 2. The Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) Act: Mandates retirement benefits. 3. The Employees' State Insurance (ESI) Act: Provides health benefits for employees. 4. The Factories Act: Governs working conditions in manufacturing industries. 5. The Shops and Establishments Act: Regulates work hours, leave policies, etc. Managing HR Audits and Reporting These audits ensure that the organization is following all relevant labor laws and regulations. Documentation and accurate record-keeping are key to a smooth audit process. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 7: Performance Management Basics of Performance Appraisal Systems Performance management is about guiding employees toward optimal performance through goal-setting, regular feedback, and formal evaluations. HR Generalists help implement and manage performance appraisal systems, ensuring that they are fair and aligned with organizational objectives. Setting and Managing Performance Goals Performance goals should be: Specific Measurable Achievable Relevant Time-bound (SMART framework) Conducting Performance Reviews and Feedback Sessions Performance reviews are critical touchpoints for employee development. Legal Considerations in Performance Management Ensure that performance appraisals do not discriminate against any protected groups and are conducted fairly. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 8: Talent Acquisition and Recruitment Understanding the Recruitment Process The recruitment process involves multiple stages, including job posting, sourcing candidates, screening applications, interviewing, and hiring. Strategies for Attracting Talent Employer Branding: Promote your company as a great place to work. Job Descriptions: Create clear and compelling job descriptions. Sourcing Channels: Utilize job boards, social media, referrals, and campus recruiting to find candidates. Screening, Interviewing, and Selecting Candidates Screening resumes and conducting interviews are vital steps in the recruitment process. Develop a structured interview process with a standardized set of questions to ensure fairness and consistency. Onboarding Best Practices A successful onboarding process helps new hires adjust quickly to their roles and company culture. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 9: HR Technology and Analytics Introduction to HR Software and Tools In today’s digital world, HR Generalists must be familiar with HR software like HRMS (Human Resource Management Systems), payroll software, and other tools that automate and streamline HR functions. Popular HR Tools Zoho People: HRMS for employee data management, attendance, and more. BambooHR: Employee records, performance reviews, and reporting. Workday: Comprehensive tool for HR, finance, and analytics. Basics of HR Analytics for Decision-Making HR analytics involves using data to make informed decisions about hiring, retention, performance, and employee engagement. Key metrics may include employee turnover rates, time to hire, absenteeism, and more. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 10: Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) Importance of DEI in the Workplace Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) initiatives are vital for fostering an inclusive work environment where all employees feel valued and respected. Implementing DEI Strategies Recruitment: Ensure diverse representation in candidate pools. Training: Provide regular DEI training for employees and managers. Policies: Develop policies that support diverse employees, such as flexible work arrangements or affinity groups. Creating Inclusive Policies and Practices Work to eliminate bias in all HR processes, from recruitment to performance reviews. Measuring the Success of DEI Initiatives Track DEI metrics, such as the representation of diverse groups in leadership, employee satisfaction with DEI efforts, and diversity in hiring, to measure progress and identify areas for improvement. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 11: Learning and Development (L&D) Identifying Training Needs HR Generalists must assess the skills gaps within the organization and work with department heads to identify training needs. This could include technical training, leadership development, soft skills training, or compliance-related workshops. Designing Effective Training Programs Develop training programs that are aligned with organizational goals. Use a blend of in-person workshops, online courses, and experiential learning to cater to different learning styles. Managing Employee Development Initiatives HR Generalists are responsible for overseeing development initiatives, tracking participation, and evaluating the effectiveness of training programs. Measuring Training Outcomes and ROI Measuring the impact of training programs is key to demonstrating their value. Use metrics like performance improvements, employee feedback, and the return on investment (ROI) to assess success. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Chapter 12: Employee Engagement and Retention Understanding Employee Engagement Metrics Employee engagement reflects how committed and motivated employees are toward their work and the organization. Measuring engagement levels can help identify areas where the company needs to improve. Strategies to Improve Retention Career Development: Provide clear pathways for advancement. Recognition Programs: Reward and recognize employees for their hard work. Work-Life Balance: Offer flexibility to support employees' personal and professional lives. Creating a Positive Work Culture Foster a culture of trust, collaboration, and open communication. Employees are more likely to stay in environments where they feel respected and valued. Employee Recognition and Motivation Programs Develop programs to regularly acknowledge employee achievements, Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Conclusion Mastering the HR Generalist role requires a blend of technical HR knowledge, interpersonal skills, and a strategic mindset. By focusing on the key areas outlined in this handbook, you will be well-equipped to handle the challenges of the role and contribute meaningfully to your organization’s success. As an HR Generalist, you are the backbone of the HR department, wearing many hats and ensuring that the HR function operates smoothly. By mastering these areas, you'll not only succeed in your role but also position yourself as a valuable asset to any organization. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Introducing Maxpro HR Management Training Institute (MHRM) At Maxpro HR Management Training Institute (MHRM), we are committed to empowering HR professionals with the skills, knowledge, and hands-on experience needed to excel in their HR careers. Whether you're an HR fresher or a mid-career professional looking to transition into an HR Generalist role, our comprehensive HR Generalist Practical Training Program is designed to equip you with real-world expertise. Our program covers everything from HR compliance, payroll administration, and employee relations to advanced HR analytics and generative AI for HR professionals. Delivered by industry experts, the course combines theoretical knowledge with practical sessions, including live projects and case studies, to help you master the skills you need to succeed in the competitive HR landscape. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com Why Choose Maxpro HR Training Institute? Experienced Trainers: Hands-on Training: Flexible Learning: 100% Placement Support: Internship Opportunities: Take the Next Step in Your HR Career Are you ready to accelerate your career in HR and become an HR Generalist? Enroll in our HR Generalist Practical Training Program and start your journey to success. Visit our website at www.maxprohrtraining.com to learn more about our courses and offerings. Call us at 9791065092 / vijay@maxprohrtraining.com to speak with an advisor and discuss your training needs. Follow us on LinkedIn for the latest updates, HR tips, and job openings. Maxpro HR Management Training Institute www.maxprohrtraining.com