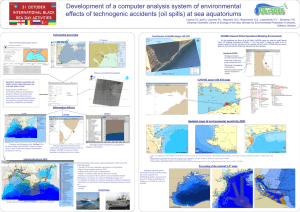
GNOME ITLSA1-22 Content: • 1. What is GNOME? • 2. Important points about GNOME • 3. GNOME aims • 4. GNOME functions • 5. GNOME commands • 6. Step by step installing GNOME on Linux • 7. Commands to remove GNOME on linux • 8. GNOME Shell extensions • 9. Install GNOME Tweak Tool What is GNOME? • GNOME, which stands for GNU Network Object Model Environment, is a free and open-source desktop environment for Unix-like operating systems. It provides an intuitive and attractive graphical user interface for users, along with a suite of applications and tools for everyday tasks. Important points about GNOME: • User Interface: GNOME features a simple and modern user interface with a focus on ease of use. It includes elements like the GNOME Shell, which provides core interface functions like the top bar, system status area, and an overview mode for switching between applications and virtual desktops. • Applications: GNOME comes with a range of built-in applications, such as the Nautilus file manager, the GNOME Terminal, the Gedit text editor, and the GNOME Software app for managing software installations. These applications are designed to integrate Important points about GNOME.. Continue • Customization: While GNOME aims for simplicity, it also allows for extensive customization through extensions and settings. Users can install GNOME Shell extensions to add new features and change the behavior of the desktop environment. • Development and Community: GNOME is developed by the GNOME Project, which is a part of the larger GNU Project. It is maintained by a community of contributors and is supported by organizations like the GNOME Foundation. The development follows a regular release cycle, with new versions typically released every six Important points about GNOME.. Continue • Compatibility: GNOME can be installed on various Unix-like operating systems, including Linux distributions such as Fedora, Ubuntu (with the default Ubuntu GNOME flavor), Debian, and others. It also runs on some BSD systems. • Philosophy: The GNOME Project emphasizes accessibility, internationalization, and adherence to free software principles. The aim is to create a desktop environment that is usable by people all around the world, regardless of their physical abilities or Summary • Overall, GNOME provides a cohesive and userfriendly desktop experience, making it a popular choice among users of Unix-like operating systems. GNOME aim • The aim of the GNOME project is to provide a free and open-source desktop environment that is user-friendly, accessible, and functional. The core objectives and principles guiding GNOME's development include: • Usability: GNOME strives to create an intuitive and easy-to-use interface, making it accessible for both new and experienced users. The design focuses on simplicity, minimizing clutter, and providing a consistent user experience. GNOME aim ..continue • Accessibility: Ensuring that the desktop environment is usable by people with various disabilities is a key aim. GNOME includes features and tools to assist users with visual, auditory, and motor impairments, ensuring that everyone can use the system effectively. • Internationalization: GNOME is designed to be used by people all over the world. It supports multiple languages and regional settings, making it adaptable to different cultural and linguistic contexts. GNOME aim ..continue • Free Software Principles: The GNOME project adheres to the principles of free software. All of its code is freely available, and anyone can modify, distribute, and use it. This openness fosters a collaborative development environment and aligns with the broader goals of the GNU Project. • Consistency: GNOME aims to provide a consistent user experience across all its applications. This includes uniform interface elements, behavior, and appearance, which helps users feel comfortable and confident while using the desktop environment. GNOME aim ..continue • Innovation: While focusing on simplicity and usability, GNOME also aims to innovate and incorporate new technologies and design paradigms. This ensures that the desktop environment remains modern and capable of meeting users' evolving needs. • Community and Collaboration: The GNOME project values the contributions of its community. It encourages collaboration among developers, designers, translators, and users to continuously improve the software. The GNOME Foundation supports and coordinates these efforts, helping to guide the project's GNOME functions • GNOME offers a range of functions and features that make it a versatile and user-friendly desktop environment. Here are some of its key functions: • 1. GNOME Shell: • Overview Mode: Provides an overview of all open windows and virtual desktops, allowing users to quickly switch between tasks. • Activities Hot Corner: Activating the top-left corner brings up the overview mode for easy navigation. • Search: Integrated search functionality lets users quickly find applications, files, and system GNOME functions .. continue • 2. Applications: • Nautilus (Files): A file manager that allows users to browse, manage, and organize their files and directories. • GNOME Terminal: A terminal emulator for command-line access and tasks. • Gedit: A simple and powerful text editor suitable for basic and advanced editing tasks. • GNOME Software: A software center for browsing, installing, and managing applications and updates. GNOME functions .. continue • 3. Customization and Extensions: • GNOME Tweaks: A tool for adjusting advanced settings and customizing the desktop environment. • GNOME Shell Extensions: Plugins that add new features and functionality to GNOME Shell, such as additional system indicators, applets, and interface modifications. GNOME functions .. continue • 4. System Settings: • Settings: A centralized application for configuring system preferences, including display settings, network configurations, power management, user accounts, and accessibility options. • 5. Accessibility: • Universal Access: Features such as screen readers, magnifiers, and on-screen keyboards to assist users with disabilities. • Keyboard Shortcuts: A variety of shortcuts to facilitate navigation and improve GNOME functions .. continue • 6.Notifications: • Notification System: An integrated notification system that provides alerts for system events, application updates, messages, and more, with the ability to manage and respond to notifications. • 7. Multitasking and Productivity: • Virtual Desktops: Support for multiple virtual desktops to organize and separate different tasks and workflows. • Window Management: Efficient window management with features like snapping, tiling, and GNOME functions .. continue • 8. File and Application Management: • Drag and Drop: Simplified file management with drag-and-drop functionality. • Application Menus: Easy access to applicationspecific menus and settings from the top bar. 9. System Monitoring and Control: • System Monitor: An application for monitoring system performance, resource usage, and running processes. • Power Management: Tools for managing power settings, battery life, and sleep modes. GNOME functions .. continue • 10. Security and Privacy: • Privacy Settings: Options for managing data collection, location services, screen locking, and history. • User Accounts: Management of user accounts, including parental controls and login settings. • GNOME's functions are designed to provide a seamless and efficient desktop experience, catering to a wide range of user needs and preferences. GNOME commands • To install the GNOME desktop environment on various Linux distributions, you typically use the package manager associated with your distribution. Here are the commands for some of the most popular distributions: GNOME commands ..continue • Ubuntu • On Ubuntu, you can install the full GNOME desktop environment with the following command: • sudo apt update • sudo apt install gnome GNOME commands ..continue • If you prefer to install the GNOME Shell without all the additional GNOME applications, use: • sudo apt update • sudo apt install gnome-shell Step by step installing GNOME on Linux • Installing GNOME on Ubuntu • Step 1: Update your system • First, ensure your system is up to date. Open a terminal and run: • sudo apt update • sudo apt upgrade • Step 2: Install the GNOME Desktop Environment • To install the full GNOME desktop environment, use the following command: • sudo apt install ubuntu-gnome-desktop • Alternatively, to install a minimal version of GNOME, you can use: • sudo apt install gnome-shell • Step 3: Configure the Display Manager • During the installation, you may be prompted to select a display manager. Choose gdm3 (GNOME Display Manager) if you want to use GNOME. • Step 4: Reboot your system • Once the installation is complete, reboot your system: • sudo reboot • Step 5: Log in to GNOME • After rebooting, you should see the GNOME login screen. Select GNOME from the session menu, and log in with your user credentials. NB • OR • AFTER STEP 2: • sudo service gdm restart Commands to remove GNOME on linux • The commands to remove GNOME from your Linux system will depend on the specific Linux distribution you are using. • Removing GNOME on Ubuntu/Debian • Step 1: Update the package list: • sudo apt update • Step 2: Remove GNOME and related packages: • sudo apt remove ubuntu-gnome-desktop gnomeshell • sudo apt autoremove • Step 3: Reinstall the default desktop environment (optional, e.g., for Ubuntu with default Unity or other DE): • sudo apt install ubuntu-desktop • Step: 4 Reboot your system: • sudo reboot GNOME Shell extensions • Install and configure one specific GNOME Shell extensions (applets) of your choice from the official GNOME Extensions website. • 1. Install GNOME Shell Extensions: Ensure you have GNOME Shell Extensions installed. You can typically install it using your distribution's package manager. For example, on Ubuntu or Debian-based systems, you can run: • sudo apt-get install gnome-shell-extensions GNOME Shell extensions .. continue • 2. Install GNOME Shell Integration Add-on for Web Browser: You'll need to install a browser extension to manage GNOME Shell Extensions from your web browser. Install the appropriate extension for your browser: • For Firefox: GNOME Shell Integration • For Chrome/Chromium: GNOME Shell Integration GNOME Shell extensions .. continue • 3. Install Dash to panel: Once the browser extension is installed, visit the GNOME Shell Extensions website: • Go to extensions.gnome.org • Search for “Dash to panel" in the search bar. GNOME Shell extensions .. continue • 4.Enable Dash to panel: • Click on the extension listing for Dash to panel. • Toggle the switch to enable the extension. • You might see a prompt to confirm installation; accept it. Install GNOME Tweak Tool • To install GNOME Tweak Tool on a Linux system with the GNOME desktop environment, follow these steps based on your specific Linux distribution: • Open a Terminal (virtual box linux): You can open a terminal by searching for "Terminal" in your applications menu or by pressing Ctrl + Alt + T. • sudo apt update • sudo apt-add-repository universe • sudo apt install gnome-tweaks Install GNOME Tweak Tool ..continue • After Installation: • You can launch GNOME Tweaks by searching for "Tweaks" or "GNOME Tweaks" in your applications menu. • Use GNOME Tweaks to customize various aspects of your GNOME desktop environment, including appearance, extensions, fonts, and more. • By following these steps, you should be able to install and use GNOME Tweaks on your Linux system with GNOME. THANK YOU