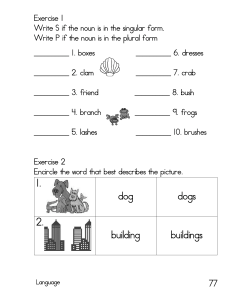
LEXICAL CATEGORIES OBJECTIVES Explain the lexical categories and their subtypes. Identify the rules based on three criteria: meaning, morphological form, and syntactic function. Determine the categories according to how they are used in a sentence. NOUN Nouns are naming words. They are usually thought of as words that name a/an: Person Place Thing Idea Examples: Allen is from Wyoming. The dog sleeps in her bed. Most Filipinos practice Christianity. Thunder rattled our windows. Sandra's courage and curiosity made her a good explorer. CLASSES OF NOUNS 1. COMMON and PROPER A common noun names anyone of a general class of persons, places, or things. A proper noun names a particular person, place, or thing. 2. COUNT, MASS, and COLLECTIVE A noun that can be counted individually is called a count noun. A noun that cannot be counted but can be quantified as a unit is called a mass noun. A collective noun denotes the number of persons, places, or things as one group. COUNTERS OF MASS NOUN bar/s of dozen/s of meter/s of barrel/s of gallon/s of ounce/s of bottle/s of glass/es of pair/s of box/es of gram/s of pint/s of can/s of herd/s of piece/s of carton/s of kilo/s of sack/s cup/s of liter/s of sheet/s of 3. CONCRETE and ABSTRACT A concrete noun names a thing that is actual or real. An abstract noun names an idea or quality that the senses cannot perceive. PROPERTIES OF NOUNS 1. NUMBER OF NOUNS A singular noun denotes ONE person, place, or thing. A plural noun denotes MORE THAN ONE person, place, or thing. RULES IN FORMING THE PLURAL NOUNS 1. Most nouns form their plural by adding s to their singular form. 2. If the singular noun ends in s, x, z, ch, or sh, add es to form the plural. 3. Nouns ending in o preceded by a consonant form their plural by adding es. 4. Nouns ending in o preceded by a vowel form their plural by adding s. 5. For Nouns ending in f o fe, change the f or fe to v and add es to form the plural. 6. Some nouns ending in f form the plural by adding s. 7. For Nouns ending in y preceded by a consonant, change the y to I and add es. 8. Nouns ending in - form their plural by changing -is to -es. 9. Nouns ending in y preceded by a vowel form their plural by adding s. 10. Some nouns have irregular plural forms. 11. Some nouns of foreign origin have the same plural forms as their original foreign ones. 12. Some nouns borrowed from a foreign language have both a foreign and an English plural. 13. Compound words form their plural by adding -s to the most important word. 14. Letters, numbers, signs, and words regarded as words form their plural by adding ‘s. 15. Add s to nouns with the suffix -ful. 16. Some nouns have the same form in the singular and plural forms. 17. Some nouns are plural in form but singular in meaning. 18. Some nouns have only plural forms, no singular forms. 2. GENDER OF NOUNS Gender is the property of a noun that distinguishes sex/gender. There are four genders. MASCULINE - denotes males FEMININE - denotes females COMMON - denotes either male or female NEUTER - denotes noun without sex. 3. CASES OF NOUNS Nouns under the nominative case may function as the subject of the sentence, predicate nominative or subject complement, noun of address, and appositive. The subject tells what the sentence is about. Henry Sy owns SM Supermalls. The girl works in a telecommunications company. The predicate nominative explains, restates, names, or stands for the subject. Dr. Narcita Ouano is the dean of the College of Education. Dr. Alegado is a language and literature professor. A noun used to call the attention of the person addressed or spoken to is called a noun of address. Kelly, please make up your mind. Submit the needed documents by Monday, Miss Dela Cruz. A noun used to explain another noun just before it is called a noun in apposition or appositive. Dezmonde, a shih tzu, is turning three on September 18. My landlady, Lola Rose, wants everything to be always in order. Nouns in the possessive case indicate the possessor of the referent of that noun. RULES IN FORMING THE POSSESSIVE FORM OF NOUNS 1. If a singular noun does not end in s, add ‘s. The boy’s delivery van caused traffic. The mayor’s attempt to end the problem was successful. 2. If a singular common noun ends in s, add ’s --- unless the next word begins with s. If the next word begins with s, add an apostrophe only. This includes words with s and sh sounds. The witness’s version of the story was inconsistent. The witness’ story did not match the statement. 3. If a singular proper noun ends in s, add an apostrophe. James’ score on the exam was high. Jess’ dream is to own a house. 4. If a noun is plural in form and ends in s, add an apostrophe only, even if the intended meaning of the word is singular (such as mathematics and measles). The Research and Statistics’ office… 5. If a plural noun does not end in s, add ‘s. Gabriela is concerned with women’s rights. The media’s coverage was comprehensive. 6. If there is joint possession, use the correct possessive only for the possessive closest to the noun. PNoy and Drillon’s campaign was a success. Mayet was worried about her mother and father’s marriage. 7. If there is a separate possession of the same noun, use the correct possessive form for each word. The owner’s and the manager’s relatives were present. 8. In a compound construction, use the correct possessive form of the word closest to the noun. Avoid possessives with compound plurals. The father-in-law’s message was addressed to the couple. Nouns under the objective case may function as direct object, indirect object, objective complement, and object of the preposition. The direct object is the noun that is used as the receiver of the action. The waiter served beer-battered fish and chips with sesame brown rice. The faculty and staff of AdNU visited the tourist spots in Ilocos. The indirect object tells to whom/what or for whom/what action is intended. The grammar teacher taught Nil and Lin the ways to edit a run-on sentence. Allan gave the students home reading assignments. The objective complement (sometimes called a second object or predicate objective) names the direct object. The faculty club elected Mr. Reyes as president. The body has named the organization Guild of English Major Students. As an object of the preposition The students received high marks in Structure of English. Due to the ongoing construction on the campus, some classes are held under the trees. FORMS OF COMPOUND NOUNS 1. SOLID OR CLOSED COMPOUND-jellyfish, wheelchair, raincoat, wallpaper 2. HYPHENATED COMPOUND NOUNS-editor-in-chief, self-service 3. TWO-WORD OR SPACED COMPOUNDS-mother tongue, real estate Twin Words/English Binomials are words that ordinarily go hand in hand because they are closely related. It is sometimes called English binomials.