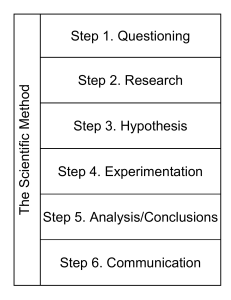
SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, AND SOCIETY STS | 1ST SEMESTER | A.Y. 2024 - 2025 SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY, TECHNOLOGY, AND IMPACT ON SOCIETY MILESTONES IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF SCIENCE Thales of Miletus ● 624-546 BC ● Miletus = Place in Greece ● A Milesian philosopher renowned for his idea that the essence of matter is called "water". ● Material Monism: All matter is composed of one material. ● Aristotle regards him as the first philosopher In the Greek tradition. ● Also "flat earther". ● One of the philosopher to study of Cosmology. Phytagoras ● 571-491 BC ● A well-known mathematician who demanded that truth should not be accepted but proved. ● He believed that everything in the universe can be explained in "numbers". ● Legends say that he believed that eating beans is sinful and he drowned a student for revealing the existence of irrational numbers to the world. Aristotle ● 384-322 BC ● Considered the founder of both science and philosophy of science. He wrote extensively about the topics we now call physics, astronomy, psychology, biology, and chemistry, as well as logic, mathematics, and epistemology. ● A philosopher with vast contribution in the different disciplines of science who first articulated the concept of induction and deduction. ○ Induction: Specific -> General ○ Deduction: General -> Specific Ptolemy ● Claudius Ptolemaeus ● AD 127-145, Alexandria ● Ancient astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. ● He believed that Earth is the center of the universe in the concept known as Geocentrism or Geocentric Model. ○ Geocentrism: All the planets, including the sun, revolves around the earth. MODERN PERIOD OF SCIENCE Francis Bacon ● 1561-1626 ● He is known for his idea that scientific knowledge is obtained after observation then utilizing inductive reasoning to interpret the observation. Ptolemy ● He believed that Earth is the center of the universe in the concept known as Geocentrism or Geocentric Model. Rene Descartes • 1596-1650 • He has been credited as the "Father of Modern Philosophy". • He is known but the saying "cogito, ergo sum" or "I think, therefore I am" and believes that science Is based on mathematics. • Cartesian Plane Karl Raimund Popper • 1902-1994 • A very significant philosophical twist in the scientific method was championed by him. • An Austrian-British professor at the London School of Economics. He rejected the classical inductivist views on the scientific method, in favour of empirical falsification –view that a theory in the empirical sciences can never be proven, but it can be falsified. Realism or logical empiricism, modified with the views of Popper, probably is the “most received view” of Western science in the modern period. KSNDRNCL | 1 SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY, AND SOCIETY STS | 1ST SEMESTER | A.Y. 2024 - 2025 William Overton • He laid the rules for a statement to be classified as scientific; o It must be guided but natural law. o It must be explanatory by reference to natural law. o It is testable against the empirical world. o Its conclusions are tentative. o It is falsifiable. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. SCIENTIFIC METHOD Observation Hypothesis Experimentation Results Conclusion Share THEORY OF LAW Theory A well substantiated statement that DESCRIBES a natural phenomenon. Law A well substantiated statement that EXPLAINS a natural phenomenon. Similarities 1. Both are based on tested hypotheses. 2. Both are supported by a large body of empirical data. 3. Both are widely accepted by the vast majority (if not all) scientists within a discipline. 4. Both are falsifiable. Example 1: Observe - A student scores poorly on a math test. Hypothesis - The student didn’t study enough. Experimentation - The student studies for two hours every day for the next test. Analysis of Results - The student’s score improves significantly on the next test. Conclusion - Increased study time leads to better test scores. Share - Share this study strategy with classmates. Example 2: Observe - The bread is not rising while baking. Hypothesis - The yeast might be expired. Experimentation - Use fresh yeast and bake another loaf. Analysis of Results - The new loaf rises properly and turns out well. Conclusion - Expired yeast prevents bread from rising. Share - Advise other bakers to check the expiration date on their yeast. KSNDRNCL | 2