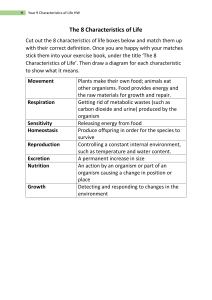
BIOLOGY DEFINITIONS Movement An action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place Sensitivity It is the ability to detect or stimuli in the internal or external environment and to make responses Growth It is a permanent increase in size and dry mass by an increase in size number or cell size or both Excretion The removal from organisms of the waste products of metabolism,toxic materials and substances in excess of requirements Species A group of organisms that can reproduce to produce fertile offspring Binomial system An internationally agreed system in which the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and species Diffusion It is the net movement of molecules and ions from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration down a concentration gradient as a result of their random movement Osmosis It is the net movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane Active transport It is the movement of molecules and ions in and out of the cell through the cell membrane ,against concentration gradient ,using energy from respiration Enzymes Protein molecules that act as biological catalysts Catalyst A substance that increases the rate of chemical reactions without being used up or changed Photosynthesis A process by which plants make carbohydrates from simple raw materials using energy from light A balanced diet It is a daily intake of seven nutrients;carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, water and fibers in a correct amount to provide energy required and raw material for healthy growth and tissue repair Ingestion Taking of substances into the body through the mouth Digestion Large insoluble molecules are broken down to small and soluble molecules by mechanical and chemical digestion Absorption The movement of small and soluble food molecules and ions through the wall of the intestine into the blood Assimilation The movement of digested food molecules into the cells of the body where they are used and become part of the cells Egestion Passing out of food that has not been digested or absorbed Transpiration The loss of water vapour from plant leaves by evaporation of water at the surfaces of the mesophyll cells followed by loss of water vapour through stomata Translocation The movement of sucrose and amino acids in phloem from the regions of production(source) to regions of storage or regions of utilization in respiration or growth Pathogen A micro-organism that causes disease Transmissible disease A disease caused by a pathogen and can be passed from one host to another Antigens Chemicals found on the surface of the pathogen that are recognised by the body as foreign Active immunity Defence against a pathogen by antibody production in the body Passive immunity A short-term defence against a pathogen by antibodies acquired from another individual Respiration Chemical reactions inside the cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy Aerobic respiration Chemical reactions inside the cells that use oxygen to break down nutrient molecules to release large amount of energy Anaerobic respiration Chemical reactions inside the cells that break down nutrients to release small amount of energy per glucose molecule without using energy Deamination The removal of the nitrogen-containing part of amino acids to form urea Synapse A junction between two neurones Reflex actions They are automatic,rapid,integrating and coordinating responses to stimuli Sense organs Groups of receptor cells that respond to specific stimuli (light,sound,chemicals.....) Hormone A chemical substance produced by a gland and carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs Gravitropism A response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from gravity Phototropism A response in which parts of a plant grow towards or away from the direction from which light is coming Homeostasis The maintenance of a constant internal environment Drugs Any substance taken into the body that modifies or affects the chemical reactions in the body Antibiotics Substances which kill bacteria, but do not harm other living cells, mostly made by fungi Reproduction The process that makes more of the same kind of an organism; it can be sexual or asexual reproduction Asexual reproduction A process resulting in the production of genetically identical offspring from one parent Sexual reproduction A process involving the fusion of nuclei of two gametes to form a zygote, and the production of offspring that are genetically different from each other Gametes They are sex cells produced by meiosis (reduction division)which reduces the number of chromosomes to half the number found in ordinary cells, so when gametes fuse together the zygote will regain the ordinary number of chromosomes Self-pollination The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or different flower on the same plant Cross-pollination The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species Fertilisation The fusion of nuclei of sperm and egg forming diploid nucleus and zygote is formed Implantation It is the sinking of the embryo into the spongy lining of the uterus Sexually transmitted They are infections that can be transmitted via body fluids during sexual infections(STIs) intercourse, they are caused by bacteria or viruses Inheritance The transmission of genetic information from generation to generation Chromosome A thread like structure of DNA, carrying genetic information in the form of genes Homologous chromosomes A pair of chromosomes having the same structure, carrying genes for the same characteristics in the same position, one from the mother and one from the father Gene AA length part of DNA that codes for one protein Allele A version of a gene or any of two or more alternative forms of a gene Haploid nucleus A nucleus containing a single set of unpaired chromosomes Diploid nucleus A nucleus containing two sets of chromosomes Mitosis A nuclear division which giving rise to two genetically identical cells Stem cells Un-specialized cells that divide by mitosis to produce daughter cells that can become specialized for specific functions Meiosis(reduction division) A nuclear division in which the chromosome number is halved from diploid to haploid resulting in formation of for four genetically different cells Genotype The genetic make-up of an organism phenotype The observable features of an organism Homozygous individual The one having two identical alleles for a particular gene Heterozygous individual The one having two different alleles of a particular gene Dominant allele An allele that is only expressed if it is present (represented by a capital letter e.g. B) Recessive allele An allele that is only expressed where there is no dominant allele of the gene present (represented by a small letter e.g. B) Family pedigree Diagram for the inheritance of a given characteristic within the family used to predict the results cross Sex-linked characteristic A characteristic in which the gene responsible is located on a sex chromosome Variation Differences between individuals of the same species Mutation A sudden unpredictable change in the base sequence of DNA Adaptive feature The inherited functional features of an organism that increases its fitness Fitness The probability of an organism surviving and reproducing in the environment in which it is found Evolution Changes in the adaptive features of a population over time as a result of natural selection Adaptation Process resulting from natural selection by which populations become more suited to their environment over many generations Population Group of organisms of one species living in the same area at the same time Community All of the populations of different species in an ecosystem Habitat A place where an organism lives Ecosystem A unit containing the community of organisms and their environment, interacting together Niche Role played by an organism in an ecosystem Ecology The study of the interaction between living organisms and their environments Food chain A diagram showing the flow of energy from one organism to the next starting with a producer Food web A network of inter-connected food chains Trophic level The position of an organism in a food chain,food web or pyramid of biomass or numbers Producer An organism that makes its own organic nutrients usually using energy from sunlight through photosynthesis Consumer An organism that gets energy by feeding on other organisms Primary consumer(herbivore) An animal which eats plants Secondary An animal which eats another animal consumer(carnivore) Decomposer An organism that gets its energy from dead matter or waste organic materials,they are extremely important because they help to recycle substances Biotechnology Using living organisms (usually micro-organisms) to make substances that we want Genetic engineering Changing the genetic material of an organism by removing, changing or inserting individual genes Eutrophication Reduction in the level of 02 in water which leads to death of all aquatic life that respire aerobically Sustainable resource A resource that s produced as rapidly as it is removed from the environment that it does not run out Sustainable development Development providing for the needs of an increasing human population without harming the environment