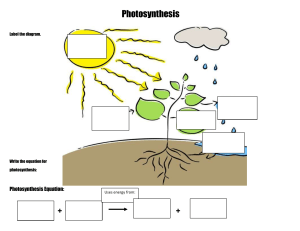
Explore Photosynthesis is a biological process by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabolism1. Here’s a simplified explanation of the process: 1. Light Absorption: Photosynthetic organisms absorb light energy, usually from the sun, using pigments like chlorophyll1. Chlorophyll absorbs the red and blue spectrums of light, reflecting green, which is why most plants appear green1. 2. Conversion to Chemical Energy: The absorbed light energy is used to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds2. This process chemically converts carbon dioxide (CO2) and water into food (sugars) and oxygen3. 3. Storage and Use of Energy: The chemical energy produced is stored within intracellular organic compounds like sugars, glycogen, cellulose, and starches1. To use this stored chemical energy, an organism’s cells metabolize the organic compounds through cellular respiration1. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth’s atmosphere, and it supplies most of the biological energy necessary for complex life on Earth1. If photosynthesis ceased, there would soon be little food or other organic matter on Earth2. It’s important to note that some bacteria perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, which uses bacteriochlorophyll to split hydrogen sulfide as a reductant instead of water, producing sulfur instead of oxygen1. In summary, photosynthesis is a vital process that enables life on Earth by converting light energy into chemical energy, producing oxygen, and providing food for organisms. It’s a fascinating example of nature’s ingenuity and efficiency.