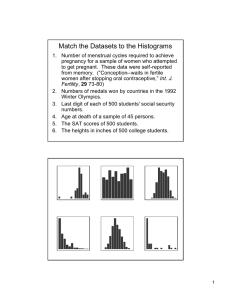
1 RPD Module – Intake 2023 Flipped Classroom Note - Contraceptives ● Types of contraceptives can be divided into two broad categories as below. Temporary / Reversible ● Natural methods Periodic abstinence Withdrawal Lactational Amenorrhea ● Barrier methods ⮚ PHYSICAL Male/ female condoms ⮚ CHEMICAL Spermicides ● Hormonal contraceptives Combined Oral Contraceptive pill Progesterone only pill Injectable preparations Subdermal implants Emergency Contraceptive pill ● Intrauterine devices IUCD Permanent ● Female sterilization Ligation and Resection of Tubes (LRT) ● Male sterilization Vasectomy 2 ● NATURAL METHODS/Fertility awareness-based methods (FAB) ● Are based on observation of naturally occurring signs and symptoms of the fertile and infertile phases of the menstrual cycle. ● To avoid pregnancy, it is necessary to abstain from intercourse on potentially fertile days of the menstrual cycle. ● Use of FAB requires motivation and a regular menstrual cycle, and so cannot be used for women at extremes of reproductive age. Typical failure rates are high. ● These methods include. a. Calendar method/ Rhythm method (this will be discussed here) b. Basal body temperature method c. Cervical mucus method d. Sympto thermal method CALENDAR METHOD Day 1- 1st day of menstruation First day of the fertile period (1st unsafe day) = 27 – 20 = D7 Last day of the fertile period (last unsafe day) = 30 – 10 = D20 ⮚ A woman must first keep a strict record of her menstrual cycle for at least six consecutive cycles. ⮚ The cycle is from the first day of her period starts. ⮚ To calculate the fertile time, first, you subtract the number 20 from your shortest cycle. (DC Dutta's Textbook of Gynecology) ⮚ This gives you the probable first day of your fertile time. ⮚ Then you subtract the number 10 from your longest cycle. ⮚ This gives you the probable last day of the fertile time. ⮚ You need to avoid sexual intercourse during this fertile period. 3 ⮚ This requires the partner’s cooperation. ⮚ This method is never practiced if the difference between cycle length is more than 10 days, recent pregnancy or abortion, and chronic medical illness. Fertile period The fertile period is the period that is optimal for fertilization. SAFE PERIOD The part of the menstrual cycle between the previous period and a few days before ovulation, during which unprotected sexual intercourse is less likely to lead to fertilization than intercourse at other times. It is the basis for the rhythm method of family planning, but its safety is only relative. (oxford reference) ● H0RMONAL CONTRACEPTION ❖ ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES 1. Combined oral contraceptives Combined oral steroidal contraceptives are the most effective reversible method of contraception. (DC Dutta's Textbook of Gynecology) This contains estrogen and progesterone combined in one tablet. Most used COCPs are low doses and contain ethynyl estradiol. (Ten teachers,20th ed.) This is given for 21 days followed by hormone-free 7 days during which iron tablet is given to complete 28 days cycle. These are taken daily. Efficacy is about 99% if used correctly. Mode of action: The probable mechanism of contraception is: 4 1. Inhibition of ovulation — (principal mode) Both hormones synergistically act on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis. The release of gonadotropin-releasing hormones from the hypothalamus is prevented through a negative feedback mechanism. There is thus no peak release of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary. So follicular growth is either not initiated or if initiated, recruitment does not occur. 2. Producing static endometrial hypoplasia. 3. Alteration of the character of the cervical mucus. 2. Progestin-only pills ⮚ These must be taken daily from 1st day of the cycle without pill-free intervals. ⮚ POP does not contain estrogen and the progestin content is less than the COC pill. ⮚ Examples: norethisterone (commonly used), Levonorgestrel ⮚ Mechanism of action: It works mainly by making cervical mucus thick and viscous, thereby preventing sperm penetration. Also, the endometrium becomes atrophic, so, implantation is hindered. ❖ INJECTABLE CONTRACEPTIVES ⮚ This is the most popular contraceptive method in Sri Lanka. (DMPA) (prof. Randeniya’s book) 5 ⮚ a depot injection of medroxyprogesterone acetate (long-acting progestin). ⮚ It can be administered intramuscularly (buttock, upper arm, lower abdomen) within 5 days of the cycle) as the formulation Depo-Provera or subcutaneously. ⮚ Administered once in 3 months. From the injection site, steroids are slowly released into circulation, accounting for the drug's lasting action. ⮚ Mechanism of action: 1. Inhibition of ovulation — by suppressing the mid-cycle LH peak. 2. cervical mucus becomes thick and viscid thereby preventing sperm penetration. 3. Endometrium is atrophic, thus, preventing implantation. (DC Dutta) ⮚ No estrogen, therefore ideal method for lactating mothers. (Negative feedback diminishes on the anterior pituitary during postpartum) ⮚ Efficacy is very high. ❖ SUBDERMAL IMPLANTS ⮚ A less popular method where low-dose progesterone is used as an implant system. ⮚ A reversible long-acting method is effective for usually 3 - 5 years. ⮚ An ideal method for spacing and limitation of the family. ⮚ The mechanism of action is like the above hormonal contraceptive methods. ⮚ High efficacy. ⮚ Examples: jadella, Norplant 6 ❖ EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTIVES Available as, • Hormones • IUD - CU • Anti-progesterone •Others HORMONAL EC ⮚ The available products are levenorgestrel and ulipristal acetate. ⮚ Mode of action: The exact mechanism of action remains unclear. The following are the possibilities: 1. Ovulation is either prevented or delayed when the drug is taken at the beginning of the cycle. 2. Fertilization is interfered with. 3. Interferes with the function of corpus luteum or may cause luteolysis. (DC Dutta's Textbook of Gynecology) (But this does not interfere with an established pregnancy. Thus, do not induce abortion.) ⮚ Postinor 2 - Contains two tablets. The 1st should be taken within 72hr of exposure and the second 12hr after the intake of 1st. ⮚ postinor 1 - contain only one tablet that should be taken within 72hr of exposure. this is more convenient than postinor 2 due to single dose. ⮚ COC in higher doses can be used as ECP. The mechanism is the prevention of ovulation by feedback inhibition on LH, and FSH. 7 IUCD EC ★ However, The Cu-IUD is the most effective method of emergency contraception (EC) available (failure rate 1 in 1,000) and should ideally be offered as first choice to women. ★ Its effect on the endometrium is thought to prevent implantation if fertilization has occurred. ★ The Cu-IUD can be removed once pregnancy has been excluded or can be left in place for ongoing contraception. ★ an emergency Cu-IUD can be inserted up to 5 days after the unprotected sex or 5 days after predicted ovulation. ● IUCD ⮚ This is a device placed in situ and efficient in preventing pregnancy. ⮚ Copper IUCDs prevent fertilization by direct toxicity and causing local inflammation hostile to sperm, possibly to eggs. They also stimulate a noninflammatory macrophage reaction on the endometrium causing anti implantation effect. ⮚ These effects are further enhanced by its copper content of it. ⮚ Progesterone-releasing IUCD converts the endometrium unsuitable for implantation. ⮚ Results are, Inhibit ovum transport Inhibit sperm transport in the upper female genital tract Inhibit fertilization Inhibit implantation 8 Advantages and disadvantages of contraceptive methods Common to all contraceptives: a) Reduce the incidence of ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy outside the uterine cavity) as well as a normal pregnancy. BARRIER METHODS Advantages Disadvantages Protect from STDs Just in case of emergency ALLERGY No protection from STDs. HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION ● ORAL CONTRACEPTIV ES 1. COCP Contraceptive Benefits 1. Efficacy – about 99% if used correctly. 2. Sexual intercourse is not affected by usage. 3. On reversal of the method, fertility returns rapidly. Has non-contraceptive benefits also. 1. Improve menstrual irregularities, dysmenorrhea, and premenstrual syndrome (pain, vomiting, discomfort before menstruation) 2. Reduce the risk of ovarian and endometrial carcinoma. 3. 3. Reduce the incidence of iron deficiency anemia in menstruating women. 1. With prolonged use, women might gain weight. 2. Since taken daily, patient compliance is the biggest disadvantage. . 9 POP/PROGESTERONE ONLY PILLS Same as above are MOSTLY the Same as above. 2. ● POPs INJECTABLE CONTRACEPTIV ES (DMPA) Since there is no estrogen, it is good for lactating women and women in their 40s. Contraceptive Benefits 1. The success rate is more than 99%. So, this is a high-efficacy method. 2. As administered once in 3 months, the patient’s compliance is high. 3. No estrogen, thus an ideal method for lactating mothers. 4. Easy to use. Has non-contraceptive benefits also. 1. weight gain 2. irregular bleeding 3. Inability to stop effects immediately after stopping usage and delay to return fertility. (Average duration is 7 – 12 months) Therefore, not suitable for shortterm methods. 4. Contraindicated in pregnancy, >40 years with DM, HTN, smoking, severe migraine, and valvular heart diseases. 1. Reduce the risk of endometrial carcinoma, pelvic inflammatory disease, and fibroids. 2. Symptomatic relief from endometriosis. ● SUBDERMAL IMPLANTS Contraceptive Benefits 1. Efficacy is very high. (But slightly reduced in obese people) 1. Mostly the Same as above hormonal contraceptives. 2. Insertion and removal require minor surgery. 10 2. An ideal method for spacing and limitation of the family. 3. Long acting, but reversible. 4. Easy to use. 5. can be used by breastfeeding women. 3. Cannot be initiated or discontinued with the provider. Has non-contraceptive benefits. ● EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTIV E PILLS As COCP 1. Nausea and vomiting are much more. Intense with estrogen use. IUCD form. (An intrauterine device (IUD) has a lower failure rate than oral methods of emergency contraception. Also, once in place, it can be used on an ongoing basis) ● IUCD Contraceptive Benefits 1. Very safe and efficacy is more than 99% in Cu IUCD. 2. Suitable for spacing and limitation of the family. 3. Long lasting and reversible., thus, rapidly returning to fertility. 4. No systemic side effects. And complications are rare. 5. Can be used by breastfeeding women. 1. Insertion and removal require a trained provider as improper insertion may lead to perforation of the uterine wall at the time of insertion. 2. Not suitable for women at risk of STD s. 3. no HIV/AIDs protection in CU IUCD too. 4. prolonged or heavy menstrual bleeding is possible between menstrual periods and may occur as a side effect. 11