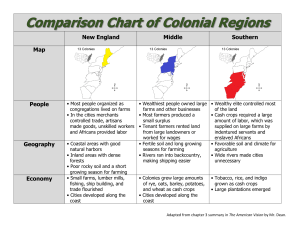
Directorate: Curriculum GET: LESSON PLAN TERM 3 SUBJECT and GRADE SOCIAL SCIENCE – GRADE 4 GEOGRAPHY TERM 3 LINK TO TEACHING AND ASSESSMENT PLAN Week 1-3 AIMS OF LESSON The learner will be able to use enquiry skills to investigate geographical and environmental concepts and processes, and investigate and draw conclusions from the past. INTRODUCTION • • • Introduction to the topic: Food and farming in South Africa People and food Food people eat – from plants and animals (classifying) People and food Ways people get their food – buying, growing, collecting, fishing, hunting Ways of farming Farming for self and family (subsistence farming) Ways of farming Farming crops and animals to sell (commercial farming) Growing food in towns and cities Learners should already know some knowledge about how and where we obtain food. Make a link to a previous lesson or teaching in a previous grade Explain purpose of lesson (further learning and/or functioning in the world) People get the food they need in different ways: Buy food o At a shop, stall or someone on the street. Grow plants and keep animals o People on farms can grow their own food and keep animals o People in towns and cities sometimes has a vegetable garden or fruit trees. Food collectors GET CURRICULUM / 1 o Catch fish and hunt animals o Find and eat plants that grow in nature o They know what is healthy and what is poisonous. o They pick fruit, berries and mushrooms and dig out carrots. Most of our food comes from farms o Farmers work on farms and produce the food we eat, like mealies, meat, vegetables and eggs. Fish o Most of the fish we eat gets caught at sea. o We also find freshwater fish in dams and lakes. Subsistence farming: Farming for self and family People who grow their own crops and keep their own animals for food. They eat most of the food and might sell a small amount thereof. The money is then used to buy other things they need but cannot produce themselves. Farmers who farm to feed themselves and their family, are called subsistence farmers. Most of the work on subsistence farms are done by women, children and elderly people. The men usually work far away in towns. Much of the work is done by hand or by using simple tools like spades and hoes. Commercial farming: Farming crops and animals to sell The food that we buy in shops comes from big commercial farms. Example – bread comes from wheat that is grown on commercial farms. Commercial farms grow crops or keep livestock to sell. Crops that are grown to sell are called cash crops. Most commercial farms only grow one crop, but a lot thereof to sell. Examples are sugar cane and mealies. Commercial farmers also keep livestock such as sheep, goats, pigs, cattle and chickens. Commercial farms are usually very big. Farmers use machines, like tractors, to help them. Farm workers also work on the farm and earn a salary or wage for the work they do. GET CURRICULUM / 2 Growing food in towns and cities People who live in towns and cities can grow some of their own food – like vegetables, herbs and fruit. They usually use the food they grow themselves, or give it away to friends and family. They cannot grow everything they need and have to buy other food. They cannot keep livestock like people on farms. SKILLS • • Explain/describe the key concepts / definitions that learners need to know or be able to do with the necessary detail. Explain clearly and step by step GET CURRICULUM / 3 ACTIVITIES/ASSESSMENT Refer learners to activities/assessment they can complete/do in their textbooks. Where there is more than one textbook rather refer to sections instead of specific page numbers. OR if necessary include an activity/assessment 1. Draw a table with two columns and sort food according to their source into the correct column. Cabbage; beetroot; bread; lattuces; apples; eggs; spinach; milk; corn flakes; tomatoes; chicken legs; steak FOOD FROM ANIMALS FOOD FROM PLANTS CONSOLIDATION RESOURCES (if necessary) 2. What do we call a farmer who farms for himself and his family? 3. What are crops? 4. List 4 examples of different crops. 5. What is a commercial farmer? 6. What do we call crops which are grown with the only intention of being sold? 7. Name 2 examples of cash crops. 8. The bread we buy at a shop is made of wheat. Is wheat a grown by a subsistence or commercial farmer? New words: Food collector – someone who collects and eats food growing in the wild. Poisonous – something that can make you very ill when you eat or drink it. Freshwater – water that is not salty (it does not come from the sea) Crops – plants that people plant and grow to use Subsistence farmers – farmers who grow crops and keep animals to feed themselves and their families Commercial farmers – farmers who farm as a business to make money Cash crops – Crops that people grow to sell Livestock – Animals kept by farmers Paper based resources Digital resources Refer learners to specific Sections / Topics/ Pages in the textbook / that learners will have on hand Refer to the relevant digital resources e.g. links on the WCED ePortal https://www.thelearningtrust.org/asp-treasure-box GET CURRICULUM / 4 NOTES SUBJECT SOCIAL SCIENCE GEOGRAPHY GRADE 4 TERM DATE Skills Teaching Methodologies/ Approach (WHAT I am going to teach/guide/support…) (HOW I am going to teach/guide/support…) Read through the Notes, and work through the activities. 1. 2. 3. 4. Analyze the source externally Analyze the source internally Categories of investigation Analyze the information TEACHER’S ACTIVITIES Similar to what teachers would teach, etc. as indicated above – this could be a repeat of the teacher’s info – just so that parents are aware of content. Keep it simple. PARENT’S ACTIVITIES Step 1: Appropriate background knowledge is set out and the key topic is introduced. Step 2: Learners read information answer leading questions and complete in their notebooks. Step 3: The whole class discusses the central theme of the lesson and give feedback. Could include tips to parents, e.g. Help your child search for a magazine/ newspaper to find appropriate pictures. Parents could show learners around the house, in the room, how one could represent certain items, like the cupboard, bed, chair, etc. 3 Week 1-3 Resources / LTSM (WHAT I am going to use to teach/guide/support…) Worksheet and Notes provided. Visual resources Archaeological sources Written sources Landscape resources Physical resources Oral sources Please indicate resources that can be found at home: magazines, newspapers, dictionary, etc. Learner activities: step by step, practical, keep it simple. LEARNER’S ACTIVITIES Read the notes below and complete the questions above with the help of the words provided. Discuss and illustrate by means of pictures from magazines and newspapers different ways in which people get their food through buying; growing; collecting, fishing, hunting, different types of farming, etc. GET CURRICULUM / 5