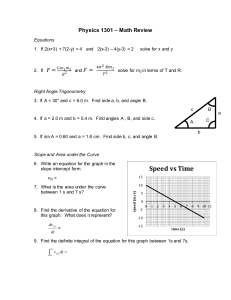
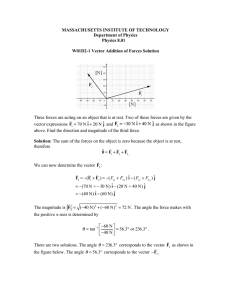
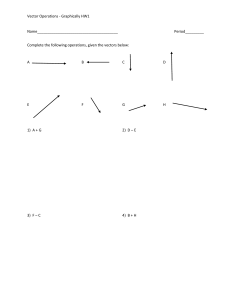
1. The set of all possible inputs of a function is called a. Domain b. Function c. Period d. Periodic Function 2. An operation that assigns a correspondence from elements of one set to elements of another set is called a. Domain b. Function c. Period d. Periodic Function 3. The repeating interval of a periodic function is a. Domain b. Function c. Period d. Periodic Function 4. A function that repeats itself in regular intervals; it follows this equation: f (x + c) = f (x), where c is a constant. a. Domain b. Function c. Period d. Periodic Function 5. The set of all possible outputs of a function. a. Trigonometric Functions b. Range c. Reference Angle d. Rule 6. The positive acute angle formed between the terminal side of an angle and the xaxis. a. Trigonometric Functions b. Range c. Reference Angle d. Rule 7. The part of a function that dictates the exact correspondence between the elements of one set and the elements of another set. a. Trigonometric Functions b. Range c. Reference Angle d. Rule 8. There are six trigonometric functions: Sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent. a. Trigonometric Functions b. Range c. Reference Angle d. Rule 9. The circle whose center is at the origin and whose radius is one. a. Unit Circle b. Range c. Reference Angle d. Rule 10. The square root of the sum of the squares of its real and imaginary coefficients. a. absolute value of a complex number b. algebraic vector c. amplitude of a complex number d. amplitude 11. An ordered pair of numbers representing the terminal point of a standard vector. a. absolute value of a complex number b. algebraic vector c. amplitude of a complex number d. amplitude 12. Same as the argument of a complex number. a. absolute value of a complex number b. algebraic vector c. amplitude of a complex number d. amplitude 13. The vertical stretch of a function. a. absolute value of a complex number b. algebraic vector c. amplitude of a complex number d. amplitude 14. The measure of rotation. a. angular velocity b. angle c. angle of depression d. angle of elevation 15. An angle measured below the horizontal. a. angular velocity b. angle c. angle of depression d. angle of elevation 16. An angle measured above the horizontal. a. angular velocity b. angle c. angle of depression d. angle of elevation 17. Defined in terms of angle of rotation and time. a. angular velocity b. angle c. angle of depression d. angle of elevation 18. The angle formed between the positive x-axis and a line segment between the origin and the number. a. argument of a complex number b. asymptotes c. bearing d. circular functions 19. The lines representing undefined values for trigonometric functions. a. argument of a complex number b. asymptotes c. bearing d. circular functions 20. An angle measured clockwise from due north to a vector. a. argument of a complex number b. asymptotes c. bearing d. circular functions 21. The functions whose domains are angles measured in radians and whose ranges are values that correspond to analogous trigonometric functions. a. argument of a complex number b. asymptotes c. bearing d. circular functions 22. The fundamental identities that involve the basic trig functions of complementary angles. a. complex plane b. component vectors c. cofunction identities d. cofunctions 23. The pairs of trigonometric functions of complimentary angles whose trigonometric ratios are equal. a. complex plane b. component vectors c. cofunction identities d. cofunctions 24. A coordinate system for complex numbers. a. complex plane b. component vectors c. cofunction identities d. cofunctions 25. The horizontal and vertical component vectors of a given vector. a. complex plane b. component vectors c. cofunction identities d. cofunctions 26. The ordered pair of numbers representing the vector. a. components b. conditional equation c. conditional trigonometric equations d. components of an algebraic vector 27. The individual vectors that are combined to yield the resultant vector. a. components b. conditional equation c. conditional trigonometric equations d. components of an algebraic vector 28. An equation that is valid for a limited number of values of the variable. a. components b. conditional equation c. conditional trigonometric equations d. components of an algebraic vector 29. True for only a limited number of replacement values. a. components b. conditional equation c. conditional trigonometric equations d. components of an algebraic vector 30. The reciprocal of the sine function. a. coterminal b. cosecant c. cosine d. cotangent 31. A trigonometric ratio equal to the adjacent side divided by the hypotenuse. a. coterminal b. cosecant c. cosine d. cotangent 32. The reciprocal of the tangent function. a. coterminal b. cosecant c. cosine d. cotangent 33. The two angles in standard position that share a terminal side. a. coterminal b. cosecant c. cosine d. cotangent 34. A unit of angle measurement equal to 1/360 of a revolution. a. dot product b. equivalent vectors c. degree d. directed line segment 35. A line segment of a given length and a given direction. a. dot product b. equivalent vectors c. degree d. directed line segment 36. A process of combining two vectors yielding a single number. a. dot product b. equivalent vectors c. degree d. directed line segment 37. Two vectors that have the same magnitude and direction. a. dot product b. equivalent vectors c. degree d. directed line segment 38. A function is even if f(-x) = f(x). a. even function b. odd function 39. The solutions defined over entire domain. a. De Moivre's theorem b. General solution c. Geometric vector d. Heron's formula 40. A quantity that can be represented by a directional line segment. a. De Moivre's theorem b. General solution c. Geometric vector d. Heron's formula 41. A formula for finding the area of a triangle given the lengths of the three sides. a. De Moivre's theorem b. General solution c. Geometric vector d. Heron's formula 42. A theorem involving powers of complex numbers. a. De Moivre's theorem b. General solution c. Geometric vector d. Heron's formula 43. The fundamental identities that involve the basic trig functions of negative angles. a. Trigonometric identity b. Imaginary axis c. Initial point d. Identities for negatives 44. An equation made up of trigonometric functions of an angle that is valid for all values of the angle. Also called a. Trigonometric identity b. Imaginary axis c. Initial point d. Identities for negatives 45. An axis in the complex plane. a. Trigonometric identity b. Imaginary axis c. Initial point d. Identities for negatives 46. The beginning point of a vector. a. Trigonometric identity b. Imaginary axis c. Initial point d. Identities for negatives 47. The side of angle where angle measurement begins. a. inverse cosine function b. inverse cotangent function c. initial side d. inverse cosecant function 48. Defined in terms of the restricted sine function. a. inverse cosine function b. inverse cotangent function c. initial side d. inverse cosecant function 49. The inverse of the restricted cosine function. a. inverse cosine function b. inverse cotangent function c. initial side d. inverse cosecant function 50. Defined in terms of the restricted tangent function. a. inverse cosine function b. inverse cotangent function c. initial side d. inverse cosecant function 51. The notation used to express an angle in terms of the value of trigonometric functions. a. inverse notation b. inverse secant function c. inverse sine function d. inverse tangent function 52. Defined in terms of the restricted cosine function. a. inverse notation b. inverse secant function c. inverse sine function d. inverse tangent function 53. The inverse of the restricted sine function. a. inverse notation b. inverse secant function c. inverse sine function d. inverse tangent function 54. The inverse of the restricted tangent function. a. inverse notation b. inverse secant function c. inverse sine function d. inverse tangent function 55. A relationship between the lengths of the three sides of a triangle and the cosine of one of the angles. a. Law of sines b. Law of cosines 56. A relationship between the ratios of the sines of angles of a triangle and the side opposite those angles. a. Law of sines b. Law of cosines 57. A method of approximating values in a table using adjacent table values. a. linear interpolation b. linear velocity c. magnitude of a vector d. mathematical induction 58. Defined in terms of arc length and time. a. linear interpolation b. linear velocity c. magnitude of a vector d. mathematical induction 59. The length of the directional line segment. a. linear interpolation b. linear velocity c. magnitude of a vector d. mathematical induction 60. A method of mathematical proof. a. linear interpolation b. linear velocity c. magnitude of a vector d. mathematical induction 61. The largest value of a function in a given interval. a. minimum value b. minute c. modulus of a complex number d. maximum value 62. The smallest value of a function in a given interval. a. minimum value b. minute c. modulus of a complex number d. maximum value 63. An angle measurement equal to 1/60 of a degree. a. minimum value b. minute c. modulus of a complex number d. maximum value 64. Same as absolute value of a complex number. a. minimum value b. minute c. modulus of a complex number d. maximum value 65. The results from clockwise rotation. a. odd function b. one-to-one c. negative angle d. norm 66. Another name for the magnitude of a vector. a. odd function b. one-to-one c. negative angle d. norm 67. A function of f(-x) = -f(x). a. odd function b. one-to-one c. negative angle d. norm 68. A characteristic of functions where each element in the domain is pairs with one and only one element in the range and vice versa. a. odd function b. one-to-one c. negative angle d. norm 69. A process used to add together two nonparallel vectors. a. period b. periodic functions c. phase shift d. parallelogram rule 70. The smallest value of q such that f(x) = f(x+q) where f(x) is a periodic function. a. period b. periodic functions c. phase shift d. parallelogram rule 71. A trigonometric functions whose values repeat once each period. a. period b. periodic functions c. phase shift d. parallelogram rule 72. The horizontal displacement of a function to the right or left of the vertical axis. a. period b. periodic functions c. phase shift d. parallelogram rule 73. A ray extending from the pole in a polar coordinate system. a. polar axis b. polar coordinate system c. polar coordinates d. pole 74. A coordinate system using distance and angle for position. a. polar axis b. polar coordinate system c. polar coordinates d. pole 75. An ordered pair consisting of a radius and an angle. a. polar axis b. polar coordinate system c. polar coordinates d. pole 76. The fixed center of the polar coordinate system. a. polar axis b. polar coordinate system c. polar coordinates d. pole 77. The solutions defined over a limited domain. a. Principal nth root b. Projections c. Pythagorean identities d. Primary solutions 78. The unary root of a complex number. a. Principal nth root b. Projections c. Pythagorean identities d. Primary solutions 79. Another name for component vectors, the horizontal and vertical component vectors of a given vector. a. Principal nth root b. Projections c. Pythagorean identities d. Primary solutions 80. The fundamental identities that relate the sine and cosine functions and the Pythagorean Theorem. a. Principal nth root b. Projections c. Pythagorean identities d. Primary solutions 81. An angle in standard position with its terminal side on a coordinate axis. a. radius vector b. reference angle c. quadrantal angle d. radian 82. The measure on an angle with vertex at the center of a circle that subtends an arc equal to the radius of the circle. a. radius vector b. reference angle c. quadrantal angle d. radian 83. Another name for a standard vector, a vector in standard position. a. radius vector b. reference angle c. quadrantal angle d. radian 84. An acute angle whose trigonometric ratios are the same (except for sign) as the given angle. a. radius vector b. reference angle c. quadrantal angle d. radian 85. The result obtained after vector manipulation. a. scalar quantity b. secant c. sector d. resultant vector 86. The value of a dot product of two vectors. a. scalar quantity b. secant c. sector d. resultant vector 87. The reciprocal of the cosine function. a. scalar quantity b. secant c. cosecant d. resultant vector 88. A portion of a circle enclosed by a central angle and its subtended arc. a. scalar quantity b. secant c. sector d. resultant vector 89. One-half the perimeter of a triangle. a. tangent b. semiperimeter c. sine d. static equilibrium 90. A trigonometric ratio equal to the opposite side divided by the hypotenuse. a. tangent b. semiperimeter c. sine d. static equilibrium 91. The sum of all the force vectors add up to zero. a. tangent b. semiperimeter c. sine d. static equilibrium 92. A trigonometric ratio equal to the opposite side divided by the adjacent side. a. tangent b. semiperimeter c. sine d. static equilibrium 93. The ending point of a vector. a. terminal point b. terminal side c. unit circle d. static equilibrium 94. The side of angle where angle measurement ends. a. terminal point b. terminal side c. unit circle d. static equilibrium 95. A circle with a radius of one unit. a. terminal point b. terminal side c. unit circle d. static equilibrium 96. The process of combining two vectors. a. terminal point b. vector addition c. vector quantity d. velocity vector 97. A quantity that has both size and direction. a. terminal point b. vector addition c. vector quantity d. velocity vector 98. A vector representing the speed and direction of a moving object. a. terminal point b. vector addition c. vector quantity d. velocity vector 99. An extension of De Moivre's theorem involving roots of complex numbers. a. nth root theorem b. vertical shift c. zero vector d. velocity vector 100. The vertical displacement of a function above or below the horizontal axis. a. nth root theorem b. vertical shift c. zero vector d. velocity vector