A2 Physics Homework: Circular Motion, Oscillations, Newton's Laws
advertisement

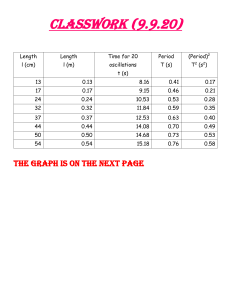
Explore Science Elite Camp Explore Science Elite Camp – A2 Physics Homework – Week 15 教学资料属于@探索国际教育教学部,不得转发或做其它⽤途。 1. The angle subtended by an arc of a circle that has a length equal to the circle radius a = w^2r F = ma a = F/m F/m = w^2r w^2 = F/mr W = mg m = W/g w = sqrt(F/mr) = sqrt((18-3)/((3/9.81)*0.85)) = 7.6 7.6 2. Repeated back and forth movements on either side of an equilibrium position Ideal condition where the oscillation movements are not affected by any external force Oscillations when acceleration is proportional to displacement from a fixed point and in the opposite direction, which is towards a fixed point Not simple harmonic as acceleration of ball is constant due to gravity 3. Loss of energy from a system due to resistive forces Light damping as the mass has many oscillations period = 0.6/2 = 0.3 1/0.3 = 3.3 3.3 KE = 1/2 mv^2 v = wr KE = (1/2) *(65*10^-3)((2[pi]/0.3) *1.5*10^-2)^2 = 0.0032076... = 0.0032 = 3.2 mJ 1.5 -1.1 = 0.4, 1.1-0.4 = 0.7 so it would suggest linear decrease, but amplitude does not decrease linearly so after 8 further complete oscillations the amplitude would not be 0.7cm 4. Newton's third law is that that an action force has a equal and opposite reaction force. Therefore the weight should create a equal reaction force opposite to it if the pair an example of Newton's third law. However a part of the normal contact force would originate from the centripetal force, which means the force from weight is not equal in magnitude to the reaction force from it. v = wr w = 2[pi]/T = 2[pi]f = 2[pi](1600/60) v = 2[pi](1600/60) *(0.5/2) = 41.888 = 42 ms^-1 100/1600 * 41.888 = 2.618 = 3 42 F = ma F = mv^2/r ma = mv^2/r a = v^2/r gravity = centripetal acceleration for zero force 9.81 = v^2/0.25 sqrt(9.81*0.25) = 1.6 1.6 3 5.