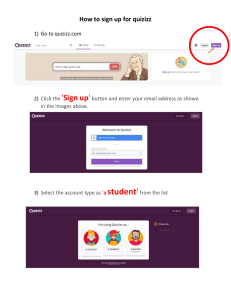
UNIT 2: The Web Task 1: A- Back button B- Forward button C- Refresh button D- View site information button E- Address bar. F- Reader view G- Favorites button H- Search bar I- Clickable hyperlink J- Clickable Image K- Home button Task 2: URL Address: E Go back one page: A Go forward one page: B Go to home page: K Stop the current transfer: D Search box: H Feed button: F Refresh the current page: C Show favorites: G Clickable image link: J Clickable hypertext link: I Task 3: 1. Country code: the company is in the UK 2. Web service: this is the webpage 3. Protocol prefix: the type of transmission standard your browser must use to access the data 4. Domain: this points to the computer where the webpage is stored 5. Directory path: this is where the webpage is stored in the computer 6. Domain name extension: this is a company 7. Document name: this is a Web file Task 4: .aero - f (aviation industry) .biz - k (businesses) .com (.co in UK) - g (commercial) .coop - a (cooperatives) .edu (.ac in UK) - h (educational and research) .gov - d (government) .info - l (general use) .int - i (international organization) .mil - c (military agency) .net - b (gateway or host) .org - j (non-profit organization) .pro - e (professionals) Task 5: To search for information on the Web: Google To buy books and DVDs: Amazon To participate in political campaigns: MoveOn.org To view and exchange video clips: YouTube To manage and share personal photos using tags: Flickr To buy and sell personal items in online auctions: eBay To download music and movies, sometimes illegally: Bit Torrent To look up the meanings of new terms: Wikipedia To make free phone calls or video conferencing: Skype To set up a virtual world in which users can pretend to be whomever or whatever they want to be: Second Life. Task 6: 1-e 2-c 3-a 4-b 5–d Task 7: Open source, editable web pages: Wikis The same as electronic retailer, or online store: E-tailer A blog that includes video: Videoblog A program that allows you to make voice and video calls from a computer: Skype An audio broadcast distributed over the Internet: Podcast Task 8: 3 Simple Sentences: - The Internet isn't just about email or the Web anymore. They're trading songs on illegal file-sharing networks. eBay, for instance, wouldn't exist without the 61 million active members who list, sell, and buy millions of items a week. 3 Compound Sentences: - - They're posting opinions on online journals – weblogs, or blogs; they're organizing political rallies on MoveOn.org; It's the emergence of the 'Power of Us'. Thank to new technologies such as blog software, peer-to-peer networks, open-source software, and wikis, people are getting together to take collective action like never before." Many are music fans, who can blog, email friends, upload photos, and generally socialize." 3 Complex Sentences: - It's the emergence of the 'Power of Us'. Thanks to new technologies such as blog software, peer-to-peer networks, open-source software, and wikis, people are getting together to take collective action like never before. - - But less obvious is that the whole marketplace runs on the trust created by eBay's unique feedback system, by which buyers and sellers rate each other on how well they carried out their half of each transaction. Another successful example of a site based on user-generated content is YouTube, which allows users to upload, view and share movie clips and music videos, as well as amateur videoblogs. 2 Mixed Sentences: - Increasingly, people online are taking the power of the internet back into their own hands. But less obvious is that the whole marketplace runs on the trust created by eBay's unique feedback system, by which buyers and sellers rate each other on how well they carried out their half of each transaction. Task 9: Streaming is a way of dealing with bandwidth problems when you download video from the Internet. One key to successful streaming is the process of buffering. If you download a movie, the video player stores part of the movie in memory while playing it. Imagine the buffer as a container filled from the top as shown in the flowchart. When the container is full, the player sends data on for playback from the bottom. Data keeps coming in while a clip plays. The user can view the beginning of the movie while the rest of the clip downloads. If connection slowdowns or interruptions occur, the amount of data in the buffer decreases but as long as some remains, playback is uninterrupted. Playback continues at a steady rate until the buffer is empty. Task 10: - Bulletin → Board (Bulletin Board) Domain → Name (Domain Name) File → Transmission (File Transmission) Graphical → Link (Graphical Link) Mobile → Phone (Mobile Phone)