Term
Motherboard Definition and Sizes
Description
Central piece to which all other components connect, make sure they are powered, and able to transfer data. Sizes for desktop: E-ATX or "Extended"
Larger size. ATX "Standard size." Laptop or small form factor applications use: micro-ATX (smaller than ATX), and mini-ITX even smaller.
Page
Book
22
1
Motherboard Sockets-Often First and Most Name given for the kind of connector that the CPU processor has. Socket from motherboard has to match the component socket to fit. Ex. CPU
processor socket has to be compatible with motherboard socket to fit slot. Ex. Processor with socket LGA 2011 needs a motherboard with LGA 2011
important decision
socket.
23
1
Motherboard buses, FSB, northbridge, system Physical connections between the components connected to the motherboard, buses are responsible for moving data between components. Come in
agent or uncore
diferent seeds depending on the quality of components. Used to connect to Front Side Bus (FSB), taking the CPU or high procesing components to
connect the Northbridge chip; this had limitations in high speed connectivity then moved to the system agent, or uncore post Intel Sandy Bridge (Intel
Core procesor Q2 32 nm) like we know today: icore 7, icore9.
23
1
23
1
24
1
Motherboard Uncore or system agent-more
info
CPU-Central Procesing Unit-Processor
Definition, Core
Term used by Intel to describe functions of microprocessor that are not in the core but must be closely connected to the core to achieve high performace.
Called "System Agent" since the release of Sandy Bridge microarchytecture.
The processor or CPU is the brain of the computer, responsible to execute instructions contained in programs or OS (Operating systems). Performs
arithmetic logic and other I/O (input/output operations) . Contains at least 1 processing core responsible for executing instructions (one thing at a
time). Modern procesors have multiple core allowing to multitask.
CPU/Processor-Clock Speed
How many instructions can a processor execute in one second after computer program has been broken down into a series of small instructions for the
processor to understand. FYI: one thing per second=One Hertz meaning 1Hz clock speed. Not unusual to find modern processors 4GHz = 4 billion
instructions per second.
The processor shares processor time between multiple applications, swapping back and forth between them at a speed the human mind cannot discern as
a single core processor does not perform multiple tasks simultaneusly but this capability is achieved by context switching.
CPU/Processor-Context Switching
CPU/Processor Special Caches: TLB
(Translation Lookaside Buffer)
Not with the L1 Instruction and data cahes but provides supporting capabilitiesfor frequently acessed memory addresses.
CPU/Processor CACHE L1, L2, L3,
Instruction Caches, Data Caches
Stores information frequently used and associated with the Context Switching jumping between often used information. Reduces time or energy to
access data from memory, located near the processor core (small-fast) nowhere near big as RAM or SSD in size. Often used in hierarchy: L1, L2 (not as
fast as L1 but more sizable), and L3 if you have it is typically larger (shared between cores), the higher the more storage. L1 typically sizes to the power
of 2 and not fast. Bigger these days. ex. Uncommom L4- more common with things like RAM and DDR. L1 is split into Instruction caches: has the job
of going getting those code words at the location where the instructions are in the program, copying them to the cace as a kind of pre-bufer to make sure
the CPU has them at its disposal at a fast enough speed and data cahes.
CPU/Processor components:ALU, CU
RAM Compatibility
RAM Volatility
RAM-Speed
24-25
25
1
24/slide
24/slide
1
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unic): integer arithmetic and bit wide logic operations-data inputs to operate. CU (Control Unit): Von Neuman Architecture.
Directs the operation of the CPU, and manage interaction with other devices onm the system. Ex. Memory, the ALU, and IO devices how to respond to
instructions from the processor. Like a dispatcher, sits in the middle. AGU (Address Generation Unit or address computation unit) provides parallel
24, 334(2)
circuitry separatedly for better speed to find info used by the program. Some modern computers come with multiple AGU to be able to do multile things
at once. MMU (Memory Management Unit): Broader main system memory. responsible for translating logical addresses or memory addresses to
physical addresses. Virtual memory.
1
Two factors to pay attention to with RAM: Type of RAM that is supported and matches motherboard, and speed meamimg that the motherboard handles
the speed. Ex. A motherboard states that accepts a frequency of 2133 MHz or less, then you can use DD#-2133 RAM and not DDR4 .
27
1
Why not using RAM for storing everything? Too volatile. Meaning data stored in RAM exist only temporarely. Files on RAM deleted after computer
restarts. Volatile unless is backed up by a battery or some other power source before rebooting computer. When you rebbot a computer RAM clears out,
and recycles.
27
1
Much faster to read data stored in RAM than in Hard disk while actively using it. Benefit of RAM is Speed. Speed measured in MHz.
27
1
RAM-Random Access Memory Definition or Volatile storage memory used to run programs/processesrunning at at that exact moment in time and cache data . It is fast but not persistent. Number
Memory-NOT VIRTUAL MEMORY
of things you can have on your computer open at once. Comes in "sticks of RAM" Ex. 8GB you can have 8Gb of software running all at once
(Operating system images, programs) Upgrading the Ram sppeds up a computer. Data moves in and out of RAM. More RAM means more addresable
memory. Often confused with storage. RAM as a piece of hardware is one contiguous piece of data storage, but it is separated into sections by
software. There are two sections of RAM, the stack and the heap.p. 338 (BK2)
RAM-"tmpfs" or "ramfs"
tmpfs= Temporary File System and "ramfs" provides a very fast but volatile temporary file system. Computer creates an area in RAM, a file system that
can be accessed more like a traditional storage mechanism. So I can create folders and disks. Its still volatile. Rebooting computer will remove data.
Benefits: if you are executing an operation that is creating a lot of files and reading at a high speed, you could create a RAM disk to enable that to occur
very quickly and do lots of computation without having to go all the way over to the disk thats comparatively very slow.
Thrashing
CPU and execution is generally blockedby the velocity of the disk as opposed to the velocity of the RAM.
RAM: Page File or VIRTUAL MEMORY
Not enough RAM to support processes? In that instance computers can use something called a page file or virtual memory. The idea is a file or a storage
mechanism is created on the DISK, not the RAM. And that file provides and overflow for RAM. Computers memory management identifies resources
will be less likely used and will stored them temporarely from the RAM to the page file where it is much slower but still referenced in memory terms,
before for
it isacces
accessed
or needed,
the Advanced
operating system
can simply
go grab that from
dat, put
it backdisks
into RAM
like it SAS
never(serial
left. attached SCSI) or fibre
Buses
like SATA
(Serial
Technology
Atachment)-came
spinning
technology,
channel. Enter NVMe (Non volatile Memory Express or Non volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification-NVMHCIS) , clear winner on
performance, super fast but VERY expensive. They are all storage interfaces that get data from point A to B.
No moving parts, reliable, more expensive. Include firmware and services to enable their fast operations with modern computers, this present
opportunities and challenges with Forensic recovery of data, or secure destruction of data. Expensive to make and buy.
Storage: SATA, SAS or Fibre Channel,
NVMe
SSD-Solid State Drives
Mechanical Drivers
Storage Definition.
Thunderbolt- See GPU
GPU-Graphics Procesing Unit
PS/2
The only hard drives we used to have. Old. Cheaper, slower, fragile (ex. Jolts-contain moving parts-unreliable). Still popular d/t cheap and sizeable
storage.
Big and slow. More permanent mechanisms than RAM. Typically a hard drive, SSD (Sloid state drive). Varous sizes depending on device. Ex 3.5" for
desktops since take much space. Laptopts usually use 2.5"-since it have less space but capacity getting bigger and smaller in physical form. down side of
laptop storage is not replaceable. Each drive has a maximum capacity, the largest amount of data that can be stored on the driver itself. Drives usually
have a slighly lower capacity than advertised ex. 4TB drive will have a capacity of 3.8TB.
26-27, 338340
1
slide
26-27
slide
26-27
Slide
26-27
29
1
29 B
1
29
1
28
1
Compatible with USB C devices. Thunderbolt port means that a single cable is all you need to push power and transfer large amounts of data like video
data for two or more 60 Hz, 4K resolution external monitors to and from a computer. Surpass USB C in that it can connect 4k monitors together and
thunderbolt expansion docks to a computer. A EGPU (external) can be connected through a thunderbolt port.
Very Costly. Has utility in graphics (Faster and more effcient, useful on mobile devices with battery concerns, video game consoles, or high end gaming
or video production PCs), operations at a great speed but is also useful for cyber security tasks! Optional component. Hardware is hosted on a graphics
card-electronic circuitry and architecture towards graphics. Can be on the motherboard, or a separate device such as a PCle (peripheral component
interconnect express) GPU. The card not only contains the GPU but its own dedicated RAM where computers graphics are stored for use by the GPU.
GPU is another kind of processor that excels at number crunching. CPU can do the same as GPU but less efficiently if the computer had a dedicated
GPU. It does more than NUMBER CRUNCHING. Used also for matematically demanding tasks as 3D rendering, or speed up encryption. In
CYBER, often used to crack passwords, ofensive or defensive. EGPU ( External Unit) can be connected through mPCle (Mini-PCl Express card suitable
for mobile and vibtration/shock sensitive application)mobile, or thunderbolt. SLI and Crossfire from NVidia and AMD are technologies that allows us
to bundle graphic cards and their GPUs ogether.
Input device used commonly before USB technology, Many older peripherals still support. Round ones que habian que encajar.
1
30
1
32
1
USB Type C-For Input/Output and Power
See Output Devices to support video output,
several devices inone port if monitor
supports.
Newer Connection type. Increasingly popular. Provides High speed data transfer: 10 Gbit/s. It also provides the ability to transfer power like monitors,
hard drives, charge laptop devices. Sometimes it can power and tranfer data at the same time. Need to be able to transfer a minimum of 3 amps, current
at 20 volts and 60 watts , enough for a small laptop. You can implement up to 5 ampswhich is 20 volts at a 100 watts enough for a laptop. POWERFUL
RANGE OF CAPABILITIES, FROM POWER TO DISPLAY OR USER INPUT.
USB Transfer Speeds
USB (universal Serial Port) See graphic
Input Devices DEFINITION
VGA-Output Devices-Monitors
DVI-Output Devices-Monitors
32, 35
1
USB 1 Transfer Speed: 1.5 Mbit/s or Megabits per second- color WHITE, USB 2 : 480 Mbits/s BLACK, USB 3 : 4.8 Gbit/s (port is colored
BLUE), USB 3.1: 10 Gbit/s Port will be colored TEAL/Light Purple.
32
1
Most common way of connecting and input device. USB A (Most common), USB B (printers and scanners), USB MICRO A, USB MICRO B, USB
MINI A, and USB MINI B. Type C, is newer connection type. MICRO and MINI for small factory devices like the side of a camera.
31
1
Also known as "Human Interface Devices or HIDs" because they provide humans with a way to interface with the computer. DEF: Use a variety of
connectors types with varying speeds as they have evolved over time. Devices which when connected to computers can send data to them. Ex. Mouse,
Keyboard, USB.
31
1
33
1
33-34
1
34
1
34-25
1
33
1
37
1
38-40
1
36
1
Oldest standard for A/V output that we covered. On either side of the port, there are two slots into which thumb screws on the connector connect. These
need to be tightened to provide stability to the connection. See image book.
More modern than VGA but old by modern standards. It has like VGA, two thumb screws to be tightened after connection is plugged in.
HDMI-Output Devices-Monitors See
conectors graphic
More modern and more widely used than DVI and VGA these days. Transmits both VIDEO and AUDIO as well. Some HDMI connectors include:
Standard A, Dual-Link B, Mini C, Micro D, Automotive and Connection System.
Display Port-Output Devices-Monitors See
graphic
More modern than HDMI.
Output Devices def.
Output device are peripherals we connect to our system to extend capability, they use a variety of output ports/protocols. They accept data from the
computre. Like a monitor accepts data to display an image and a printer to to print a document. PRINTER connect by USB and MONITORS by VGA
or HDMI but more and more systems are tending towards using USB C.
PSU- Power Supply Unit DEFINITION See Rated in Watts. Computer components requiere power, and the PSU (power supply unit) distributes it in the right amounts to the right places.
graphi c
Responsible for taking power from either the main power supply or a battery in the case of laptops and converting then delivering it to the computer
components.Usually conects to the motherboard, graphic card, hard drive (s), and the fans. CPU (processor usually powered by the motherboard. Each
power supply provides certain amount of power good to know to ensure you can power your computer or it will not turn on, or shut off when
components requiere more power. Power supply has a built in fan to cool it down during operation. Cables are running out of the unit, which will
connect to the computer components. Calculate needed watts and leave an extra marging. Better have extra voltage. Careful when connecting multiple
PSUs-cross conecting danger.
Connectors-Power Supply See graphics
Some of the connector power supplies use: 1. Four Pin Peripheral Connector-Usualy for powering fans. 2. SATA (Serial ATA) power Connector- For
powering hard drives, See Stotage-SATA for more. 3. Main ATX Connection Power Supply- Main ATX standard size motherboard connector. Requiere
20 pins, some requiere 24. For that reason most modern connectors provide a 20 pin connector with an optional extra 4 pins. Dont get the risks of wrong
installation. 4. 12 V (volts) power connector-runs to the motherboard. Some MB requiere 4 pins and some 8. So, commonly you will find connections
with 4 pins and an optional extra 4. 5. PCI-E (PCI-Express Connector) Power Connector-runs to a graphic card. Some cards need 6 pins, and some 8. an
optional 2 extra pins come with some cables. Rated in Watts.
Heat Sink- Cooling mechanism See graphic Used to dissipate heat as well as fans but Fans alone are not enough. The heat sink is the metal block with many fins and made of a thermally conductive
of fins
material with the purpose of moving heat away of component such as Processor (CPU) or graphic card (GPU graphic processor unit) or motherboard
which has a small version of heat sinks but too small to have fans so the case fans cool them. Need thermal paste. The cooler equipment is the faster it
can go. Overheating can damage components and heat sinks help dissipate such heat.
Thermal Paste-Heat Skins
ATX
E-ATX (Extended) size
Micro ATX-smaller than ATX size. This is
for laptops
Mini-ATX-even smaller than micro-atx
Four Pin Peripheral Connector
SATA
Main ATX Connection Power Supply
12 volts power connector
PCI-E Power Connector
mPCL-e
SLI-Nvidia See GPU
Crossfire-AMD See GPU
Boolean or Bool See Bits
Bits
KiB- 1 kibibyte (KiB) is 1024 bytes
Bytes-group of binary digits usually 8.
Alternate Number Bases-See Denary
Binary - See Alternate Number Bases
Hexadecimal p.52
ASCII See Table in notes
Encoding, def. p.59-60 Mechanism to
transformig data to be send via particular
mechanism.
Automatically Decoding Encoding
Attaches heat sink to component. Thermal paste is spread onto one of the components before the heat sink is attached. It helps conduct heat from surface
to another by filling in minute imperfections in the surfaces that can trap air. Good insulator. Provides good conductivity. can be applied on top of the
CPU,
and top
of heat
sink for and
example.
See
Mother
Board
Definition
Sizes, See Connectors-Power Supply
See Mother Board Definition and Sizes
See Mother Board Definition and Sizes
See Mother Board Definition and Sizes
See Conectors-Power Supply
See Storage: SATA, See Connectors-Power Supply (Serial Advanced Technology Atachment)
See Connectors- Power Supply
See Connectors- Power Supply
See Connectors- Power Supply
See GPU Mini-PCl Express card suitable for mobile and vibtration/shock sensitive application)mobile
technologies that allows us to bundle graphic cards and their GPUs together.
technologies that allows us to bundle graphic cards and their GPUs together.
Boolean value: 1 or 0 values can only be stored in a single bit. Just like a electrical switch only has on or off. A bit is a boolean.
Smallest unit of data that can be storedon a computer system. Bits are our fundamental unit of data and they build up into bytes and so on and so on into
larger data units. Can only have two values stored: "1" or "0" This is known as a Boolean value or bool for short; just like a switch can only have on or
off. All data in computer systems are made of bits. A bit is a boolean.
See Bytes 2^10= 1024 KiB in binary
1 byte is 8 bits, 1 kilobyte (kB): 1000 bytes (1 kibibyte KiB is 1024 bytes ), 1 megabyte (MB) is 1000 kilobytes (1 Mebibyte MiB is 1024 Kibibytes),
1 gigabyte (GB) is 1000 megabytes (1 gibibyte GiB is 1024 mebibytes), and 1 terabyte (TB) is 1000 gigabytes (1 tebibyte TiB is 1024 gibibytes). KiB
system introduced by IEC (International Electro-Technical Commission to differentiate from using kilo but people still use kilo or kB =1000 or 10
expoenent 3, instead of KiB 1024.
We usually count in base 10, also known as decimal or denary. There is also other systems: Base 12 numbering system with more factors. Base 2 called
Binary used by computers. Base 16-we usually convert binary numbers to base 16 (hexadecimal) because binary numbers get too long and tis sytem is
more readable.
36
1
1
1
1
slide
slide
44
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
44-45
1
45
1
44
1
46-47
1
computers use binary system, base of 2 system. Only two possible values 0, or 1. Binary is how computers basically store and expres information and
we need to understand this to underpin any easier representations of data we use day to day. Similar to counting in denary. Power of" rules: anything to
the power of 0 is 1. Anything to the power of 1 is its itself. 2^0=1, 2^1=2, 2^3 (2x2x2)= 8 etc. 2^10=1024 KiB
47-50
1
Base 16 system. Incredibly frequently used to represent values on computers in cyber security. Being able to express a byte as 0xFF or 0x0a is much
easier than using decimal. System can represent large numbers in small spaces. Hexadecimal goes like: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F. Nothing
beyond F. Table heading goes: 16^0=1, 16^1=16, 16^2=256, 16^3=4096, 16^4=65536
47, 52-55
1
56
1
56 , 59
1
60
1
Most commonn standard used to represent text you recognize as values as a computer can store. ASCII (American Standard Code for Information
Interchange). Simply a table that maps binary to characters. Ex. A is 0x41 or 0b01000001. When computer sees 0x41 it will draw a A on the screen.
Simplest encoder compared to Unicode. Other standard is UNICODE, see UNICODE. Original ASCII was 7 bits wide, supported 127 characters (2^7).
Now with extended, which 8 bits and 255 characters. Important in Penetration etsting to manupilate valuesto get undesarible responses from computers.
ASCII, UNICODE. Text read from storage by a computer is read as binary, what you see, the final result will depend on the type of encoding used on
the computer. Not to be confused with encryption, however encoding is often used with encryption to make results transferable. Purpose is to enable us
to fit data we need to store or transmit within a set of constraints that are suitable to the storage or transmition medium. Used for data storage and
transmit. Encoders: ASCII, UNICODE, Base 64-6 bits at at time. (larger than base32, good for images alomg ASCII), Base32 which uses fewer
characters than base 64 and has a smaller range to express data, and UTF8. Encoding is way to fit data of a specific format, shape, size and make sure
it works over a specific transfer mechanism or storage mechanism. Think of it as packaging .
Tool or manual in command line Automatically detect and reverse encoding to get back to original data. Computers use a clever search process to revert
the data even when they are not provided with any prior details of how the data was encoded.
Most file types have a header. Plain text doesn’t have a header. Even if file extension is changed, the file header stays th esame, is often more accurate,
also called "magic numbers", magic bytes, or file signatures. These are all in HEX system values. Ex. 50 4B 03 04 (for normal zip archive), 50 4B 05 06
(empty zip archive), 50 4B 07 08 (spanned zip archive). jpg file headers ex. FF D8 FF DB, FF D8 FF E0, or FF D8 FF E1. Remember 8 bites is 1 Byte.
0b11111111 =255 same as 0xFF-255.
Nibble
4 bits or half a byte
Denary or decimal or "Base 10"- See
Called Base10. Starts from 0 to 9. 10^0=0, 10^1= 10, 10^2= (10x10)= 100, 10^3 (10x10x10)=1000, 10^4 (10x10x10x10)= 10000 (ejemplo: 10^3 for
Alternate Number Bases
example is base 10 with an exponent of 3.) The Binary number 10 in denary is 2. The hexadecimal number 10 in denary is 16.
Notation: 0b=binary system, 0x=hexa system, Put notation in front of number to specify the number base it uses and avoid confusion between bases. 0d for denary. Ex. 0d10 is 10 in denary, 0b for
0d for dinary.
binary Ex. 0b10 is 10 in binary, and 0x for hexadecimal. Ex. 0x10 is 10 in hexadecimal.
Calculating from Denary to Binary
See examples on pages 49-50. You have to subtract until reaching Cero. Number will be 1s and 0s.
File Headers
Calculating from Binary to denary
Use table in separate notes to accomadate numbers. Also see example p. 48-49 book 1.
Calculating Hexadecimal to Denary
Table heading looks like: 65536, 4096, 256, 16, 1. Values to add like in binary look like this: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A=10, B=11, C=12, D=13, E=14,
F=15.
Table heading looks like: 65536, 4096, 256, 16, 1. Values to add like in binary look like this: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A=10, B=11, C=12, D=13, E=14,
F=15.
Standard that support much larger character sets so that languages that don’t use the Latin alphabet can also be supported. Unicode encoding uses up
more data since you cannot support chinese, russian, Latin, Arabic alphabets with only 255 spaces. Unicode is more complicated than ASCII.
Calculating Denary to Hexadecimalharder/needs division
UNICODE
Packaging
Logic
Truth Tables See Notes for illustration
Logical AND
Logical OR
Logical NOT
Logical NAND
Logical NOR
Logical XOR
Boolean Logic
61
1
44
1
46-48
1
47
1
49-50
1
48
52-53
1
53
57
1
using encoder/decoder like base 64 to work on sequence of bytes from ASCII to strings of data. Packaging is encoding for storage or transfer.
Logic is calculated in the logic unit of the processor via logic gates which are circuits that usually take two inputs to produce one output. Every input to
the circuit is in one of two states, depending on the voltage flowing at the time: either 0 (low voltage, approx 0 volts), or 1 (high voltage approx 5 volts).
Th ecircuit then produces an outcome, either 0, 1 depending on voltage. There are different types of logic circuits, behave differently, but together allow
the processor to function.
Or Logic tables. Shows all possible outcomes from A, B, (A, B being the input) and A&B column the output and under you have all the possible 0s and
1s in different combinations.
Checks if the two inputs in truth table are both true. If both are true then the output is true, but if theres one or more false, then it is false. The AND
connective is called a conjuction.
59
1
64
1
64
1
66
1
As long as one of the two inputs is true the result is true. If neither of the inputs is true the result is false.
Logical NOT gate only takes one input. It inverts the end result, so true becomes false and false becomes true. Apostrophe and equal symbol means not
equal. !(string1 == string2): can also be written as (string1 != string2):
68
1
69
1
NAND gate is just an AND circuit followed by a NOT circuit. Just invert the final result. Revrese final anser as per NOT circuit.
The NOR logic gate is just the OR circuit followed by a NOT circuit similar like we do with NAND results that we invert the result. Invert the output
after using OR circuit rules.
Critical to many security operations, simple form of encryption and decryption. Provides very basic form of encryption-not strong, used in a lot of
cryptographic algorithms as part of the process, including AES which is the current industry standard. This gate checks for if only one side or the other
side is true but no both. XOR is exclusive, it doesnt like both inputs being true. If only ONE input is true, then the output is true. See Decryption with
XOR, Encryption with XOR
70
1
72
1
74
1
64
1
64
1
64
1
Boolean Statement See Proposition
when talking about logic in computer science they usually mean Boolean Logic. A boolean value is perfect for computers which talks in bits: can be true
or false, on or off, 1 or 0. Bits are boolean values. Programs use it all the time-and programmers. Not always intuitive. Bugs in computer programs stem
from incorrect usage of Boolean logic.
One which only can be true or false is known as a proposition. Ex. Tomorrow is Friday. This can be either true or false and therefore a proposition.
Proposition See Boolean Statement
One which only can be true or false is known as a proposition. Ex. Tomorrow is Friday. This can be either true or false and therefore a proposition.
Connective See Logical
and,or,not,nor,xor,nand
Conjuction See Connective
Disjunction See Connective
Negation See Connective
Alternative denial See Connective
Joint denial See Connective
Exclusive disjuction See Connective
AES Advanced Encryption Standard
A connective is used to connect two or more propositions. AND (conjuction), OR (disjunction), NOT (negation), NAND (alternative denial), NOR
(Joint denial), XOR (Exclusive disjunction).
AND connective
OR connective
NOT connective
NAND connective
NOR connective
XOR connective
Specification for the encryption of electronic data by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001. Related to Logical XOR
Tautology
Contradiction
Contingency
Decryption with XOR
Encryption with XOR
File Systems-Lays foundation for
Forensics:getting data back
Assertion or formula which is always true no matter the inputs. No matter the inputs is always true.
Opposite of tautology (always true no mater the input). Here results of a logical statement are always false no matter the inputs.
ssentially anything that isnt a tautology or a contradiction. A logical statement where the outcomes could be true or false contingent the inputs.
If we XOR the Ciphertext against secret key we get decryption.
If we XOR the Plaintext against the secrettext (key) we get encryption.
Helps us organiza data, come in different standards with varying capabilities. Each drive must be formatted with a file system which determines how
files wil be stored on device and its features. Operating system usually has a list of files systems supported. OS will not support all. Access and storage
files to a physical storage media (ex. hard drive or SSD). Storage device is broken down to into a series of clusters determined by the file system used. A
cluster is the smalles section of the disk that can be used to store a file. Ex. file 64KB will be spread to 2 clusters if your cluster is 32kb in size. * 2 files
cant use the same cluster. Also, if the smaller cluter is 32kb for example, and you have a smaller file than 32kb the remaining space in that cluster will
be wasted known as "slack space." EACH FILE SYSTEM STORES AT LEAST 2 PIECES OF INFORMATION PER FILE. (Content and
Not as common on USBs now after new kid in the block: exFAT. The FAT part came from it using a File Allocation Table to map each cluster. Doesn’t
support more than 4GB which s nothing. It doesn’t support permissions because it doesn’t store metadata such as who created a file but that lack of
permission support is actually a bonus for a file system designed for USB drives and other removable media. Introduced with Windows 95.
FAT32 -File System
exFAT -File System 2006
NTFS: New Technology File System
Journaling File System
EXT3 Extended File System 3 2001
EXT4 Extended File System 4 2008
HFS+ Hierarchical File System Plus
Delta
File system desiged for USB and other removable media, so it doesn’t support premissions. Based on FAT32 but it has been completely modernized.
The file size limit is so large that it effectively has no maximun file size. It support Windows (not Windows 95), MAC, and Linux. In some instances
you need special drivers to use it with Linux. Although in many cases it can be used in some fixed media.
Used by modern versions of Windows. Advance file system with many features like: Permission support (what usernames can access a file), encryption
support and shadow copies (effectively backups files), to a limited extent it can heal data from corruption. File size is extremely large but it has a limit.
More reliable than older systems like FAT32. Downside: limited support for among non-windows operating systems. If you connect a NTFS formatted
drive to a MAC, you can read the files on th edrive but not write to the drive.
Is a journaling file system that means that the changes to the disk are tracked in a separate part of the file system known as jounal. This can help to
recover the drive in the event of a disk corruption that might result from a sudden shutdown or jolt.
Older file system often used in Linux. Supports permission and encryption but no shadow copy which is stricly a Microsoft thing. Maximum file size of
2TB. Is a journaling file system that means that the changes to the disk are tracked in a separate part of the file system known as jounal. This can help
to recover the drive in the event of a disk corruption that might result from a sudden shutdown or jolt.
Modern file system used in Linux. Older EXT3 extended file system. Suppports permissions, encryption, but no shadow copy. In practical terms no
maximum file size since it is so large. Allows you to turn off the journal, and features a faster disk check process.
Propietary File system created by Apple for Mac OS operating system only. Was the one used by apple until recently with APFS creation for Mac OS
High Sierra ; the one used now. Supports files so large it has no limit size. Like EXT3 and EXT4, it supports journaling. As with most moderns systems,
it supports permissions and encryption among other features. *there are some linux versions
Technology used by network filers and now Apple beginning with Mac OS High Sierra. duplicate files can be stored without using addional space, with
changes to one copy of a file being saved as a delta to lower space requirements.
1
66
68
69
71
73
75
1
1
1
1
1
1
75
1
78
78
78
77
76
1
1
1
1
1
81
1
83
1
83
1
84
1
85
85
1
85
1
86
1
86
1
AFS-Apple File System-Current in use,
default on most Mac
NVMe
SAS or Fibre channel
Slack space
Cluster- See Drive, See File Systems
Drive
Metadata
Recover Files See Deleting Files, See
Overwrite
Deleting files See Recover Files, See
Overwrite
Overwrite See Recover Files, See Deleting
Files
Securely deleting Files
File Allocation Table p.82
Clusters-Multiple, Rules for excess kb
Partition
Volume See Partition
Parted - in the command section
Cloud Computing
SaaS - Software As a Service (Ex. Slack,
ZenDesk,SalesForce)
Another proprietary file system created and recently introduced by apple with Mac OS High Sierra. Supports permissions and encryption. Main
difference with previous apple file system (HFS+) is that duplicate files can be stored without using addional space, with changes to one copy of a file
being saved as a delta (tehnology already in use by network filers way before) to lower space requirements. Modern and robust file system designed
with resilience and security in mind.
NVMe (Non volatile Memory Express or Non volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification-NVMHCIS) , clear winner on performance,
super fast but VERY expensive. See Storage . P. 29, but info from Slide
SAS (serial attached SCSI) or fibre channel. See Storage
Wasted space in space disk cluster when saving files smaller than the cluster size.
Sections of a drive to store and access files. 2 files cannot use same cluster. Rules p. 81-82
Stores files in separate clusters. See File Systems
Data which describes other data. Second piece of information stored in file. First piece of information to be stored is data or content of file being saved.
Metadata contains usually at least the name of the file and the address where the contents of the file can be found. Some file systems will store more
metadata like user who created the file, and the last modified time and so on. The metadata is store in an index which provides a list of files and the
locations where they can be foundon the disk. If a file is deleted, the index entry is removed (metadata) but the content of the file isn't removed from the
disk, instead that cluster is marked as overwritable, meaning the contents of a new file could ovewrite the data there. Efficiency
you can sometimes recover deleted files from a hard drive; the content of the data remains even if the metadata has been removed by overwriting it.
.There is always a chance the deleted file 's content has been already overwritten by a new file, and the old deleted file will not be recoverable.
If a file is deleted, the index entry is removed (metadata) but the content of the file isn't removed from the disk, instead that cluster is marked as
overwritable, meaning the contents of a new file could ovewrite the data there. Efficiency
Mark a cluster as overwritable when file is deleted, that cluster allows a new file to overwrite the contents of the previous file. Efficiency This is also the
reason why you can sometimes recover deleted files from a hard drive; the content of the data remains even if the metadata has been removed.There is
always a chance the deleted file 's content has been already overwritten by a new file, and the old deleted file will not be recoverable.
Data is written over the contents of the file when the file is deleted, instead of just marking the cluster overwrittable.
Some file systems use file allocation table to map each cluster, so the first cluster will poin to the table entry, which contains the addresses of the next
cluster. And that cluster will also have an entry in the table, which points to the next cluster and so on until the file has been read.
*If the first cluster the file is stored in has a cluster immediately after it that is free, then the rest of the file will be placed there. * If there is no
immediate free cluster, then the rest of the file will be put into a different cluster and the address of the next cluster will be added to the end of the first
cluster. *Some file systems use file allocation table to map each cluster, so the first cluster will poin to the table entry, which contains the addresses of
the next cluster. And that cluster will also have an entry in the table, which points to the next cluster and so on until the file has been read.
Portion of the disk that is provided by the driver. A slice of the cake (disk/device)
Set of partitions…that volume then lays way to a file system.
to see a graphical list easier to read for list of devices /file systems
Is very much the default way to host applications ad services in the modern world. Business are trading ownership of those servers/hardware for more
flexibility, service delivery, reliability, and costs. The cloud is simply a data centre that someone else owns. You rent someone else hardwareand services
for a perios of time getting rid of operational costs and ou can rent more servers for a shor tem without having to buy them. Models of service: SaasSoftware as a Service,
IaaS-Infrastructure
a Service,
as awith:
Service.
service, you
get the softwareasbut
someoneand
elsePaaS-Platform
will have to deal
the physical hardware, managing the operating systems, deploying
and configuring updates. Make sure software matches your needs since you have less customization options. Great for avoiding operational burden but
translated to service costs. Application could be installed locally or hoste dby the provider of the software so that you dont need to matain server, OS and
application; you just configure it and use it. Saas is often more expensive in the license/service sense. Like renting an unfinished house you can modify
much. See table Notes
86
1
1
81
81
81
1
1
1
1
81
1
81
1
81
1
81
1
82
1
82
1
82
1
slide
slide
slide
1
1
1
89
1
89, 369
1
IaaS - Infrastucture as a Service (Ex.Amazon
Web Services EC2) You build what you
need. Rent parts of a house to make "like"
own.
PaaS -Platform as a Service (customizable)
(Ex.AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku,
Symfony Cloud)
AWS Elastic Beanstalk See PaaS
AWS Web Services EC2 See IaaS
Sympony Cloud See PaaS
Operating Systems
Kernel
Process
Interrupt
Interrupts-Hardware
Interrupts-Software
Bootloader, see BIOS Startup for process
You get infrastucture like networking, virtualization, storage, availability, power, connectivity. Someone host the physical harware for you. You
build what you need. Like renting the foundations of a house, with great power and utilities connected. You will need to build on top and customize
the house. Very elastic-you can burst to whatever capacity you need and slim down seconds later. Be aware: you can ask for too much or not downsize
when needed and overspend easily! Expertise to use it ritght is important. Slighly different data center someone else hosts, but you manage. Unlike
Saas, you build your OS, configuration and software as you need on a server (s) you rent for capacity only as you don’t own the server that
feels like yours. You can deliver traditional applications and on-premise services via IaaS by lifting and shifting them to the cloud. Each piece
of configuration is your responsability. Typically delivered with a pay-as-you-go and based-on-what-you-use model. See AWS Web Services EC2, See
Table Notes
Focused on developers. Mostly focused on application or service delivery. Perfect if you want to deliver for example a great accounting application and
focuse on coding and creativity to support it. You don’t want to manage operating systems or know how to configure a MySQL database. You want the
components to be set up sensibly and heavily managed so you can just deliver your application. Want a database? Ask in code/config and get a sensible
default! Hugely varied in complexity, costs, and flexibility depending on your needs. Faster than IaaS unless you "need" to own more. Ex. Symfony
Cloud: Designed to enable framework applications to be delivered where you can "ask" for a database with code rather having to know how to set one
up. Ex. AWS Etic Beanstalk: Enables you to supply code, and it does the work of stiching together infrastucture components with sensible defaults to
deliver it. See table Notes
Enables you to supply code, and it does the work of stiching together infrastucture components with sensible defaults to deliver it.
Unlike Saas, you build your OS, configuration and software as you need on a server (s) you rent for capacity only as you don’t own the server that feels
like yours. You can deliver traditional applications and on-premise services via IaaS by lifting and shifting them to the cloud.
Designed to enable framework applications to be delivered where you can "ask" for a database with code rather having to know how to set one up.
Provides the translation of software requirements into actions on hardware. Manages shared resources. They are the layer that powers most of the
computing experience. OS is software (Windows-most common, Ubuntu Linux, Mac OS, Android, and many many others) that runs on the computer,
which manages how the computer operates. Provides functionalities such as Window management, which allows drag programs around screen, copy
and paste, the ability to plug in peripherals such as mice, and keyboards as well as networking. Most notable difference between OS is their look or
Interface (what you see when you open your computer)
Provides the capabilities to normal applications for hardware interactions or more core functions on your system, like opening data on disk. First part of
the operating system code to be loaded, has complete control over the computer. Responsible for controlling access to the most sensitive infomation
and funcionality. It is loaded into a protected region of memory to prevent accidental or malicious corruption by other programs. Responsible as well for
the loading of new programs deals with input and output between peripherals, manages access to the hardware's shared resources like RAM, and hard
drive. Kernel code is executed when pluggin in a usb device. Part where all protected functions that power the computer are executed. In sum: The
kernel is the core of an OS, the part that interfaces directly with the hardware components.
By the processor. "A series of actions or steps taken in order to achieve a particular end." In computer: A process is created on a computer when a
program is requested to be loaded. The computer will load the code in the program, such as Google Chrome browser, and will create a process that
contains all the necessary information for execution by the processor. Each time you run a program in your computer, a new process will be created in
order for the program to serve the purpose you intend. Some programs create many processes in order to get more work done.
Signal that is sent to the CPU, which alerts the CPU to a task requiring its immediate attention. It will halt the CPU and cause it to begin executing the
corresponding interrupt handler.
A hardware interrupt is generated by some sort of hardware either inside or outside of the computer. This includes a keyboard or mouse, which will send
interrupts when new input is available. The interrupt handler will then be executed, and the window which is currently in focus will receive the keyboard
input via the operating system.
Interrupt that is generated by software. Ex. Program wants to open a file: The program has to generate an interrupt software because the act of opening a
file is a priviledge operation, and as such the kernel has to be consulted before the operation takes place. Software interrupts act as an interface between
the kernel and the program. In short, the program can use a specific interrupt to askthe kernel to perform an operation on its behalf.
Is a program that is loaded by the BIOS when a computer is first turned on, is responsible for loading the operating system. A bootloader is necessary
due to the complexity that would be involved in creating a BIOS capable of loading hundreds of different operating systems. Due to this the bootloader
is usually installed at the same time as th eoperating system, and is loaded from a known place on the hard drive by the BIOS.
89
1
90
1
90
1
89
1
90
1
94
1
96
1
97
1
98
1
99
1
100
1
101
1
BIOS "Basic Input Output System"
BIOS: UEFI "Unified Extensible Firmware
Interface"
UEFI "Unified Extensible Firmware
Interface"
BIOS Startup
Virtualization
Hypervisor, see Virtualization
Vmware, see Hypervisor
Host Operating System
Guest Operating System
Type 2 Hypervisor, see Hypervisor
Type 1 Hypervisor, see Hypervisor
Virtual Box, see Hypervisor
vSphere, see Hypervisor
Responsible for loading the Bootloader. Is a program stored ROM on the motherboard of your computer. When the computer is first turned on, it is the
first program that is loaded and prepares or initializes the hardware ready to load the bootloader. Modern computers almost exclusively use UEFI
"Unified Extensible Firmware Interface". UEFI is the succesor of BIOS. Modern computers support both but usually UEFI is the default. Very smilar
but UEFI has more updatability and security, versatile.
Modern BIOS. Responsible for loading the Bootloader. Is a program stored ROM on the motherboard of your computer. When the computer is first
turned on, it is the first program that is loaded and prepares or initializes the hardware ready to load the bootloader. Modern computers almost
exclusively use UEFI "Unified Extensible Firmware Interface". UEFI is the succesor of BIOS. Modern computers support both but usually UEFI is the
default. Very smilar but UEFI has more updatability and security, versatile.
Modern BIOS. Responsible for loading the Bootloader. Is a program stored ROM on the motherboard of your computer. When the computer is first
turned on, it is the first program that is loaded and prepares or initializes the hardware ready to load the bootloader. Modern computers almost
exclusively use UEFI "Unified Extensible Firmware Interface". UEFI is the succesor of BIOS. Modern computers support both but usually UEFI is the
default. Very smilar but UEFI has more updatability and security, versatile.
Process: 1. Start up computer 2. we jump to our BIOS 3. We jump across to our Bootloader that knows how to load OS and it begins loading the kernel
first which is the part where all protected functions that power the computer are executed.
Virtualization is where we create a virtual computer ot virtual machine out of software that behaves like a separate computer. All the hardware
components of that VM are actually software. The software that is the VM, uses the hardware resources of the computer it is running on. This is achieve
by using a hypervisor (creates a thin layer that breaks the traditional 1:1 relashionship between OS nad hardware). Virtualization one of the most
instrumental technology architecture changes to occur in a long time: changed the way we deploy systems, test systems, and the cost of ownership of
services and applications. It broke the 1:1 relashionship of OS and hardware, with all kinds of performance, costs, and testing benefits.
hypervisor (creates a thin layer that breaks the traditional 1:1 relashionship between OS nad hardware) The software that is the VM, uses the hardware
resources of the computer it is running on. Layer of code that allows multiple OS to share same hardware resources. direct traffic deciding which bits of
memory are used on which VM, where the hard disk for that VM is kept in storage and so on. Broker of resurses. Two Types: Type 2 Hyperviso r-First
type of virtualization. Virtualizationis done by a software program that runs on an OS. Most populars are VMware, Workstation, and Virtualbox. Then
Type 1 Hypervisor- This is second type of virtualization. Virtualization occurs at the firmware/hardware but still software with no OS as host. The
virtualization software is actually the host OS. Commonly used in server environmnents such as data centers, particularly ones that form " the Cloud."
More efficient than a Type 2 hypervisor but not convenient for the commomn people. Requieres specific hardware for scalability and performance
purposes. Ex. VMware, vSphere, Proxmox.
Popular virtualization software. You run a virtual computer with a different OS from the main computer. Ex/ computer with Windows 10 OS running a
VM on Linux. Type 1 hypervisor for data centers etc and type 2 hypervisor for personal computers.
We call the OS that runs the virtualization software the host OS. It is the master, the OS that loads when you first turn on your physical computer. Main
OS in physical computer. Ex. Windows as host, Linux as guest.
This is the OS that runs inside the VM which is separate from the host OS, and cannot directly access resources on the host.This is key in cyber! This
separation help in analysing computer viruses for example, you do that on your VM to prevent it from spreading to your host OSand potentially escaping
out onto the internet from there. Or great to replicate environments of a complex nature with various OS. Ex. Windows as host, Linux as guest.
Type 2 Hypervisor-First type of virtualization. Virtualizationis done by a software program that runs on a host OS. Most populars are VMware,
Workstation, and Virtualbox.
Type 1 Hypervisor- This is second type of virtualization. Virtualization occurs at the firmware/hardware but still software with no OS as host. The
virtualization software is actually the host OS. Commonly used in server environmnents such as data centers, particularly ones that form " the CLOUD."
More efficient than a Type 2 hypervisor but not convenient for the commomn people. Requieres specific hardware for scalability and performance
purposes. Ex. VMware, vSphere, Proxmox. The physical hardware is controlled by type 1 hypervisor.
virtualization software. You run a virtual computer with a different OS from the main computer. Ex/ computer with Windows 10 OS running a VM on
Linux. type 2 hypervisor for personal computers.
virtualization software. You run a virtual computer with a different OS from the main computer. Ex/ computer with Windows 10 OS running a VM on
Linux. Type 1 hypervisor for data centers etc and type 2 hypervisor for personal computers.
102
1
102
1
102
1
102
1
105
1
105, 107
1
105
1
105
1
105-106
1
107
1
107
1
107
1
107
1
Proxmox, see Hypervisor
virtualization software. You run a virtual computer with a different OS from the main computer. Ex/ computer with Windows 10 OS running a VM on
Linux. Type 1 hypervisor for data centers etc and type 2 hypervisor for personal computers.
Workstation, see Hypervisor
virtualization software. You run a virtual computer with a different OS from the main computer. Ex/ computer with Windows 10 OS running a VM on
Linux. type 2 hypervisor for personal computers.
Virtualization-Uses: Security & Development Large portion of the internet runs now on virtualized servers. (ex. Cloud-type 1 hypervisor) Virtualization offers huge efficiency improvements for largescale applications. Virtualization gives a company the opportunity to turn one VM for low traffic and if all of the sudden a lot comes VM are up to take
care of the traffic and then you delete them when traffic goes down. Amazon AWS offers this service. USES in SECURITY- Virtualization is highly
used in CYBER.
Virtualization: Use in CyberSecurity, see
In Cyber we use virtualization a lot, we run type 2 hypervisor: software that runs as an applicattion on your host operating system. BC often we have to
Virtualization-Uses
run multiple OSs all at once since some tools will run only on Windows and others in Linux for example. Use #1: With virtualization we can run
Windows for example as the OS host and Linux as the guest OS or viceversa. Virtualization has created more efficiency. Use #2: Virtualization offerst
separation. Applications running in the guest OS cannot interfere with the host OS. Meaning we can wotk on dangerous tasks like analysing the latest
malware without risking infecting our host OS. DISCLAIMER: For malware analysis, make sure to disable all VM communication methods such as
vitual network adapter.
Virtualization: Use-Development, see
Many programmers make use of VM to test their programs in different environments (OS).
Virtualization-Uses
Virtualization: Snapshots
A snapshot of a powered on system has the contents of RAM as opposed to just the changes in the file system, making it signicantly larger than a
snapshop where the system is powered down. *Snapshots taken when a VM is powered off are typically smaller than when powered on.
Virtualization: Snapshot Definition, see
A Vmware snapshot is a copy of the VM disk file (VMDK) at a given point in time. Snapshots provide a change log for the virtual disk and are used to
Virtualization: Snapshot Definition
restore a VM to a particular point in time when a failure or system error occurs. Snapshots alone do not provide backup.
Vmware VM Byte Disk Storage
By default the disk grows dynamically as a set of files stored on th ehost. The guest VM might well see "x" GB of data but the storage is only taken up
as real data if written to the disk. This can be changed but it is the default on most systems. False Statement: -->A VMware VM defaults to allocating
every byte of the virtual disk as real storage to make sure is available in the future. This is mostly zeros, like carving out space it will use.< ---This is all
false.
Linux -What it is?
When we talk about Linux, we are really talking about the Linux Kernel. The kernel is the core of an OS, the part that interfaces directly with the
hardware components. Linux is more of a class of PS than one single OS; all these OS share in common: they ALL use the Linux kernel. All OS that
use the Linux kernel are called "distributions". linux is powerful and customizable; no wonder all the distributions available. Theres a Linux distribution
for for almost every specialist task in cyber.(111 N)
Linux Kernel
The kernel is the core of an OS, the part that interfaces directly with the hardware components.
Linux Distributions (many for desktop or
All OS that use the Linux kernel are called "distributions." Desktop distribution come with a GUI (Graphical User Interface). There are many
server)
DESKTOP distributions and also SERVERS distributions. Come in all shape and sizes. Ex. Ubuntu Budgie, Ubuntu, Arch (pick your own needscustomizable), Elementary OS (for non-tech people), Kali Linux (for cyber)
Elementary OS-Linux distribution
Is a Linux distribution focused on providing an OS that is easy as possible for non-tech people to use as a replacement for Windows or OS X (MacOS).
GUI-Linux
Kali Linux-Linux
Linux Desktop Distributions
Linux Server Distributions
Enviroment Variable-Shell-Linux
Linux Prompt Root User
Graphical User Interface. KDE, Gnome
Distribution built for cybersecurity professionals, comes with most of the cyber security tools you might need pre-installed.
Desktop distribution come with a GUI (Graphical User Interface). There are many DESKTOP distributions. Come in all shape and sizes. Ex. Ubuntu
Budgie , Elementary OS (for non-tech people), Kali Linux (for cyber).
Focused on providing services instead of whole desktop experience. Leaves more memory available for other processes to run. Don’t come with GUI
installed at all just like original Linux was in the beginning. (command line only) Everything must be done text-based commands in the "Terminal." To
this day, the most powerful way to to get something done with Linux is to use the terminal, even on desktop distributions with a GUI.
Echo the type of shell used.
root@james - virtual - machine:~# NOTE: root in the beginning as user name and symbol is # text color chages too which means the environment
changed too.
107
1
107
1
108
1
108
1
108
1
108
1
1
1
114
1
114
1
114-115
1
115
1
115
116
1
1
115
1
116
1
1
1
Prompt
user@SANS: ~$ This is called the prompt. You type your commands in there as its prompting you for input. This prompt is common by default but like
a lot of things in Linux is customazible. Information you get with the prompt we will know our username, the name of the computer and where we are in
th efile system. user= user account, SANS= host name or computer on the network, (~) the tilde character is shorthand for the home folder (home
directory) of the current user. As the root user, (the highest priviledge level, level of permission) this prompt will typically change from a $ to a # to
signify the shift and the user to root user. ex. root@james - virtual - machine:~# and the color text changes too which means the environment changed.
Dollar $ means normal user, hash # means system administrator or root user, and in C shell the prompt ends with a % sign.
Linux Prompt-Command line asking for input user@SANS: ~$ This is called the prompt. You type your commands in there as its prompting you for input. This prompt is common by default but like
a lot of things in Linux is customazible. Information you get with the prompt we will know our username, the name of the computer and where we are in
th efile system. user= user account, SANS= host name or computer on the network, (~) the tilde character is shorthand for the home folder (home
directory) of the current user. As the root user, (the highest priviledge level, level of permission) this prompt will typically change from a $ to a # to
signify the shift and the user to root user. ex. root@james - virtual - machine:~# and the color text changes too which means the environment changed.
Dollar $ means normal user, hash # means system administrator or root user, and in C shell the prompt ends with a % sign.
Linux-BASH (Boorn Again Shell)
Linux-Shell, for Terminal
Terminal-Linux p. 116, 124
Arch-Linux
Ubuntu-Linux
Logical Volume Manager (LMV, Ubuntu
Installation Type), Linux
Zettabyte File System (ZFS), See Logical
Volume Manager
GRUB Error Messages-Linux
Intalling Linux Servers
There are many Shell programs but Bash is the most common. Bourne Shell was one of the earliest shell programs then Bash was written as a modern
program to replace it. The default path for Bash is /bin/bash. The first / means the root of the file system, from the root of the file system, in the 'bin'
folder is the bash program.
Program that runs automatically when the Terminal is opened. The Shell is responsible for displaying the prompt, interpreting the commands you type,
running programs, and displaying the output to you. There are many Shell programs but Bash is the most common. Bourne Shell was one of the earliest
shell programs then Bash was written as a modern program to replace it. The default path for Bash is /bin/bash. The first / means the root of the file
system, from the root of the file system, in the 'bin' folder is the bash program. You can select a different shell and customize it heavily. (Bourne Again
Shell, Bash, SH, ZSH)
Text-based area, Command line. You can use the icon or right click on the desktop itself and pick open terminal from menu. Prompt in terminal:
user@SANS:~$
Linux OS distribution for users who desire a do it yourself approach, allows users to customize for their own needs
Linux distribution with pre-configured system. Modern open source OS for the enterprise server, desktop, cloud, and IoT.
Installation type, Erase disk and install Ubuntu, click advanced features, you get None, Use LMV with new Ubuntu installation, or
EXPERIMENTAL:Erase disk and use ZFS (Zettabyte File System). Encrypts the new installation with a security key for security purposes. Key unlocks
your hard drive and your OS instalation. Files stored in your home directories or navigating around Linux are going to be protected against attackers. A
bit of disk encryption.
Powerful experimental tools like copy on write where data is put on anew block and verified in its new location before removing the old.More fautlttolerant. Or the pooled storage which enables you to add a new disk and have that turn up as part of the available space in the file system.
They can appear after installing and restarting your Ubuntu-Linux OS as error message from the installation/compatibility.
No GUI, default to a simpler text-based set up, more designed to work on servers that may be headless being used by some kind of remote access or
control device like KVM. Sets up process that enables to do set up from the cloud. Needs mirror address-where it should go to get all of its packagesall
the software, by default sometimes, or specific in a corporation, proxy address-in case that is requiered to get out of a corporate environment, network
connectivity details. Space bar becomes the Toggle Key on or offbecause mouse cannot be used. LVM-security key for disk not needed in this case-too
many servers to boot in case of power outage. Pick server (ex. docker, juju, nextcloud, heroku, aws-cli...) Professor picked Docker. Then rebbot after
server installation. You can upgrade and add any packages you want later. TAB, Space, Up, and Down, Enter to configure options.
Linux GUI Navigation, See Illustration Notes No single GUI layout, every distribution different but lots of common features/software even if locations change. 1. Dock: saves frequently used
applications or any running application. Compares to Dock on OS X or Taskbar on Windows. 2. Start Menu: Click it and it will bring a search bar and a
list of all applications. 3. System Tray: (top right corner) you can shut down, reboot, update, or access other settings such as volume, bluetooth,
notifications, and network settings. 4. "Terminal" application Icon (black text based area, command line) Occupies first position on the dock to giv eyou
an idea of its importance. 5. File browser application folder or file manager: works like explorer does in Windows, You can navigate through the folder
structure of your installation. 6. Wen Browser: Installed by default- Chromium (a version of Google Chrome)
124
1
124
1
124
1
124
1
116
1
118
118
1
1
118
1
1
1
119
1
120
1
LibreOffice Writer (blue icon)-LibreOffice
Located on top of Chromium web browser in GUI. Basically copies of Microsoft Office, except open source and free.
Calc (green icon)
Chromium Web Browser Version of Chrome Version of Google Chrome. Default for Linux Oss.
Linux-Configuring Networking with GUI
Superuser on Linux OS
Superuser on Windows OS
Switch User Accounts Steps
su' Substitute User (su - Vs su - username)
dash symbol Linux Terminal
sudo' (sudo su -)
Sudoers File
visudo' command
Groups Linux
User proviledge Specification
Tilde ~ symbol
Permissions folder/files Lists
Listing Files
ls'
-l' command (print long form )
Best way to configure networking on a Linux System is from the command line but here re the steps to do it through the GUI. Steps: 1. Find the
Network settings Preference page- 2 ways for that: A. right click on the network icon in the system tray on the top bar and go to "Edit Connections." B.
Go to Start Menu (left upper corner where search bar appears with apps), select Settings, Networks, select the connection you want to edit (Wired, or
Network Proxy), click on "gear" icon on bottom right, from there select IPv4 (or IPv6 if that is what you use) and change it from DHCP which is
automatic, to "manual" and assign custom settings if you wish, to apply changes click on "Apply."
Administrative account. Has permissions to perform anything and everything on the OS. Always at least 1 superuser account, account name usually
named root but since Linux is very customizable there can be a distribution that doesn’t follow convention. Does not do are you sure ? prompts..it just
performs the command you wrote without questioning like Windows. Always log in as a norrmal user account, is bad practice to use the root user
account for daily activities. The superuser is important for executing high-priviledge operations on teh system, andsudo enables us to briefly assume
rights to do something.
Administrative account, however cant do anything he/she wants on the system like a Linux superuser does. Typically a Windows superuser cannot do
things that will break the OS irrevocably. (on linux even that is allowed to the superuser)
p.127-128
Switch users in Linux, needs the password of the account you want to switch to. After done with that account type "exit" to get to regular user account.
Usually people switch to root account but it can be any. You must authenticate to any account you want to switch. su defaults to running an interctive
shell as root unless another user is specified. su - for root user, su - name of account, for any other user account.
If you switch accounts and forget the dash - symbol in the command, you will switch accounts but not environments. Is like a halfway switch. You will
know because you will not see the tilde or home directory.
Is a program installed in some Linux systems. Allows accounts on the 'sudoers file list' to take on root priviledges temporarely after the command runs
and using the "sudo" acronysm. When you want to run a command with priviledges, you append "sudo" before the command. You will be prompted for
your normal account password (not the root password) and the command will run with superuser priviledges. Many that come with sudo installed will
ramdomly generate root password and throw it away to encourage users to ALWAYS use 'sudo' which is a good practice. Enables us to brifly assume
rights to do something. *Also used to change file permissions: sudo chown name of account you want to change to, file name.
List of accounts allowed to what a superuser do when using the 'sudo' command. Only root user can edit this list.
to edit sudoers file. Is a command line text editor that will check your sudoers file for any errors before it saves it, it lowers your chances to lock yourself
out of the superuser account entirely. It lowers the chances but not at 100%. You type 'visudo' only if you already have the root user privilege or 'su
visudo' to get the priviledges and start working on the sudoers list file.
In Linux, a user account can belong to groups. Each group ex. Sudoers group, are allowed to execute any command as a root if allowed; you check that
on the section of user proviledges. The most important piece is a section labeled user priviledge specification. It has lines that define user rights such as
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL Allowing sudo group users in this example to run any command.
The most important piece is a section labeled user priviledge specification. It has lines that define user rights such as %sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
Allowing sudo group users in this example to run any command.
Tilde symbol is home folder. Also, (:~$) this part in this diagram tells us where in the system we are.
Directory folders will start with 'd' and files with '-' which makes ot easy when you have no access to a GUI or colors to differentiate.
ls' command for file, '-l' for print long form. (to print long form you do: ls - l) When we do list of files with 'ls' we get a list of all the files and folders in
system (in this case teal for folders and white for files) and toget the info of those like: permissions, user, group, file size, creation time stamp, file/folder
name you 'ls -l'. Directory folders will start with 'd' and files with '-' which makes ot easy when you have no access to a GUI or colors to differentiate.
(p. 131) We can also ask to list files and folders on a different directory ex. 'ls -l Desktop' this will list all files and folders on Desktop directory
(folder).
command that stands for list
write -l after ls (ls= list) command to print long form. (ls -l) you get to see al info of creation, user name, file size, permission, group, file/folder name.
121
1
121
1
122
1
127
1
127
1
127
1
128
1
1
128
1
129
1
129
1
129
1
129
1
130
131
1
1
130
1
130
1
130-131
1
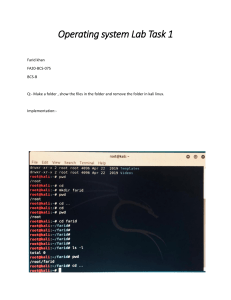
Chaging Directory Linux Terminal, See cd
command
cd' command. Allows to change directory into a different folder. To go back to home folder you have 3 choices: 'cd/home/user', 'cd ~' Remember the
tilde is shorthand for current user home folder, and last one 'cd ..' '..' is shorthand for directory one level above the current directory also known as
parent directory, not to be confused with single '.' which is shorhand for the current directory. It doesnt requiere always to type the full path.
cd' command
pwd' command
dot, dots '.' '..' Metalocations
Absolute file Systems Paths
Slash (/)
Relative Styles
root of the system
bin
boot
cdroom
dev
etc
home
lib
lost+found
media
mnt
opt
proc
root
run
sbin
srv
sys
tmp
usr
var
132
1
change direcory command. Allows us to change derectory into a different folder. It doesn’t always requiere typing the full path.
it will show us the path to our current working directory. Stands for Print Working Directory
metalocations on terminal. One dot= current directory, two dots= to access parent directory, directory one level above the current one.
/var, /log
it says start from the beginning of the file system and work forward. / means go to the root of the file system (first slash, second is read then go to blah
blah, and third / same thing.
~/Downloads' 'ls' 'll'
navigate to the root of the system 'cd /'
The bin folder is typically used to store executable files (binary files). These will usually be system files, as opposed to ones the user installed.
The boot folder holds the files that Linux uses during the boot up process. Better not mess around in here unless you know what you are doing.
The cdrom tray will usually be mapped to this folder, so if you have a cdrom plugged in you can usually access the files on it from here.
The dev folder will contain a folder and associated files for every hardware component on the system. For example, there is /dev/cpu, and there are even
entries for your hard drives. Usually, you don't want to mess around in here.
The etc folder will usually contain configuration files for installed programs. If you need to change a setting for a program you've installed (for example,
a web server), then this is the first place you'll want to look.
The home folder contains the user directories for every user on the system (that a user can log into) with the exception of the root user. Our user is called
'user', so you can find our home directory in /home/user.
The lib folder contains shared libraries and kernel modules. These are resources that the system uses to function, usually best not to mess around in here
either.
If your hard drive has errors and files get lost, the 'orphaned' files may get placed here.
The folders here can be used for mounting USB keys and floppy disks (if anyone can still use one). To mount one is basically to load the file system that
exists on it so you can access the files.
The folders here can also be used for mounting external drives, USB keys and floppy disks. It's up to you if you want to mount stuff here or in media.
132
132
131
133
1
1
1
1
133
1
133
134
134
134
134
1
1
1
1
1
134
1
134
1
134
1
134
1
134
1
134
1
135
1
The opt folder is usually empty to start with; any user-installed programs can go here (if you want). It stands for 'optional'.
The proc folder stands for 'process'. Every running program will have an entry in the proc folder along with associated files.
The root folder is the home folder for the root user. Remember, it isn't in /home.
The run folder is a temporary file system which stores runtime information for programs that start early during the boot up process.
The sbin folder is used to store binary executables (similar to /bin), but the programs stored here are typically used for administrative purposes.
The srv folder usually holds data used by services running on the system (such as a web server, or an FTP server).
The sys folder contains information about devices on the system (as seen by the Linux kernel). Usually, you don't want to mess around in here.
The tmp folder is a temporary file system. The files in there are temporary and will be deleted periodically, and after reboot. Programs will usually use it
frequently. Just don't use it to store your important files!
The usr folder is the folder for user-controlled files. It has its own folder structure, which maps to the root folder structure. For example, there is a
/usr/bin folder which is for user-installed binary executables.
The var folder contains system files which tend to increase in size over time (hence it's a variable size folder). Things like log files, the mail directory,
and so on, go here.
135
135
135
135
135
135
135
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
135
1
135
1
135
1
File Permissions on Linux
r
w
x
Setting File Permissions with chmod (1st-3
way of doing it)
chown' command
chgrp'
chmod +r filename
Setting File Permissions with chmod and
denary number 2nd way
Binary setting file permissions, see Setting
file permission with denary number
chmod +r denary number
Setting File Permissions-Short way 3rd way
Hidden Files
touch command
ls -a' command
ls-la'
cat command
Environment Variables ($PATH, $HOME,
etc)
Each file is owned by a user and also by a group. Position one is the name of user, and position 2 the group user name. Ex. A file owned by an account
named USER and by a group named www-data group (typically used by web servers). Three permissions mode we can set for each owner of the file: r:
Read Permission, w: write Permissions, and x: Execute Permissions. Each owner gets a set of those 3 permissions. Ex. -rwxr-x-w- The first '-' is for
special permissions, or to indicate a directory or file. If it is a directory this will show a 'd' in its place. The next 3 are reserved for the user permission.
(rwx). Then the next 3 are reserved for the group permission. (r-x), all group member will have the same permission. and last, the final 3 are for anyone
else, meaning if you are not the user owner and you arenot the group owner, this will tell you what kind of access to that file you will have. In this case,
write (-w-) but not read or execute.
read permission-file permission mode for each owner of file
write permission-file permission mode for each owner of file
Execute permission- file permission for each owner of file
You need the rights to change permissions. (a root account or use sudo chown). Ex. Sudo chown root permissions_example Then to set file permissions
you use chmod +r filename (do the same for +w, +x), problem with this way of setting is that it applies permissions at once ofr all sets of permissions.
(to remove them you use -r,-w-x for example) There's a better way and more secure way:
changes the user file owner of a file to a different user account. ('chgrp' changes the group file owner instead of the user file owner) Good to use when
you hav eno access to root account to change permissions. Use with sudo chown, nam eof account user one wants to change to, file name. Ex. Sudo
chown root permissions_example
changes group file owner name. Ex. sudo chgrp pink permissions_example and this will change the name of the group from lets say www-data to pink.
Adds READ permission to a file. Ex. Chmod +r permissions_example (use +w, +x to add others) (To remove permissions use -w, -r-, -x) This will add
Read permission to every set of permissions: the user owner, the group owner, and every other user in the third area of ---. This is problematic for
security reasons.
You need the rights to change permissions. (a root account or use sudo chown). Ex. Sudo chown root permissions_example Then to set file permissins
using numerical value . Do a little table containing R for read, W for write, and x for execute. Under each letter put a 0 or a 1 depending if you want that
feature on of off. you will get a 3 digit number in buinary that you have to transfer to denary. Ex. 111= 7 means all permissions, 101= 5 meaning only
read and execute, 001=1 only execute, 010= 2 write only. After calculating your denary number, type: chmod 512 permissions_example This will set all
different permissions levels separate permissions.
111= 7 means all permissions, 101= 5 meaning only read and execute, 001=1 only execute, 010= 2 write only.
ex. chmod 512 permissions_example This sets different permissions to all 3 groups. (User, group, and anyone else )
Read=4, Write=2, Execute=1 Setting read and execute? That’s 4 +1= 5 What about read and write? 4+2=6.
To hide files from user '.' use the dot symbol. Ex. '.myfile' to create a hidden file that doesn’t exist 'touch .myfile' If we use 'ls' to see it listed we will not
because it is hidden, however, if we use 'ls -a' it will show us ALL hidden or not files in the directory. You can also use '-a' alongside '-l' like 'ls -la' to
show all files with more info in columns including hidden ones. Hidden files on Linux are a normal mechanism used to hide configuration or temporary
files from a user casually navigating into them, but they also make for a useful tool for attackers to hide data or binaries.
If you use touch command on a file that doesn’t exist, it will create a file with that name which is emty. Ex. touch myfile for a hidden file ex. 'touch
.myfile'
Shows/list all files in directory, hidden or not. Note: One dot= current directory, two dots= to access parent directory, directory one level above the
current one. It even shows directories starding with d.
shows all files organized with all the information in columns including hidden files in system.
prints the content of a file and also group them (concanate) before printing them. Ex. 'cat .secret-config-file' also lots of info on p. 169 Stands for
'concatenate.' It's used for joining the contents of several files together and then printing the result to the terminal. Most commonly it's used on just a
single file to print the contents to the screen quickly. But you can give it as many files as you want to concatenate. cat printme1.txt printme2.txt *To
save reconnected files as one file: cat printme1.txt printme2.txt > newlog.txt
These are created fresh every time the terminal opens, they dont exist when the terminal is not open. Linux terminal can store data that can be used by
many progtam sbut is temporary, it is gone after you clos ethe terminal. The data is all stored in environment variables. You can print these using the
'echo' commnand along environment variable name. ex. echo $HOME Environment Variables denote an $ symbol in front.
136
1
136
136
136
1
1
1
137
1
137
1
138
1
138
1
139
1
139
1
140
141
1
142
1
142
1
142
1
142
1
143, 169
1
144
1
PATH or $ PATH environment
Helps in bypassing security. Great time saver to find programs and avoid typing the full path for each program. The PATH environment variable
contains a list of directory paths separated by a colon (:) which tells the terminal where to look for the equivalent binary executable when you type that
command. 'which' command ex. 'which ls' to see where ls is located on my PATH. If you cannot find a program you installed on Linux it might be
because that executable was not installed inside the PATH environment variable. Solution: If running 'bash' shell (check with echo $SHELL), you can
edit the .bashrc file in your home folder. bash script (essentially just a list of terminal commands) to edit the .bashrc file in your home folder. It will get
executed everytime a new terminal window is open. Notice '.' is a hidden file. ex. to solution: export PATH=$PATH:/mycustomfolder expoert
PATH=/bin:/mycustomfolder
echo' command
prints an environment variable. Ex. 'echo $HOME' ex. Echo $PATH
export' command
set or modify an environment variable temporarely until terminal is close then our /home/user resets back to it, nothing in reality is changed but we make
the terminal believe in this example that tmp is now our home folder ~. Don’t use $ symbol when using 'export' Ex. export HOME=/tmp (here we
changed the value of the $home variable (no $) and we are just changing temporarely our home. ex. export PATH=/bin:/mycustomfolder ex. export
PATH:/mycustomfolder
printenv' command
prints a list of all of the environment variables in the system.
cd $HOME'
to go back to my home directory quickly
which' command
it shows us where a program is installed on our system. Ex. 'which ls' tell me where 'ls' is : /bin/ls
.bashrc file
bash script (essentially just a list of terminal commands) to edit the .bashrc file in your home folder. It will get executed everytime a new terminal
window is open. Notice '.' is a hidden file.
ls'
Using this parameter causes ls to print files in a long listing format, which includes file permissions. Not hidden ones; need for that ls -la
root
home folder for root is in /root.
Tab Completion
Modern feature to make typing faster and easier, like auto completion when typing stuff on terminal. Most modern shells support some form of tab
completion. Ex. Insteadof typing 'cd Templates' to go to the templates folder, We can do: 'cd D' double TAB and it will take me to theDesktop,
Downloads, and Documents file choices. 'cd T' and 1 TAB iwill take me to the Templates file bc theres only one file that starts with T. In sum, the
terminal will look into the current folder and it will know what you meant to type depending on what you type. For one match is 1 TAB and for multiple
matches press TAB twice quick one after the other. *Tab completion also work for terminal commands. ex. '$ wh' brings all the commands installed on
the system (in the PATH) that start with 'wh'
Previous Commands, see Reverse Command Another feature for usability that can be found on most terminals is the ability to scroll back through previously typed commands. Use the arrow kys. UP
Search
arrow key for to access the last command typed, if you keep pressing the arrow key you will see more and more commands you typed. Same for down
arrow key, to come back to your more recently typed commands if you went past what you needed. There is a second way of looking to the command
history: Reverse command search. Faster and avoid error.
Reverse Command Search, see Previous
Another way of looking to the command history. Instead of using the arrow keys to navigate through your command history, you can perform a serch
Commands
using CTRL+R in the terminal, it will bring up a search prompt. You can then enter your search term at the prompt and it will auto complete with the
most recent commnad that matches the search. If you get the command you were looking for just hit enter and the command will run. If that wasnt the
command, just press CTRL+R again and every time you do it, it will go further back in your history. Faster and avoid errors.
Bash History
This is where all previously typed commands are stored. Every user has their own hostory file which keeps track of every command run by that user on
the terminal. Every terminal shell has a different name for the history file <but in the BASH shell the file is stored in the users home folder and it is
called '.bash_history' It's a hidden file.> The history file is just a text file you can read with any text editor. The 'history' command, lets you reads the
history file but results will be just within same current session and memory, not past or previous sessions. This is a little better tho because it list the
number of commands used. You can also clear the history: 1. Delete the .bash_history file (a new one will be created the next time you run a command).
2. Then use the command: $ history -c This tells the program to clear the history file that is stored in memory. ***At the end of a terminal session, the
file in mmeory is written to the .bash_history file in the users home folder. To cover your tracks, you must clear both, the hx file and bash file.
Parameters
Several different forms: 1. Single letter parameters. These are like 'ls -a' where the single letter follows a dash (-). If you have multiple parameters, chain
them together with a singlw dash or use one dash for each. Ex. 'ls -al' or 'ls -a -l' 2. Next form can take take is full word parameters. Usually requiere
double dash (--) ex. 'ls --all' In this case, '--all' is the same as '-a.' Some commands only take a long form or a short form, some both; it depends who
wrote the program. There are even cases where no dash (-) is required at al. ex. 'ps' command.
145
1
144
1
144
1
144
144
146
1
1
1
146
1
142
1
1
150
1
153
1
154
1
155
1
157
1
Interrupts
Clearing the Terminal
history' command
history file
c command, -c needs the - but excell didn’t
let me put in front.
q command
man' command
--help' or '-h' command
top' command
CTRL + C
CTRL + Z
jobs command
history -c'
cp command, Linux
mkdir command, Linux
A. 'CTRL + C' Is a method to send an interrupt to the program to quit. Press CTRL + C in the terminal whe a program doesn’t have a specific way to
quite like 'q' command. CTRL + Q was thrown here too in class session but not in book. After we do CTRL + C we will be dropped to a prompt again
and the information will stop being updated in th ecase of 'top' command. B. The next interupt is to pause/suspend a running program which pauses the
program execution. Do that with : 'CTRL + Z' Once suspended, you have different choices to proceed: you can resume it by typing 'fg' which stands for
foreground. This will bring back in this case 'top' program/command back up and show it to you again. We can aldo do 'bg' which allows the program to
run in the background while you do something else on the terminal. To bring it back to the foreground (in your view on screen) type 'fg'. Note; if instead
of typing CTRL + C , you typed CTRL + Z, just do 'fg' and the CTRL + C to exit.
clear' is method one for cleaning the terminal of output that was there already. Or use 'CTRL + L'
The 'history' command, lets you reads the history file but results will be just within same current session and memory, not past or prevous sessions.This
is a little better tho because it list the number of commands. You can also clear the history: 1. Delete the .bash_history file (a new one will be created the
next time you run a command). 2. Then use the command: 'history -c' This tells the program to clear the history file that is stored in memory. ***At the
end of a terminal session, the file in mmeory is written to the .bash_history file in the users home folder. To cover your tracks, you must clear both. To
guide yourself use on when to use what type '-h' or '-help' for the built in help feature ot 'man and the command' for the manual.
where all commands used by an user are stored. Bash hx. Is a text file you can read with any editor. Its stores at the users home folder. Is a hidden file.
'.bash_history'
command to clear ex. 'history -c' to clear history
quit command
for manual (commands explanation) ex. 'man ls' will ive me all the info on this command. There is also 'h' or 'help' commands for for the built in help
page but it has less info than using the manual. Press 'q' to take you out of the manual.
--help', or '-h' access to buitl in page for help with commands. Not as throughout as using the 'man' for manual command. Manual is more extensive.
command that shows information about the system you are on, a bit like task manager in Windows. You can see how busy the CPU is, how much
memory is in use, and which processes are running. The view constantly updates with new information. The only way to quit 'top' command is 'CTRL +
C' or 'CTRL + Q'
Get you out of some commands ike 'top' where 'q' like quite don’t work. Also, CTRL + Q
Pause/suspend running programs in terminal Linux. Once suspended, you have different choices to proceed: you can resume it by typing 'fg' which
stands for foreground. This will bring back in this case 'top' program/command back up and show it to you again. We can also do 'bg' which allows the
program to run in the background while you do something else on the terminal. To bring it back to the foreground (in your view on screen) type 'fg'.
Note; if instead of typing CTRL + C , you typed CTRL + Z, just do 'fg' and the CTRL + C to exit.
Lists paused/suspended processes and number them. Use number next to them to switch between them. Ex. 'fg 2'
clears the history stored in memory. Does not delete history file written to the disk. Both need to be clear; bash file and hx file. 'history -c' This tells the
program to clear the history file that is stored in memory. ***At the end of a terminal session, the file in memeory is written to the .bash_history file in
the users home folder. To cover your tracks, you must clear both. To guide yourself use on when to use what type '-h' or '-help' for the built in help
feature ot 'man and the command' for the manual.
short for copy. Allows us to copy a file from one location to another, keeping original intact. 'cp' ex. cp myfile mycopiedfile cp needs 2 parameters
(name of file you wish to save and path where you want to save the file) You can also specify full path to copy like: cp myfile
/home/user/Desktop/mycopiedfiles You can also use cp to copy Folders with the '-r' -R' parameter like 'cp -r myfolder mycopiedfolder' Stands for
'recursive.' Means 'look inside any folders and copy those files too' It also copy folders within that folder. ***use cp --help if you want to at options on
how to use cp. Most used are cp by itself or cp -r.
Used to create a directory (folder). Ex. mkdir mynewfolder or type the full path: mkdir /home/users/mynewfolder Also, to create multiple folders
(directories at the same time like mkdir test1 test2 test3 To create folders within folders use -p: Ex. mkdir -p afolder/asecondfolder/athirdfolder ***
don’t forget to use --help to view a more complete listing of parameters. We cannot assign sensible defaults to the permissions of our structure while
creating them. Afterwards we use '-m' to do that.
160
1
162
1
155
1
155
1
156
1
159
1
158
1
157
1
160
1
160
1
161
1
161
1
156
1
165
1
166
1
-p' command
mv command, Linux
used to create multiple folders within each other. A folder within a folder, within a folder, etc. but at the same time. Ex. mkdir -p
afolder/asecondfolder/athirdfolder We cannot assign sensible defaults to the permissions of our structure while creating them. Afterwards we use '-m' to
do that. *** don’t forget to use --help to view a more complete listing of parameters.
Stands for move. Used for moving files and folders from one location to another, removing the original unlike copy command. Ex. mv afile
firstFolder/afile In this example we moved 'afile' into 'firstFolder There are no parameters for 'mv' ut there are some useful ones like '-n' for no-clobber
which prevents the move from overwritting a file that already exists at that location. We also have '-u' for update which only overwrites a file if the
timestamp on the file you are moving is newer. **The 'mv' command is also used to rename files since there is no rename command. so you have to use
'mv' to move a file to the same location but with a new name. ex. mv afile arenamedfile ex. mv aubergine.txt vegetable/eggplant.txt
cannot remove directories by itself, but removes files. Ex. rm afile Be careful to use rm as a root user, you could delete everything on a system file and
corrupt the operating system. *To delete folders add -r or -R along rm ex. rm -r afolder **To delete multiple folder at a time use: rm -r directory-a
directory-b directory-c
less command, Linux
Newer version of 'more' command that is installed in older systems. 'less' is used for reading long files. It opens the file in an interacttive program and
use the arrow keys to scroll through the file. You can only quit the program hitting 'q' on your keyboard, CTRL + C will not work. 'lees' doesnt load the
whole file into memory at once, it only loads a portion of the file at a time. A text file with several gigabytes in size opened in other text editor and with
not enough RAM, cause your computer to crash. With 'less' you can read text files of any size no matter how large. The less command is one of our go
to commands for viewing and searching data quickly. Space bar= one page at a time, to search within the text file: / word 0g for example takes you to
the beginning of the page, also put any number after the : and hit enter to skip pages.
-iname' parameter
find / iname ".hid*" 2>/dev/null Remember -iname searches for filename matches on a case insensitive basis.
find command- 2>/dev/null
if there are errors in my search results I domt want to see them. find / iname ".hid*" 2>/dev/null
find command, Linux
Used to find files on a system. Most common method to find a file is by name. You can also use partial by using the '*' like such: find / -name '*.mp3'
You can also search by date the file was created, the owner of th efile, or by which files have what permissions. The combinations for search are
endless. The parameters are 3: A. directory you want to search in (it will include all subfolders), If you want to search the whole file system, you can
direct it to search in '/' or if you want it to search in the current folder and all subfolders use '.' (remember '.' is current directory). B. The second
parameter is search method. we are searching by file name. C. Third parameter is the search term. Supress errors based on permissions: 2>/dev/null (if
you add this yo udont get files where you are denied to read) ex. find / -name "passwd" 2>dev/null
Case sensitive (-name) including errros is ex. find
/ -name "passwd" iname search: find / iname ".hid*" 2>/dev/null Remember -iname searches for filename matches on a case insensitive basis. --help
to look for more options.
Recursive 'r' or '-R' command/parameter, see Stands for 'recursive.' Means 'look inside any folders and copy those files too' It also copy folders and files within that folder/directory even permissions.
cp command
***use cp --help if you want to at options on how to use cp. Most used are cp by itself or cp -r. ex. 'cp -r myfolder mycopiedfolder' 'grep -R "root" /etc/
2>dev/null'
-u' command Linux
update. We also have '-u' for update which only overwrites a file if the timestamp on the file you are moving is newer.
-n' command Linux, no-clobber
There are no parameters for 'mv' but there are some useful ones like '-n' for no-clobber which prevents the move from overwritting a file that already
exists at that location.
semi colon ; for linux terminal
helps with spped to write more commands together. Ex. rm remove-me.txt; ls
grep command
Used for searching for text witin files. Ex. Grep "room" afile (here we grep for room, meaning we searched for room witihn afile file. First parameter is
the word we search for in the file and the second parameter is the name of file we wil be searching in. Like with the 'find' command a wild card operator
(*) can be used as such: grep Greg* afile In this case it will search for anything that starts with Greg and finishes with anything else. 'grep is casesensitive, to make it insensitive use '-i' ex. ' grep -i gregor afile' to know more use 'grep --help' With recursive option -R to make copies of files with
permissions grep -R "root" /etc/ 2>/dev/null ex. grep "home" grepfile1.txt Search every file in a directory: grep -1 "whole" *
166
1
167
1
168
1
170
1
rm command, Linux
which command
asterisk, linux & Google
shows you where in your PATH a tool is installed. Ex. which ls Useful to find out 'which' binary you will run and where. Useful for resolving version
or path confusion issues. If no results it doesn’t exist in your PATH. You have two choices: Move the program you installed into a folder in your PATH
or add the folder that the program was installed into to your path.
asterisk * (can be used either side on words depending what you are searching) searches all of it, amplifies search. For Linux means 'every' in some
commands. In google search if you don’t know one of the words you need to search for use a * as this: "The internet is a series of *" It will follow the
excat format and sequence you set. p. 223-P
1
1
171
1
165
1
167
1
167
1
1
174
1
174
1
174,223
Wild card operator, used in Linux commands asterisk * (can be used either side on words depending what you are searching) searches all of it, amplifies search. For Linux means 'every' in some
& google search
commands. In google search if you don’t know one of the words you need to search for use a * as this: "The internet is a series of *" It will follow the
excat format and sequence you set. p. 223-P
insensitive (use -i parameter for it)
when searching for words and commands are case-sensitive like 'grep' command, use -i to make it insensitive like' grep -i gregor afile'
Pipe Character | (shift + key under backspace This symbol is called Pipe |. Used to send the output of one command and feed it in as the input to another command. Combines two or more programs
on my lenovo)
to achive a complicated task. Ex. ps aux | less Here we are taking the output of ps command and use that output as input for less command to not have
as many results. Search example with grep: ps aux | grep bash To avoid our search for appearing in results: ps aux | grep bash | grep -v grep Opening
the result of all in less: ps aux | grep bash | grep -v grep | less
apropos command
Similar to man command, Is used to search man (manual) pages for keywords, usually to find the 'appropiate'(=apropos) tool to use in a particular
situation. Ex. Which tool could I use to display the manual for a tool? Ex. Apropos "manual" You then pick the result you need and find more. ex. for
this case: $ man man
supress errors in results search
2>/dev/null
nano command, tool
Command line based text editor. To edit a file: run nano on the file name. ex. nano a file To create one: nano newfilename It gives you the prompts
even on how to exit. CTRL + X You will be prompted to save changes and the put in the filename to save as. The default option is to overwrite the
existing file. Easier than Vim editor.
vim command, tool
Not as easy as nano text editor but more powerful. Is a modern version on 'vi' which was the original program. Type 'vim' and a file name, and it will
open it or open a newly created one with such name. To be able to start typing in your file you need to enter into 'insert' mode by hitting 'i' and the
bottom of the editor will state INSERT at the bottom. To get out og insert mode, type CTRL + C (in video he said ESC key). To quit vim type :q but it
will send an error if you have not saved your work, if you dont care about saving your work type :q! to force quit. If you want to save your work use
either :wq or :x Ex. vi newfile.txt
insert mode, vim editor
allows you to start typing in vim text editor, to get out of insert mose type CTRL + C
file command
Tell us the filetype of a file. Linux isnt keen on file extensions like Windows who uses both file headers and file extentions, , instead relies on content,
specifically every filetype has its own file header like a signature. Identifies the type of file you are working with on a system where extentions are not
necessary or necessarily right. Ex. file azipfile It will accurately tell us is a zip file.
Executable file ELF binary on Linux
ELF' Linux version of an EXE on Windows, an executable file. A program.
string command
Used for pulling text sequences like ASCII characters out of binary files to screen. Prints the sequences of printable characters in file. Frequently used
in cyber. Used with other commands like cat command. You get for example ASCII characters that are 3 or more characters long in a row. Makes it
more readdable thatn looking at ASCII characters. All steps: cat strings.c gcc -o strings-compiled.c; ls file strings-compiled cat strings-compiled
strings strings-compiled strings strings-compiled | grep r3a11y
gcc
compiler. String command sectoin p.183 ex. gcc -o strings-compiled.c; ls
wget command
stands for web get. Allows us to download files from the internet from the command line. Looks like Googles homepage but the url is actually the file
you download. Non interactive network downloader. Supports HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols as well as retrieveal throgh HTTP proxies. Follows
linkns in HTML, XHTML, and CSS pages.
man command
ex. man wget Here we are searching wget in the manual. Man=manual
chaining commands & Basic scripting
Ex. A. ls; sleep 5; ls This little snippet list files, waits 5 seconds,and the runs ls again. We can chain commands together to run one after the other on
one line. Ex. B Using Pipes and Redirects: cat /etc/passwd | grep root; sleep 2; ps aux | grep root This command will search /etc/passwd for details of
the root user, and then sleep for 2 seconds, before listing running processes that reference root.
chaining commands DEMO
ex. ps aux | grep smbd | grep -v grep | awk ' { print $2 } ' | kill -9 combines different commands together to create a solution to a problem.
ps aux command
chained with grep to filter for a specific set of processes that match the term searched. Ex. Ps aux | grep smbd Def. Tool to monitor processes running
on your Linux system. Linux syntax or BSD syntax (most preferred. doesnt requiere dash (-) as prefix) ex. ps aux and ps auxf
commad: -v
To for example, to remove false matches. You can do negation option. Ex. Ps aux | grep smbd | grep -v grep (def. -v flag to print inverts the match. That
is; it will match only those lines that do not contain the given word.
awk command
Allows users to process and manipulate data and produce formatted reports. Ex. ps aux | grep smbd | grep -v grep |awk ' { print $2 } ' You can chamge
the number to differetn ones since they represent columns or combine them. Column one for name etc.
Xargs command
Builds and execute commands provided through the standard input. Enables us to take items delimeted by spaces, other characters and or returns. Can
be used alone or in combination. ps aux | grep smbd | grep -v grep |awk ' { print $2 } ' | sudo xargs -n 1 kill -9 Allows us to take each line of data or
each field of data and and do something with it.
174
1
1
195
1
176
1
1
177
1
179-181
1
180
1
182
1
182
1
183-184
1
video
1
185
1
1
186
1
187
1
187
1
187
1
187
1
187
1
kill -9 command
Processes, Linux
top command
killing processes, kill command, Linux
PID
Pipes & Redirects
Redirects , single > double >>
Passwd File
nologin, passwd file
Shadow file, passwd file, linux
scheduled tasks, cron
crontab command
cron
Package Managers, see apt-get, see yum
apt-get 'apt' command, packet manager
yum command, packet manager
Debian, Ubuntu
Fedora
packages, piece software linux
Hard terminates a process will be executed for each of the lines, terminating the processess one by one. Ex. ps aux | grep smbd | grep -v grep |awk ' {
print $2 } ' | kill -9
Views full list of running processes. By default it will only show processes under current user. To view a more complete list you need to add more
parametres like: Linux syntax or BSD syntax (most preferred. doesnt requiere dash (-) as prefix) ex. ps aux and ps auxf if you want the full list you
previously got with subprocesses and more detail on the parameters th eprocesses were launched with. 'top' command only sees the list of the processes
that uses the most resources.
Views running processes but only the ones that takes the most resources. To see full list of processes do 'ps' command.
Ex. Run 'top' to find the process you want to search. Look at the PID number and proceed with kill command. Ex. Kill 43630 Sometimes you may try to
kill a processs and nothing happens, the process may be unresponsive, in that case force -quit the process with kill -9 <<PID>> PID = your process
number ex. kill -9 43630
Process ID number, used to kill processes. Ex. kill 43630
Both let us flow data from one command to another, or into files. Let us chains commands, which is very extensible.
They take the output of a command and write it to a file. Similar to pipe but think output to a file instead of to another program. Two forms: A.
Overwrite, which uses a single 'greater-than' sign (>) It will create a file for th eoutput if it doesn’t exists, if if it does exists it will overwrite (replace)
with which is dangerous and one shoulb be careful of not losing data. ex. echo "hello one" > afile B. Appended or double redirect >> It will create the
file if it doesnt exists and if it does, it will append or add the output of the command to the end of the file making this form safer but each form has it
own time and place of use. ex. echo "hello two" >> afile
Key file on Linux system. Located /etc/passwd The X beside every user means where the password hash used to be. The 'nologin' in accounts refers to
them being accounts that cant be logged into bc those acounts are software installed in the system. Holds info about what user account exists on the
system. (on older linux systems it also stores each uses password hash; a type of one way encryption). On modern systems password info is no longer
stored in the passwd file, instead is stored in the shadow file /etc/shadow. The long random string on root user is the password hash that only the root
user sees. Attacker are very keen on attacking and trying to get access to the passwd file and shadow file.
The 'nologin' in accounts refers to them being accounts that cant be logged into bc those acounts are software installed in the system.
stores root user password hash (a type of one way encryption) only root user has access
Scheduling tasks to be performed in the future. Version on Linux is called cron, and all the scheduled tasks are stored in the crontab. To add/edit events:
crontab -e To view all sheduled events: crontab -l
place where all the scheduled tasks are stored. To add/edit events/edit: crontab -e , then select editor and follow istructions. To view all sheduled events:
crontab -l crontab structure: Minute Hour, DayofMonth Month DayofWeek Command can use wild card operator * to specify 'every' like every day
every month. Dashes (-) for date ranges. ex. 31, 59 * * * * /bin/date >> /home/user/test This will run on th e31st and 59th minute of every hour, on
every day of the mont, on every month and every day of the week.
Linux version of scheduled tasks is called cron. To add/edit events: crontab -e To view all sheduled events: crontab -l
Programs designed to simplify the installation of new software on Linux. Present on most modern distributions. Make installing software easy. Two
most common package managers: apt-get and yum.
Present on most Linux distributions that are based on Debian which is a popular Linux distribution that many other distributions are built on top of like
Ubuntu that’s why Ubuntu has the 'apt' package manager. Works by having a list of sources and these servers contain info on available packages,
download links, and version info. First thing you do: make sure available sources list is up to date: sudo apt update (run apt as root), then if you wan tto
upgrade software in your system: sudo apt upgrade, To install a program: sudo apt install cowsay, Run the program you just downloaded and if you
want to Remove it: sudo apt remove cowsay To access it either use 'apt' or 'apt-get' ^enables quick resolution and satisfying dependencies that are not
on melike with dpkg and yum.
Package manager found in Fedora and fedora based distributions. Similar to 'apt-get' but you don’t need to update the sources list yourself since it gets
updated automatically whenever you run a command that involves looking up sources. To upgrade all installed software: sudo yum update, To upgrade
only a specific program: sudo yum update cowsay, To install a package: sudo yum install cowsay, To remove a package: sudo yum remove cowsay
Popular Linux distribution that many other distributions like Ubuntu are build from it.
fedora based distribution, Linux distribution
a piece of software that isnt available in the package manager (missing software) we might find it 'packaged' for our Linux distribution as .deb or .rpm
depending on which type of distribution it was packaged for.
187
1
191
1
191
1
193
1
194
195
1
1
196
1
198
1
199
198
1
1
200
1
200
1
200
1
203
1
203
1
206
1
203
206
1
1
207
1
dpkg
.deb
.rpm
Building from Source code
SSH Security SHell
Shell command, see SSH Security Shell
NAT
keyfile
PuTTY
Search Engine
crawlers
search engines work?
Google search & keywords
Google Commands & Colons (filetype)(site)
Google Dorks
Google Quotes
Google calculator
Program needed to install .deb packages for Debian distributions or Debian based distributions like Ubuntu. Unlike with a package manager, dpkg
doesn’t install dependencies, so if the program you install requieres several other packages to be installed you will have to make sure to read which are
required and install them yourself. Ex. Sudo dpkg -i /home/user/cowsay.deb To list installed packages with dpkr: dpkg -l, To remove package: sudo
dpkg -r cowsay
A .deb file is a package that was generated for the Debian distribution or a Debian based distribution as Ubuntu. Is installed with a program called dpkg
for debian. Unlike with a package manager, dpkg doesn’t install dependencies, so if the program you install requieres several other packages to be
installed you will have to make sure to read which are required and install them yourself. Ex. Sudo dpkg -i /home/user/cowsay.deb To list installed
packages with dpkr: dpkg -l, To remove package: sudo dpkg -r cowsay
An .rpm file is a package generated for the Fedora distribution and Fedora based distributions. Just like dpkg, .rpm wont install any dependencies your
install needs, those are on you. To install: rpm -Uvh /home/user/cowsay.rpm To list installed programs: rpm -qa To remove programs: rpm -e cowsay
When your package manager cant find the package you need you can still install it as long as you can find the source code for the program. Google helps
too. Process vary depending on the software you are dealing with. Best to check the documentation before tryinh to install it, also read the install.txt For
most programs the procedure is: change directory into the folder that contains the source code. change directory into folder that contains source
code/program run: ./configure run: make
Is a way of letting people log into a Linux computer over the internet. Encrypted. Is terminal only, no GUI. Most Linux distributions come with it. Needs
a username and password to your Linux computer (and set up port forwarding on your router if you are behind NAT (Network access translation. Is a
way to map multiple local private addresses to a public one before transferring the information.), along with the IP Address. To log in use the ssh
command when in Linux or Mac OS. For Windows, download an SSH client such as PuTTY. The command to log: ssh username@1paddress Some
SSH servers need a keyfile (text file that contains an encryption key)instead of or as well as password. ssh -i /path/to/keyfile username@ipaddress
The command to log: ssh username@1paddress
Network access translation. Is a way to map multiple local private addresses to a public one before transferring the information.
text file that contains an encryption key, sometimes needed with or without a password.
Free an open source terminal emulator, serial console, and network file transfer application. Connects to a serial port.
They run software called Crawlers. Google (keyword-based search eng.), Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, archive.org
Search engines run software called crawlers. They start by visiting a webpage, looking at all the links on that page, making an index, of all the words on
that page, then the crawler will follow th enext links on that page and do the same. Eventually it will have indexed every publicly accessible page on the
web. Algorithms still unknown and they are all different but we do know if many pages that contain the keyword all link to one page, that page is the
authority on that search term.
Search engines run software called crawlers. They start by visiting a webpage, looking at all the links on that page, making an index, of all the words on
that page, then the crawler will follow the next links on that page and do the same. Eventually it will have indexed every publicly accessible page on the
web. Algorithms still unknown and they are all different but we do know if many pages that contain the keyword all link to one page, that page is the
authority on that search term.
keyword-based search engine, each word is taken on its own ans not as part of a sentence no matter the order. Google looks for all the pages that contain
those words and rank them all. The more keywords, the broaer the search and less relevant. Google will strip out some words like "I" "we" "the" but still
wont catch everything. Good example of a search ex. troubleshoot internet computer
A. google search a specific website 'site: ex. site:bbc.co.uk hacker' that is the 'site: website wordyouarelooking for' B. Narrow down a search to files of a
particular type: filetype:pdf fun that is: 'filetype: typeoffileyouarelooking wordyouarelookingfor'
Clever google searches that can be used to find content from people that never intended to be put online (this are called google dorks). Ex. Unsecured
security cameras, files with passwords, vulnerable software, documents that were not supposed to be shared with people. Google has indexed all those :)
using quotes in google vs. "using quotes in google" Quotes will give better exact results, refined search (less hits which is good) and same exact order.
The other way gives you separated hits for each term.
google search bar can be used as a calculator too.Type ex. 256*88 or sqrt 100 results will appear on a digital calculator. or just get to the blank calculator
by searching 'calc' on seach bar
207
1
207
1
208
1
211-213
1
214
1
214
214
214
214
218
1
1
1
1
1
218
1
218
1
219
1
1
222
1
224
1
226
1
calculator, google
Alternative Search Engines
Troubleshooting, Google
web servers, see generic web server, see
custom web server
HTTP Protocols-Steps
HTTP Protocol in Depth
HTML
JavaScript
PHP ?php
Client Side vs Server Side
Local Storage
Cookies up to 4 kilobytes in size
URI
google search bar can be used as a calculator too.Type ex. 256*88 or sqrt 100 results will appear on a digital calculator. or just get to the blank calculator
by searching 'calc' on the seach bar
All search engines are dfferent, different algorithms for displaying results which they wont share with others. Same term under two different seach
engines will give different results which could be a good thing if you are struggling finding some info.
Google has lots of info on how to solve IT issues that others have experinced like error messages etc.
Software applications that accept and process requests according to the HTTP protocol. In sum, it send HTML back to the browser, which will use that
HTML to render the web page. Two main types of web servers: Generic web server & Custom web server on p. 234
Hypertext Transfer Protocol. See steps at p.274 Computer A sends GET to(to GET file) web server: GET /test HTTP/1.1 plus it also sends some headers
to give some additional info to web server. Then the web server responds with a code 200 OK meaning the file exist and it can be displayed. HTTP/1.0
200 OK The web server also sends som eheaders of its own, giving the web browser some extra info. And finally the data in th efile is sent.
226
1
230
1
228
1
234
1
274-275,
236
Browser makes requests to web server, and web server returns some kind of response; this is what powers the web. There are two kinds of response:
response header and response body. Split into Response Header and Response Body. Response Body contains retrieved data. Ex. If you send a GET
236, 274request to 'http://fake/about.html' then the reponse body would contain the contents of 'about.html' Response Header will contain metadata about the
275
request (data about other data. Ex. Time stamp of the response, web server software that sent the response. Etc), including usually valid requests types
for that page, the response lenght, date, name of server, type of server being used, etc List is long.
static markup language, is a way of describing data. Its not a programming language. It uses tags, enclosed in "less than" and greater than like
<html></html> First tag is the opening tag, the second the closing tag. HTML is static on its own , it doesn’t change based on user input. Needs
238
something that generates HTML individually like PHP to make a log in page for example or anything interactive.
Is a Client side programming language designed to run inside browser. It can be used to makes changes to HTML even after it has been loaded onto the
page. JavaScript code goes inside Script tags. <script>java code </script> You can also leave it in an external file and reference it which is neater. You
239, 241
can see JavaScript if you view the page source; this is why JavaScript is not good for password protecting pages, people will see the password in the
code.
Server side programmming language meaning user doesn’t get a choice as to what happens, even when they can see the code source they would not be
able to spot the PHP code. PHP generates HTML and sends it to the clients browsing page. PHP is executed by the web server. To run PHP we need the
241
web server to support it.
Client side like JavaScript the user has the control of it since users can see code, not good for security or password pages. vs. There are many server side
programming language. Ex. PHP where users have no control, even if they see the source code they cannot spot the PHP code. Great for password
241-242
pages. Server side languages are the real heavy lifters of the internet. They are the reason we can have e-commerce, and a variety of other interactive
sites. Details of your log in info will be saved by a server-side language into a database.
Aside from cookies, Sites can also store files on your computer (up to 5MB) in the browsers local storage. Is intended to provide much more powerful
and sizeable storage to applications based on how the internet and web applications hav edeveloped. Can be used to store and track store data. Also often
243
used in powering many of the richer web application interactions one might have. This need to be cleared in your computer just as cookies.
Tiny file a web server creates on a visitors computer, it can hold any small amount of data depending on what the developers of that site want to store,
most common use is to save a unique identifier called session ID, after log in to page is complete, they have an expiry date (this is why sometimes you
can log in without putting you log info after closing a page, commonly used to track you in differet ways: A. Only the domain that gave you the cookie
can ask for it back and for the most part sites cant know which other sites you commonly visit (is an individual thing), HOWEVER; the exception is B.
Adversiting: adverts on websites are embedded to the companys web server, so the store gave you the cookie from a different site you visited, that tells
them the kind of pages ypou visit and therefore can ask for that cookie and know where you collect it. Sites also track using the local storage on your
computer. See Local Storage
Uniform resource Identifier. Facilitates interactions between and among internet and protocols. Ex. GET request combined with / or /file.text
243
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Port (def. p. 257)
generic web servers, see web servers
custom web servers, see web servers
Requests, HTTP Protocols
GET, Requests, HTTP Protocols
HEAD, Requests, HTTP Protocols
POST, Requests, HTTP Protocols
PUT, Requests, HTTP Protocols
DELETE, Requests, HTTP Protocols
Response, HTTP Protocols
metadata, HTTP Protocols
Response Codes, HTTP
HTTP/1.0
typically web servers will listen on either port 80 (associated with web servers) (HTTP Unencrypted) or 443 (HTPPS Encrypted) These are default ports.
Web servers requiere slighly higher permissions to bind to ports like :80, on most OS lower ports below 1024 requiere levated permissions to bind. Web
servers can be configured to listen to non-standard ports but that means anyone who needs to access them will need to put the port number at the end of
the domain as such: https://some-fake-domain:8008 A port is a communication channel for applicattions running on the OS to listen to. The port is
needed to separate communications destined for the web server application from other communications that the server might also need to receive. POrts
are numbered between 0-65535 (2^16=65536 counting cero total 65535, but the are 65536 but 0 port is not used) No two applications on the computer
can listen to the same port. Once an application is listening on that port, it's known to be bound to that port. Not to get confused: The TCP protocol has
their own port range which is separate from other protocols, if you have TCP port 80 and UDP port 80, they might have the same number but they are
different ports altogether which is ok.
First of the two types of web servers (other is custom web servers). easy to set up, no programming knowledge, most internet run on them and is not
going to change (these are multi-purpose applications that serve files that exist in a certain folder on the OS.) Most popular: Apache and Nginx, both are
configured to use a folder as the web root; that folder will contain the files needed to run the website. The folder should include an index file named
either index.html or index.php: this is the file that is sent when a request is made to '/'. Ex. visit https://www.google.com/ you will get the index page at
the top level of the web root directory.
these are typically programs that are purpose-built to serve/run a particular site. ex. NodeJS They don’t serve files directly from a folder like generic web
servers, instead the routes are programmed into the software. The code of the webserver will define what happens when a user tries to access a certain
path or route. It may say, ex. user is browsing '/help' then send this HTML as a response. Often used by large or complex web applications bc they grant
more freedom than generic servers like you can add or ignore features that are not needed but the downside is that you need to be a programmer to to
serve even a simple website using this method.Frameworks such as NodeJS have made building a custom server common and relatively easy.
Verbs and Commands: GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE Request can also contain other info than just the page being requested like user agent (id
string used by browser to tell site which browser is being used to view page), date, content type (in the case of POST or PUT requests), and much more.
Get request asks to retrieve a specified resource. Ex. Visiting this page: 'https://some-fake-domain.fake/about.html' you are asking to retrieve the
'about.html' file from the web root. Retrieves the base or default page at the root of a website. Ex. GET request combined with URI (uniform resource
identifier to facilitate communication between protocol and web server) / or /file.text
A HEAD request asks to retrieve a specified resource, but without the response body. Retrieve only the metadata without the data. This type of requests
is not common and is more often used when developers are testing their site.
A POST request is used to send data to the web server without expecting anything back. Commonly used by HTML forms.
A PUT requests is used to ask the web server to store the data sent in the request at the path requested. If the about.html file exist it will overwrite it. Not
common. It assumes you have the permission to put files in a location. A PUT request is used to create files on a web server if authorized. Creates a new
resource or replaces a representation of the target resource with the request payload.
A DELETE request deletes the resources specified in the request (if authorized). Not commonly seen.
Split into Response Header and Response Body. Response Body contains retrieved data. Ex. If you send a GET request to 'http://fake/about.html' then
the reponse body would contain the contents of 'about.html' Response Header will contain metadata about the request (data about other data. Ex. Time
stamp of the response, web server software that sent the response. Etc), including usually valid requests types for that page, the response lenght, date,
name of server, type of server being used, etc List is long.
data about other data. Ex. Time stamp of the response, web server software that sent the response. Etc
200: ok, I will provid eyou with the response to this request. 302: Found, but redirect over here as this resource has moved. 404: File not found, this
request doesn’t match something I can serve. 500: Whoah, something went wrong! Internal server error. (this one commonly happens if you are trying to
run server-side code and a flaw was triggered that was not handdle.) Theres a ton of codes more.
Slower, easier for humans to read-less secure all that lower compared to Binary HTPP/2.0 we can see now. Has been around the longest, has a number
of inneficiencies. Is text based ASCII protocol so you can read it but not the most efficient way for computers to communicate when a binary can yield
much more info packed into a short space. HTTP 2.0 decreased that delay/latency
234, 257,
259
1
234
1
234
1
236
1
236
1
236
1
236
1
236
1
236
1
236
1
236
1
237
1
237
1
HTTP 2.0
HTTP/3.0
TCP connection
zsh shell
powerlevel10k theme, zsh shell
Pure theme, zsh shell
network hardware
IP Addresses
MAC Addresses (Media Access Control or
Hardware Address)
Data
Packets
Protocols
TCP Protocols All about reliability), TCP
handshake
UDP Protocols
more advanced than HTTP/1.0, it has less latency/delay. So packages are hard for us to read but faster for computer faster by reworking the protocol,
http header compression, pipelining of requests, multiplexing multiple requests over a TCP connection, and fixing the head of line blocking issue with
http/1.0 (this is where you have to wait for the first part og the communication to complete before you can do more.) It can be combined with other
protocols to provide encryption and verification to secure in transit.
Will have some active implementations turning up but it has not shifted to default or widely available in browsers yet.
p.237 mentioned regarding http 2.0, p.269-271
Alternative to bash shell. Has a lot of stuff to make your shell pretty and more user friendly, even easier to read with all the color and fonts and patterns.
is a theme inside zsh shell. Customatization od formatt for how the prompt area is presented. There is also 'rainbow' and 'pure' You get the choice to pick
during zsh installation.
is a theme inside zsh shell. Customatization od formatt for how the prompt area is presented. There is also 'rainbow' and 'powerlevel10k' You get the
choice to pick during zsh installation.
Hub, NICs, Routers, Switches
Identifies your computer on the network and allow other computers to on the network to find your computer. IP addresses vary dependig on version.
(IPv4, IPv6). Each (Network Interface Card) is assigned an IP address when it connects to a network. Two types of IP addresses: Public and Private,
sometimes called external and internal. ex. 192.168.0.77 An IP address has 2 parts: Network Identifier and Host Identifier.
ex. 34:13:65:76:09:86 Used to identify computer on a local network, they stay the same, meant to be globally unique but no guarantee-if two computers
on the same network and same mac address connectivity issues would occur (hence why address is unique), the MAC address is burned into the NIC
when produced. They enable a switch to know which cacle to send the info down in order to send data to a particular computer. They are used together
with Private IP addresses (this can change but not the MAC address).
Payload
Is a unit of data transmitted over network, encapsulated into packets, before transmittion. Contains not just the data (payload), but also other info like
MAC address and destination IP address (in the packet header-where is data going). Typically quite small pieces of data, large have to be split into
several packets before transmittion. maximum size depends on several factors: protocol used in packet, but typically maximum of 1500 bytes - 65535
bytes (64 KiB) Units of data with headers applied to enable us to control state, routing, and other properties. They are what we transmit & receive.
5 types of protocols discussed so far. Set of rules that are undestood by two parties, and enable them to connect to each other and exchange info. Set of
rules which governs how to or more parties interact with one another. Interaction between computers also requieres protocols, these are rules which
define the format of data. Additionally, some protocols have checks in place to make sure the data was transmitted successfully, to make sure the data
was not corrupted in transit, an dother such rules. Two key protocols are: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) & UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
Also: IP Protocols, HTTP protocols, and FTP (file ytransfer protocol for uploading and dowloading fies to & from an FTP server.
(Transmission Control Protocol) In OSI Model its on the layer 4 and 5. Widely used on the internet. Designed with the reliable delivery of data in mind
for common tasks like web browsing. Protocol involves a connection set up called "TCP handshake" (and sequence numbers) which prepares two
computers to talk to each other, after handshake is performed, the data is sent between computers. After the TCP connection is done, the TCP teardown
closes the connection. If for some reason it cannot torn down gracefully, one part of the connection can terminate abruptly by sending an 'rst' (reset)
packet to terminate the connection immdiately. This protocol includes measures to re-transmit data lost in transit, or corrupted en route. Downside:
comparatively slow transmition. Not to get confused: The TCP protocol has their own port range which is separate from other protocols, if you have
TCP port 80 and UDP port 80, they might have the same number but they are different ports altogether which is ok. TCP is a little heavy = slower
(User datagram Protocol) Key to many applications that require fast data transmittion at the expense of reliability (does not need connection handshake,
doesnt detect packets missing, never ask for re-transmittion, if data is corrupt it will just ignore it. Commonly used in video chats, VOIP (Voice over
internet protocol, aka Voice chat), online video games, an any other applications that care more about speed than reliability. Not to get confused: The
TCP protocol has their own port range which is separate from other protocols, if you have TCP port 80 and UDP port 80, they might have the same
number but they are different ports altogether which is ok. Theres NO connection handshake, no teardown, udp doesnt care if you receive the package
or not, it just sends it. Theres no conversation between computers. UDP alone doesnt send error messages, it uses ICMP. In OSI model it is on layer 4
and 5.
237
1
237
237
1
1
215
1
215
1
215
1
249
1
253, 265
1
253
1
254
254
1
255, 273276
1
256, 268271
1
258,272
1
Topologies
Switches, Networking
Hubs
Routers
NICs (Network Interface Card)
Private IP Addresses
NAT - Network Access Translation
RFC 1918
Public IP Addresses
Network, Computer network
LAN
WAN
WiFi
Ethernet cable
Star topology
The way a network is physically laid out. Several types of network topologies: token ring, ring, bus, and star topology (recommended to set up home
networks/and most common). Star: this is where each computer in a network connects to a central point, such as a switch. Pros, is easy to mantain, any
computer or cable in the network can fail and the others would not be affected, but if central point fais thats a different story. Bus topology: all
computers are connected by the same ethernet cable. At the ends of the ethernet cable lie line terminators which discard any data that has not been read
by a computer. Not a common topology as only one computer can communicate at any one time.
Used in the center/middle of a star network topology, is the device that connects computers together. Many computers can be connected to it, it will
receive all data on the network and decide which cable to send the data through, based on which computer the information is destined for. data sent over
wires. See image book
Similar to Switches. Connect computers to a network together, it receives the data but it doesn’t know wich computer to send it to so it send it to every
computer connected to the hub. Then is up to the computer if discard or receive the data. Hubs were used before switches were common but still used
today in one capacity. Wireless access point is built into the router making them wireless routers, a wireless hub can only broadcast data ovre radio
waves, theres no way to direct data to only one device, all wireless access points are a hub. See picture p. 250
Device that connects two networks together, commonly this will be connecting the LAN to the internet but it can be used to conect any networks
together, the router will make the decision about which piece of data needs to go to which network. Most include switch funcionalities but number of
ports is limited. To add more ports you can plug another switch to one of the LAN ports on the router.
Piece of hardware attached to a computer (usually internally), allows the computer to interface to a network. A. Computer with an Ethernet port has a
NIC inside to provide the means to connect to a network. B. Computers with wireless built in will have a NIC inside that provides the appropiate
hardware for connecting to a wireless network. C. Computer that can use both wireless and ethernet, have 2 NICs. There are also UBS with an external
NIC, useful when computers dont have either wireless or ethernet capability.
Is assigned to your computer on the LAN (local network). Private IP addresses have to fall within certain ranges and are only accessible to computers on
the same LAN. People on different LAN cannot access your computer using the IP address. Each Private IP address must be unique on the LAN, if not,
one computer wont have access to the network.
The ability to share an IP address is handled by something called Network Address Translation (NAT). Ex. In Public IP addresses. (Other similar: RFC
1918 but this one for private IP.) Mascarades address when you wan to go to external network with non RFC IPs.
An RFC 1918 address is an IP address assigned by an entreprise organization to an internal host (LAN). These IP addresses are used in private networks
which are not available or reachable from the internet. Excusive private addreses for local networks, never to be routed to the internet: *192.1680.0/16:
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 *10.0.0.0/8: 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 *172.16.0.0/12: 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
A public IP address is internet facing. In most home and small business network set ups, the entire LAN will have only a single public IP address, which
is shared by all computers in the LAN. The ability to share an IP address is handled by something called Network Address Translation (NAT).
A computer network is a set of computers connected or networked together. Internet is the largest network in the world which is an example of a Wan
(Wide Area Network) which is a network covering covering a large geographical area. Smaller networks like office or school networks are called LAN
(Local Area Networks). Computers=ANYTHING with a processor in it, even a kettle. Computers typically connect over LAN using an ethernet cable or
WiFi (radio signals), the LAN will have a router to connect to the internet.
Smaller networks like office or school networks are called LAN (Local Area Networks). Computers=ANYTHING with a processor in it, even a kettle.
Computers typically connect over LAN using an ethernet cable or WiFi (radio signals), the LAN will have a router to connect to the internet.
Internet is the largest network in the world which is an example of a WAN (Wide Area Network) which is a network covering covering a large
geographical area.
radio signal to connect to internet using router
color of cable may differ but is cosmetic only, s=doesn’t indicate anything about the cable. Use witth a router to connect over the internet. LAN. At the
ends of the ethernet cable lie line terminators which discard any data that has not been read by a computer. Bus topology is not common as only one
computer can communicate at any one time.
logy (recommended to set up home networks/and most common). Star: this is where each computer in a network connects to a central point, such as a
switch. Pros, is easy to mantain, any computer or cable in the network can fail and the others would not be affected, but if central point fais thats a
different story. See image in book
248
1
249
1
250
1
250-251
1
251-252
1
253
1
253
video
253
1
247
1
247
1
247
1
247
1
247
1
248
1
Bus topology
IPv4, Internet Protocol Version 4, see
Network Address Tranalation (NAT)
IPv6, Internet Protocol Version 6, see
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Subnets, sub network, subnet mask
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Identifier, IP address
Host Identifier, IP Address
CIDR- Classless Inter-Domain Routing
Private IP Ranges
loopback address, local host
local host, loopback address
TCP Reset ('rst')
TCP Teardown
TCP Transmission
TCP Handshake
Bus topology: all computers are connected by the same ethernet cable. At the ends of the ethernet cable lie line terminators which discard any data that
has not been read by a computer. Not a common topology as only one computer can communicate at any one time. See image in book
IPv4 is 32 bits. Most familiar and so old. Only 4 bytes long. Not enough addresses as of today (2^32=4,294,967,296) Problem: we have used them all
addresses. Format: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx ex. 192.168.0.1 Uses Allows NAT (addresses turned private only in local networks) NAT which makes for a
decent firewall too since you have to set a route forwarding rule to allow outside computers connect directly to you.
Newest protocol to replace IPv4, has long addresses, brings a lot of complexity with rules to shorten them. 16 bytes (128 bites) long with 2 bytes
between each. Ex. 2001:0db8:0000:0000:ff00:0042:8329 With shortening rule: 2001:db8:ff00:42:8329 Lacks NAT which makes for a decent firewall
too since you have to set a route forwarding rule to allow outside computers connect directly to you. With IPv6 a lot of computers will be exposed to the
internet sinc ethere is no NAT.4
rovides ways to logically organiza groups of systems in networks, and to enable routers to provide connectivity between these groups. Often seen in local
networks at large organization to assign a subnet to each department for example. Minimum you need one subnet. You can determine how many
networks and how many hosts you have.
Designed to delay the problem of running out of IPv4 addresses. Bunch of addresses designated as private on local networks across the globe-avoids
clashing between addresses solving that issue but still the problem is now that those computers cannot communicate since you need at least one public IP
address for the network. That public IP address can be shared accross every computer on the network. The router will be then responsible for converting
the packets that come in from public IP addresses to private ones and vice versa. It was so effective that even whe IPv6 came, many people refused to
change and stuck with IPv4 and NAT. NAT which makes for a decent firewall too since you have to set a route forwarding rule to allow outside
computers connect directly to you.
IP Address consists of two parts: Network Identifer which identifies the netwrk, and the host identofier which identifies the individual computer
connected to that network.
IP Address consists of two parts: Network Identifer which identifies the netwrk, and the host identofier which identifies the individual computer
connected to that network.
Shorthand way of writing a submask. Ex. 192.168.0.0 in binary will be 192.168.0.0/16 because we are told 192.168 are the network id. Meaning it has
2 spaces (8 bits + 8 bits =16 bytes, hence /16) (You need to know the Network Identifier first) Another examples: 192.168.0.0 = 192.168.0.0/8 if
network identifier is 192 only (255.0.0.0) See notes in book. Number after slash (/) is number of bits for the network identifier.
Excusive private addreses on IPv4 for local networks, never to be routed to the internet: *192.1680.0/16: 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 *10.0.0.0/8:
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 *172.16.0.0/12: 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 IPv6 doesn’t need any, it creates a difficult search when looking for entore
address range of subnets looking for a device for example.
in IPv4: computer sends data to itself with 127.0.0.1 In IPv6: ::1
in IPv4: computer sends data to itself with 127.0.0.1 In IPv6: ::1
If for some reason it cannot torn down gracefully, one part of the connection can terminate abruptly by sending an 'rst' (reset) packet to terminate the
connection immdiately.
When connection ends. Connection that wants to finish connction sends a 'fin' packet (finish) with the current sequence number. ACK is not requiered
to terminate connection. Computer B rresponds with 'ack' packet and a sequence number wich is Computer A sequence number incremented by 1.
Computer B sends a 'fin/ack' packet containing sequence number and ack number which is Computers A sequenc enumber incremented by 1 only when
such has previously changed, if not remains the same like in the example of p. 270. Last, Computer A will respond with 'ack' packet containing ack
number which will be computers B sequence number incremented y 1. An RST packet is only used if something goes wrong with the protocol and it
doesnt end gracefully. A graceful teardown ends with a ACK packet.
Data message is added to the ACK number in bytes. See ex. hello world p. 269-270
Protocol involves a connection set up called "TCP handshake" (and sequence numbers) which prepares two computers to talk to each other, after
handshake is performed, the data is sent between computers. Computer A sends packet to Computer B with the SYN (synchronize) Flag enabled to the
computer it wishes to connect to. Packet contains a sequence number which is initially ramdomly generated. Computer B sends back a packet with
[SYN, ACK] flag set with a random generated sequence number and an acknowlegement number which is Computers A sequence number plus 1.
Computer A will then respond with an ack flag packet containing the sequence number computer B sent plus 1. After this connection has been
established. By monitoring sequence and acknowledgement numbers on either side you can tell if any data packet is missing and ask to be retransmitted.
248
1
262
1
264
1
265
1
263
1
265
1
265
1
266
1
267
1
267
267
1
271
1
270
1
269
1
269-271
1
SYN FLAG, TCP Handshake
ACK FLAG, TCP Handshake
TCP Three Handshake
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
Code 200 OK
SFTP
webmail
SMTP
Email
EHLO ESMTP
SMTP Protocol
MAIL Command, SMTP Protocol
RCPT, SMTP Protocol
DATA, SMTP Protocol
POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3)
Synchronize. Part of the process when the two computers are establishing communication during TCP handshake. Sent by computer A along with a
269
random sequence number.
Acknowledge. (The acknowledgement number is incremented by the number of bytes received in transmittion) Part of the process when the two
computers are establishing communication during TCP handshake. Sent by computer B to answer Computer A request. Computer B sends back a packet
with [SYN, ACK] flag set with a random generated sequence number and an acknowlegement number which is Computers A sequence number plus 1.
269
Computer A will then respond with an ack flag packet containing the sequence number computer B sent plus 1. After this connection has been
established. By monitoring sequence and acknowledgement numbers on either side you can tell if any data packet is missing and ask to be re-transmitted
when you check the Data message is added to the ACK number in bytes. See ex. hello world p. 269-270
[SYNC] seq=0, [SYN, ACK] seq= 0 ack=1, [ACK] seq=1 ack=1
270, video
used for uploading and downloading files to and from an FTP server. HTTP protocol tries to put all info together in one GET ,one time. But FTP is
different, is more of a back and forth conversation between the computer and the FTP Server. Password is sent as clear text with no encryption which is
273
its downfall. That why mnay poeple are using SFTP and other variants now. Ex. of a log in FTP Server p. 276
HTTP protocol: Web server responding to GET file that file exists and can be displayed.
275
Variant of FTP protocol with security. FTP sends password as clear text with no encryption.
276
Allows remote email access without having to install an app. Ex. Google, yahoo
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. Port 25 by default.
Text sent from one email server to another and placed in folder Inbox. Inbox syncs with computer (or access through a webmail client like the Gmail
web interface) No encryption when sitting in inbox, and until recently now we do have encryption for when it's in transit d/t most modern servers
supportig STARTTLS. Outgoing mail server= the one that sends your email, Incoming Mail server= receives your email. Process of sending email in 6
280, 369
steps p. 280. In the process of sending email there are 2 protocols working: SMTP (Simple mail transfer protocol) which is the most common, and a
protocol responsible for syncing the inbox like POP3, IMAP, or Exchange. Some email servers support all 3 but it depends on email server set up.
250 codes commands to work on STMP to send email between servers.
Most common and old on email servers for sending/transferring emails. T is for transfer. Protocol you need to transfer email/send and not retrieve or
read. Software includes: Microsoft exchange, Postfix, Sendmail, and Qmail. SMTP is used to send and receive email but doesn’t provide services for
users to get access to their inbox. Typically runs on port 25. Connection oriented text based protocol, similar to HTTP protocol. Each connection can be
re-used to send multiple emails called SMTP transactions. The transaction consist of 3 commands: Mail (establishes return path or return address,
bounce address, and sender) RCPT (establishes recipient), and DATA (start of the message, contaisn header with metadata and an email body with
email content). You dont have to log in to send email since authentication is not part of SMTP however, these days every server supports some form of
authentication, but when one log in there is nothing to stop the person to put whatever they want in the MAIL FROM (that part of the command). SMTP
is responsible for both 'sending &receiving'. Very human readable protocol compared to many.
The MAIL command establishes the return path (return address), bounce address (where to send error message if mail delivery fails), sender, among
other things.
The RCPT command establishes the addres of the recipient. You can use this command multiple times to establish multiple recipients.
The DATA command signifies the start of the message text. The DATA section of an email consists of an email header and email body. Header
contains metadata about the email, and the email body is the contents of the email itself.
Retrieves email from server but doesnt synchronize them, once retrieved is deleted from server. Responsible for syncing an email folder from the email
server to your computer. Provide a way for users to get to their inboxes and interact with their email, and used in collaboration with SMTP to
send/receive. oldest protocol, only few people use it, surpass by IMAP model. Email is stored on the email server until you sync with the email server.
After you synced with the email server then the email would be deleted from email server. Same concept as picking mail from the post office; you get it
and now they dont. Provided limited space on email serversat a time. Downside also was risk of losing emails if you lose hard drive and had no back up,
and bad for organization since you could end up with some emials on different computers or devices.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
282
1
281, 369370
1
281, 382
1
281
1
281
1
283, 369370
1
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
EAS (Exchage Active Sync)
Email Server Retrieving/Read HTTP
Email Server, which is better?
MAPI Messaging API
Microsoft Exchange
Email Spoofing (forging)
Asymmetrical cryptography
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)DNS TXT
Records
ICMP echo code
ICMP time exceeded
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)
Wireshark
Port, Ephemeral
Port, TCP
Outlook
TTL
Retrieve, read emails from server. Can synchronize with remote server for multiple email clients so email appears up to date in different locations. Most
common in use today, replaced POP3 by solving the issues that one had. Responsible for syncing an email folder from the email server to your
computer. Provide a way for users to get to their inboxes and interact with their email, and used in collaboration with SMTP to send/receive. The
mesages remain on th eserver until the user secifically deletes them, and in addition the IMAP server can track state on each email ex. unread, read).
Sync messages state accross devices and support server side search.
Protocol by Microsoft. Run in Microsoft Exchange servers. See Microsoft Exchange
Lots of email providers also provide e-mail access capabilities over HTTP and there are native mobile apps which also implement their own
synchorization protocols. They often are an alternative transport for IMAP like capabilities.
IMAP and SMPT are a very common pairing more so than POP3 these days for its synchronization features. Exchange and Web based clients are also
extremely popular these days. It depends on knowing their capabilities.
A proprietary Microsoft protocol wit lots of IMAP similarities designed to enable the state synchronization with a remote Exchange server so that a
number of Outlook clients can be up to at with their state of their mailbox data. Also has provisions for calendar, contacts, synchronization and other
features. Is built this way so that enterprises can provide the rich workplace management features that extend beyond email.
This one is not a protocol but a server sofware that implements many different protocols.In the beginning it only supported MAPI Protocol by Microsoft,
nowadays it also supports IMAP, POP3, and EAS (Exchange Active Sync). Is set similar to any other server software that implemets IMAP Protocol if
not better. Downside: restricted to Windows, cannot run an exchange server on Linux. Responsible for syncing an email folder from the email server to
your computer. Provide a way for users to get to their inboxes and interact with their email, and used in collaboration with SMTP to send/receive.
Pretending to be someone else. Anyone with access to an SMTP server (even one they set up themselves) is capable of sending an email with any FROM
address. Even though there is authentication on all modern SMTP servers, that only controls wether you are allowed to send emails through that SMTP
server. Once allowed access, you can set any FROM address you want. SPF and DKIM are two options used today to try to figth email spoofing.
Manipulate headers to increase click rate. How emai clients stop this? Using SPF, DKIM, DMARC; authentication mechanisms on headers to make sure
they know where the header and email just came from.
has 2 keys: public and private key.
In the DNS configuration for our domain, you put in a text record that is a list of all the IP addresses of mail servers allowed to send emails from your
domain. When a mail server receives an email that says is from your domain, it will look up the SPF record for your domain and compare the IP address
of the mail server that delivered the email against the list of valid IP addresses. If is not on the list is forgery.Problem with this one is whe you outsource
your email hosting services to companies like Google; if you specify in your SPF record that Google is allowed to send emails from your domai, then
anyone with a Gmail account can bypass your SPF protection. Anyone on the same server can impersonate you. To avoid email spoofing.
type 8 0 code packet. Ex. With Ping application to know if host is alive and the time it takes to receive the response is the latency.
Type 11 0 code sent by a gateway (router) to a system that sent a packet, where the TTL (number of hops the packet can travel before its considered lost
and gets discarded) of that packet has expired.
Similar to SPF Framework to avoid email spoofing but one level more advanced. You put a public key (asymmetrical cryptography has 2 keys: a pubic
and a private key) in your text record in your DNS settings for that domain. When email server sends an email legitimately, it will sign that email with
your private key and when the receiving server gets the email it will validate that signature using the public keys in your DNS records. Most email hosts
are able to have separate private keys for every domain they host email for to avoid the issue with SPF which is anyone on the same server can
impersonate you.
Tool to monitor the network connections, deconstruct packets, make sthings easier to see and graphical. *Use of follow functionality.
52892, 52896 Ports above 1024. On Windows ports above 5000 are dynamic or Ephemeral.
8081
Email client.
TTL (number of hops the packet can travel before its considered lost and gets discarded)
283, 369370
1
284
1
371
1
371
1
283, 370371
1
283, 370371
1
285, 375
1
285
285
1
299
1
299
1
285
1
277, video
1
1
1
370, 372
299
1
ICMP Protocol (Internet Control Message
Protocol)
TLS
STARTTLS
SPF How it Works?
DMARC
Out of band check
How DKIM Works?
DNS (Domain Name System) glue holds
internet together
TLD - Top Level Domain
Authoritative Name Servers
Catching
Is a protocol designed to transmit error messages and operational information between hots on a network. Used for network troubleshooting and sharing
network topology information and errors. Technically in a class with UDP and TCP, but differs in that it does not communicate data and isnt typically
used in end user applications. Used almost exclusively by network devices such as routers; in few exceptions such as the PING application (to know if
host is online or not). There are many many ICMP types codes available. 'Destination unreachable' message with UDP. But UDP alone doesn’t send
299
error messages. Each ICMP packet consists of a 'type' & a 'code' to describe packet purpose. ICMP type 8 code 0 packet (echo request packet) that PING
uses is to determine host available or not. ICMP type 11 code 0 (ICMP exceeded packet) sent by a gateway (router) to a system that sent a packet, where
the TTL (number of hops the packet can travel before its considered lost and gets discarded) of that packet has expired. (ICMP Response packet: ICMP
type 0 Code 0 packet as response to echo request packet.)
TLS certificates, encrypted. Which gives HTTPS capabilities. Ex. Lets Encrypt.com CertBots company renews them anually.
video
Supported by most modern email servers, uses similar kind of encryption used to secure HTTP to encrypt the email while in transit over network.
280
See writing on page 286 and see SPF
286
Domain Based Message Authentication. Reporting and Conformance is an email authentication protocol designed to give email domain owners the
ability to protect their domain from unauthorized used, commonly known as spoofing. DKIM combined with SPF and integrated to DMARC as a
287
framework significantly reduces the chances of spoofing when sending and receiving email.
server s way to verify emails header information for the domain and to validate data. See How DKIM Works?
287
Domainkeys Identified Mail. Email is sent, a private key held by the sending server is used to sign the message, and a hash is generated by the header,
and a portion or all the message body. Header has values like: d: the domain signing the message (ex. sans.org, b : The signature of the message
produced using the private key of the sending server; unique to the message, bh : The hash of the message that can be validated. Message arrives at
recipient server, headers can be extracted for verificatoin by using out of band check. The system will query over DNS to get the public key to verify
287
signature. The domain key selector is a value that enables multiples DKIM entries to exist for a domain, for ex. for different senders like SES, your own
mail server or O365. A query is made to: selector#. _domainkey.domain This returns TXT record that contains a 'p' value. This is the public key that
can be used to validate the signer of the message.
Hierarchical. Relies on one DNS server to the next all the way down to the one that knows the answer for that specific domain. Good in case of outages,
it doesnt affect all internet. DNS is responsible for translating your website name (domain name) into an IP address the computer can understand. Every
computer must have a DNS server configured in their network settings. Home networks:A. Your service provider wil give you one or pre-setup router
router with it. Router will use DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to tell every computer to use that DNS service. If router doesnt support
290, 300,
DHCP you will need to find a DNS server (Google and OpenDNS) have one. B. In a busines environment, you may have a separate server that supports
372-373
DHCP in which case the DHCP srver on the router will be then to be disabled to avoid clash. Type domain name in browser, computer sends request to
DNS server in your network settings for that domain, DNS server will give browser matching IP address, finally browser sends the HTTP request to IP
address on port 80 (uncrypted) or 443 (encrypted) (HTTP ports). DNS is CRUCIAL for routing correctly emails.
DNS (Domain Name System) is Hierarchical. Relies on one DNS server to the next all the way down to the one that knows the answer for that specific
domain. Good in case of outages, it doesnt affect all internet. TLD indicates which DNS server to query first. TLS is the bit at the end of the domain
name. ex. google.com TLS = com ex. google.co.uk = co.uk For google for example, you will query the name servers for com first. That name server
wont know the IP address for google.com you are looking for but it will know which name server you can ask to get to your answer.
Is the server the TLD sends you first, is the authoritative name server that points out where to start the chain around the servers to get the IP. Ex.
192.168.0.6 could be the authoritative name server for our 'com' TLD example from the domain Google.com Has the final say where the domain points.
If a name server makes a query and discovers the IP address a domain points to, it can cache the result for a time, future requests for that domain will
use the saved value to save from the name server having to make the request over time. Of course it will erase periodically and will have to get the info
again but caching provides a measure of efficiency so that not every request to a domain has to be sent to the authoritative name server each and every
time.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
291
1
292
1
293
1
Forward & Reverse Lookups, DNS
Recursive & Iterative Lookups, DNS
DNS Records
DHCP
A Record, DNS Server
AAAA Record, DNS Server
CNAME Record, DNS Server
MX Record, DNS Server
NS Record, DNS Server
PTR Record, DNS Server
TXT Record, DNS Server
Most common usage of a DNS lookup is a forward lookup: Translating domain name to IP address. Is an odity since we don’t have authoritative name
servers for IP addresses but we can do a reverse lookup= Translate IP address in to domain name. For this we have to reverse the IP address like
192.168.0.1 = 1.0.168.192 By performing a DNS query on this domain, we can look up any domains which are linked to that IP address. Of course,
generally speaking each domain must have reverse DNS configured by adding a particular DNS pointer record to the authoritative name server. Reverse
lookup format: 1.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa PTR notarealdomain.fake Reverse looup from quiz: With these requests your server will attemp to find the
website in question in its local cache, if it cannot find the answer it will query another DNS server on your behalf until it finds the address. It will be
then respond to the original request with the results from each servers query.
With a recursive lookup you ask the DNA server and it it doesn’t know it follows to th enext and the next until passing the answer to you but putting the
burden on the server; this type of lookup is not commonly seen anymore. Today we use Iterative lookups= When you ask the DNS server a question if it
doesnt know thwe answer it will respond with the IP address on a DNS server that does know but it will be your responsability to ask the next DNS
server in line and the it will either answer or or send you to another DNS server to ask. Place the burden on the host not the DNS servers.
Necessary to configure the authoritative DNS server for a particular domain you need to add DNS records for that domain. There are many but these are
the most commonly used: A Record (This is the address maping record. Key record that maps a domian name to an IPv4 address), AAAA Record (This
is the IPv6 address mapping record. Equivalent of an A Record but for IPv6 addresses.), CNAME Record (CNAME or Canonical name record is used
for creating an alias of a domain. Ex. If you wanted your domain to redirect to google.com, you would use a CNAME), MX Record (MX Record or
Mail Exchange Record specifies th email server which is responsible for handling email for that domain), NS Record (NS Record or Name Server
records points to the authoritative name server for the domain in question. Usually the NS records are configured separatedly on the domains registrar
systems to point to the DNS server of choice), PTR Record (PTR or Pointer record is used for reverse lookups. It ties an IP address to a domain name in
the format 1.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa PTR notarealdomain.fake), and TXT Record (The TXT or Text Record is used for storing any other data associated
with the domain name. Used a lot in SPF and DKIM for mail servers where a list of IP addresses which can be used for sending mail from that domain
(in the case of SPF) or apublic key (in the case of DKIM) is stored as TXT record).
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Tells computer to use DNS service in pre-installed router with DNS service. Allows DHCP server on network to
assign network configuration settings to each host automatically when they join the network. Removes possibility of IP addresses conflict (same IP to
different computers) and makes process seamless for end-user. Only one DHCP server per network. Most home routers have it built in and business use
separate computer as DHCP server. Not uncommon for DHCP to be configured with static IP address for specific devices, keep those devices at a
predictable IP address on network causng some security issues bc it opens the possibility of intercepting clients traffic. DHCP= is how most systems get
an IP address when they first join a network.
This is the address maping record. Key record that maps a domian name to an IPv4 address.
This is the IPv6 address mapping record. Equivalent of an A Record but for IPv6 addresses.
CNAME or Canonical name record is used for creating an alias of a domain. Ex. If you wanted your domain to redirect to google.com, you would use a
CNAME.
MX Record or Mail Exchange Record specifies th email server which is responsible for handling email for that domain.
NS Record or Name Server records points to the authoritative name server for the domain in question. Usually the NS records are configured separatedly
on the domains registrars systems to point to the DNS server of choice.
PTR or Pointer record is used for reverse lookups. It ties an IP address to a domain name in the format 1.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa PTR
notarealdomain.fake
The TXT or Text Record is used for storing any other data associated with the domain name. Used a lot in SPF and DKIM for mail servers where a list
of IP addresses which can be used for sending mail from that domain (in the case of SPF) or apublic key (in the case of DKIM) is stored as TXT record.
294
1
295
1
296
1
290, 300
1
296
296
1
1
296
1
296
1
296
1
296
1
296
1
OSI Model (Open System Interconnection)
Application Layer 7-data, OSI Model
Presentation Layer 6-data, OSI Model
Session Layer 5-data, OSI Model
Transport Layer 4-Segment, OSI Model
Network Layer 3-Packet/Datagram, OSI
Model
Data Link Layer 2-Frame/Cell, OSI Model
Physical Layer 1- Frame/Bit, OSI Model
Level 8 is the user, OSI Model
Physical Link or Medium, Layer 0
TCP/IP Model
Application Later, TCP/IP Model
Transportation Layer, TCP/IP Model
Internet Layer, TCP/IP Model
Network Access Layer, TCP/IP Model
Ethernet Frame, OSI Model, Packet Headers
Is a way of describing the way computers communicate with each other over the network. Ex. TCP and UDP are in 4 layer but also spans to layer 5. The
OSI model consists of 7 layers and you start at the top and work the way down the model. Each layer transforms the data somehow until at the physical
layer data is converted to electrical signals which are transmitted over the network. The computer receiving the information gets it at the physical layer,
and then works up to the application layer again until the user sees it in its original form on the receiving compuer. Layer 7: Application (data), Layer 6:
Presentation(data), Layer 5: Session (data), Layer 4: Transport(segment), Layer 3: Network (packet), Layer 2: Data Link (Frame/cell), Layer 1:
Physical(Frame/Bit). Layer 0/physical link/medium=data unit is a bit. Layer 8 user joke=human error *OSI is a way of describing computer networking
interactions. Whist a tad theoretical or 'reference', its a helpful model to understand the layers that build communications. OSI uses network layer to to
define routing standards.
Ex. HTTP or FTP. For example, an HTTP GET requests is an application layer protocol bc the web browser will form the request ncessary for
displaying a page or submitting a form. See OSI model drawing
Encryption of necessary happens here. Ex. XML or JSON. The presentation layer deals with formatting data in a way that the intended recipient can
understand. Ex. A file transfer where the file must be converted to binary data before it can be sent.
Handles opening, closing and managing connections between computers. (NOT to get confused with TCP or UDP in this layer; those are for the
transport layer 4) TCP could span up to this layer but doesn’t belong here.
Responsible for end-to-end connections between computers on a network. The TCP and UDP protocols fall into this layer, and it is at this point that the
TCP or UDP header gets added to the packet.
Responsible routing the packet over the internet. IP protocol falls here, at this point the IP header is added to the packet.
Is responsible for encoding and decoding packets into bits. At this point, the destination and source MAC address is added to the packet. (in either
Ethernet frame (header & Footer), wireless, or bluetooth) indicating which network card on the network the packet is going next. MAC source and
destination addresses use ARP (address resolution protocol) to obtain this info by a broadast request (everyone in the local network)
Responsible for converting the packet into electrical signals which are sent over the network, after packet arrives at destination, the reverse happens: the
physical layer converts electrical signals into bits, the data link removes the ethernet frame (Header & Footer) or whatever it used, the network layer
removes the IP header, the transport layer removes the TCP or UDP header and so on until application layer where data is received by the application in
a form it can understand.
layer 8 issue. Human mistake joke in security/forensics
Data unit is a bit.
Thisis another theoretical model aside the OSI model to show how computers communicat eover the network. It has 4 layers but includes everything the
OSI model has; several layers have been joined into one in places. Layer 4: Application, Layer 3: Transport, Layer 2: Internet, and Layer 1: Network
Access. Is a more focused model than OSI that looks at this protocol relashionship specifically. TCP/IP uses only the internet layer to define routing
standards.
Basically the same as the application layer in OSI model except it also includes the responsibilities of the PRESENTATION Layer, and SESSION Layer
from OSI Model. Ex. Of protocols in the application layer are HTTP and FTP, basically any protocol that applications define and use.
Direct copy of the transport layer of OSI Model, the TCP and UDP protocols are implemented here. (segment)
Is effectively the network layer from the OSI Model, responsible for routing traffic over network. (Packets)
(Combines Frame [cell & Bit] from OSI model) This layer is a combination of the data link and physical layers from OSI Model.
Consists of both a header and a footer. Data Link Layer. To find out MAC source and destinatoin address on the network the packet goes to in the data
link layer.
301
1
303
1
304
1
305
1
306
1
307
1
308
1
309
1
309
302
1
1
310
1
311
1
312
313
314
1
1
1
308, 315
1
Packet Headers
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
DoS (Denial of Service or DoS Attacks)
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service)
SME Network, Building-Video
Server Definition - Cambridge dictionary
CIS benchmarks & guides
Server Hardware
Server [Dedicated]
Datacenters
Server [Blade]
Redundancy
server in a small scale
Contain information used for mantaining state and routing connections. Starting at the applicaton level data (7) we encapsulate that data into a packet
ready for transmission over the network. Encapsulation occurs by adding header to the data. Ex. An HTTP request made by a browser GET / HTTP/1.1
Step 1: A TCP header is added to the data (TCP header consists of source port, destination port 80 or 443 usually, sequence number, acknowledgement
numberand anything else. Original data still there but TCP header now sit sin front of it. Step 2: Add IP header. IP header consist of IPv4 or IPv6,
source IP address, destination IP address, size of packet and anythign else. Step 3: Add Data Link Layer protocol: add Frame (ethernet, wireless, or
bluetooth), source MAC address, destination MAC address (ARP address resolution protocol is used to obtain these MAC addresses-by broadcast
request to the whole local network), etc. and Step 4: packet is converted into a series of electrical impulses which are transmitted over the network. On
the receiving end, the packet works it way back up through the layers, first being converted from electrical impulses to data. Then all reversed: Data link
layer protocol/Frame is removed (ethernet in this example), then the IP header, then the TCP header until the application (the web server) receives the
GET request. Web server will respond with the contents of the index page in HTML and that data will then be encapsulated into a packet and
transmitted over the network in response.
Translates IP addresses to MAC addresses for transmission purposes. It is also open to security abuse. An ethernet frame (header & Footer) requieres a
source MAC address and destination MAC address. How computer A finds that info for computer B? Computer A sends a broadcast request (a request
to everyone on the local network) asking for MAC address ex. 192.168.0.10 Computer B will respond with its MAC address and Computer A will store
that mapping in an ARP table which caches results. ARP is ONLY for the Local Network.
DoS is when attackers use large volumes of requests, huge numbers of packets or connections to overload systems and prevent legitimate users
connecting. Attack that consume resources and prevent real customers from connecting. They come in many sizes and shape. Ex. Using just a sheer
number of packets and huge bandwidth to saturate the internet connection server. They can also be more application layer: finding a website request at
/login.php that causes the server greater expense in processing. The attacker then repeatedly calls and uses this thousands of times per second,
overoading the system in processing terms. They can even target the search bar, the contact directory lookup. Even a misplaced cable receiving waves
from electromagnetic fields can cause chaos in a unintended DoS episode :)
Very problematic. More painful than DoS. Attackers use a huge number of systems; ex. Large bot network they control, and atack a system all at once.
They can also take turns and pulse. These can disrupt even the most well-connected business. In some instances DDoS attacks will be Protocol Layer
such as just having a huge number of bot systems connecting over TCP to flood the connection table. In other sit may be Application layer, such as
having a huge number of bots turn up and interact over HTTP to post to a login form.
Video of professor James Lyne shoing how to build our very own SME network using common business grade hardware for a small business.
"A central computerfrom which other computers get information." Lots of data is held. Receive connections from clients devices, they talk to computres
not humans, it is a computer to computer interaction. "A server is simply a computer which runs software that provides services. Another way we refer
to server is related to the specific software running on a computer.
Resources for a person to configure and secure common server types. Guides you through the most basic to the most rigid and secure but likely to
disrupt features. cisecurity.org
They can have specialized harware requirements to perform their specific function: ex. Rasberry Pi, Old desktop PC with Vmware EXSi installed, and
dual CPU Xeon Blade Server (10k per server).
(Computers built with the intention of using them as servers.) Tend to be more powerful than your typical desktop computer. Besides having more RAM
and storage, a server will likely have one or more specialized CPU's. They may requiere specific motherboards that have specialized functionality such
as slots for multiple CPU's, a server may have 2, 4, or more CPU's each having multiple cores, TeraBytes worth of RAM, several GPU's and hundreds
of TeraBytes of storage.
Places designed to house many servers. Having so many powerful computers in close proximity generates a lot of heat, so datacenters provide cooling
and connectivity for all those servers.
Self contained servers that are thin and can be slotted into a rack. They have the ability to swap components quickly when a part fails in a particular
server which is gtreat for continuous service. A way to ensuring continuous service is with redundancy which means having servers ready as a fallback
when another server fails.
A way to ensuring continuous service is with redundancy which means having servers ready as a fallback when another server fails.
Have a web server in your home computer or buil a server in your local area network.
315
1
316
1
317
1
318
1
319
1
321
1
321
1
322
1
322
1
322
1
322
1
322
323
1
1
Server Software
server-Types
Server [Game]
IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT Devices
Server {Challenges}*military ex.
air-gapped
Server {How are they connected to outside
world?}
Intrusion detection system
Intrusion Prevention System
Web Server Introduction
NeXSTEP
CERN httpd
Tim Berners Lee
Another way we use the term serveris related to the specific software running on a computer. For the server to do its job there needs to be some software
running that will sit and listen for connections and processes the requests. Software on a server can be called service (one computer may be running
several different services which is ok for the regular user but for a business use one service running per service is preferible.This software also create the
necessary file structures based on whatever service we are running. ex. game server (see game server), syncing on your phone, tablet, and laptop. (a
central server is sending all that dat and messages to each device, the server will allow the devices to be added to the send list.
There are many variety of servers. Few common one are: Web Server, DNS Server, DHCP Server, Log Server, Game Server, Print Server, Proxy Server,
and Streaming Server.
By login in a multiplayer game for ex. It will connect you to a server and you will be with others on the sam map. This kind of server will get updates as
you use your input device, mouse or controller. The command is sent through the internet and updates what you have just done to everyone, usually
positions and mathematical representations rather than graphically.
Everyday objects connect to servers especially with IoT devices being so prominent. IoT devices often run on web servers. They are classified as objects
embedded with sensors and connected to a network. 'Smart Devices' All the everyday smart devices are aprt of the IoT. Modern day cars may be
connected to a server usually through a 4g sim card. Many bridges have some form of IoT sensors to check for various attributes relating to stability and
safety.
IoT devices often run on web servers. They are classified as objects embedded with sensors and connected to a network. 'Smart Devices' All the
everyday smart devices are aprt of the IoT. Modern day cars may be connected to a server usually through a 4g sim card. Many bridges have some form
of IoT sensors to check for various attributes relating to stability and safety.
Cost, environmental impact, creating specific solutions to problems for the military and hospitals for example wile keeping security and redundancy in
mind. Few things to consider for military servers: will servers be not connected to untrusted networks such as the internet (aka air gapped), physical
security of the servers (perimeter entrance, robbery, etc), who do you trust to build harware. What is something goes wrong? what then? Overall, this
requieres a considerable effort to design well enough to satisfy the needs of the service, skills needed to build a server, and the facilies they are contained
in.
Not connected to untrusted networks such as the internet.
Servers are processing connections from the outside world most of the time = hence security is top. 1. First thing to consider is how to keep them
physically secure (do we need CCTV everywhere and if so, ware we going to use on site servers or cloud for that). 2. In terms of networking, imagine
website hosting companies did not connect to the internet. Servers that require internet connection, theres a for careful network infrastructure lay out.
(They will requiere a powerful router to process all the connections, just for the networking alone there would need to be several servers to run the
servers.) Also important is level of access , layers of protection intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systemswell designed internal network.
Layer of protection for companies servers and networks.
Layer of protection for companies servers and networks.
Primary purpose is to satisfy client requests on the world wide web, which translates to storing processesing web pages and delivering them to clients
using HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to communicate or HTTP these days. Fist web server created in 1990 by Tim Berners-Lee who also invented
the WWW, he worked for CERN with the goal of ease the information between scientists using HTTP. First web server ran on NeXSTEP (a
discountinued object oriented multitasking operating system based on Mach Kernel; later known as CERN httpd. "A Web server can be a piece of
software, or hardwarededicated to running server software. They also help in the configuration of home devices like printers, web cams, and routers
particularly those serving only local network in schools, and small offices. Web server can be used to install additional software on the clients computer
through a web browser. Common Mistakes: overly broad user permissions to fix issues."
NeXSTEP (a discountinued object oriented multitasking operating system based on Mach Kernel; later known as CERN httpd.
NeXSTEP (a discountinued object oriented multitasking operating system based on Mach Kernel; later known as CERN httpd.
Created the Web Server and WWW while he worked for CERN 1990.
324
1
325
1
324
1
325
1
325
1
326
1
326
1
327
1
327
327
1
1
329
1
329
329
329
1
1
1
Web Server- What are they?
Dynamic Functionality
LAMP Stack
Web Server-Why candy for attackers?
Pivoting attacker tactic
/var/www/html
Web Server -How they work?
Client Side
Server Side
URL-How to read?
Web Server Analytics
API Application Programmer Interface
Transfer data. Designed to take files or data and present them to a user over protocols such as HTTP (HTTP/1.0 ASCII based protocol-easier for humans
to read). Simple function but now it has added more like security and more efficiency with HTTP/2.0 (high transfer, binary, more difficult for humans to
read) which most web servers now support. Just an application that listens to the network on a specific set of ports and speack a specific set of protocols.
Web servers requiere slighly higher permissions to bind to ports like :80, on most OS lower ports below 1024 requiere levated permissions to bind. Web
server always want to minimize permissions, this creates high a nd lower access to people alsmot like segregation. Web servers can be configured to
listen to non-standard ports but that means anyone who needs to access them will need to put the port number at the end of the domain as such:
https://some-fake-domain:8008. Now this server suport dynamic apps and websites when it reconizes PHP suffix. It uses a defined processor or PHP
Binary to proces it and produce the outcome instead of a static page. It also works combined with a database. The database server could b ein the same
system or be a network based rresource the web server connects to. Most common set up for this is 'LAMP Stack'.
Now this server suport dynamic apps and websites when it reconizes PHP suffix. It uses a defined processor or PHP Binary to proces it and produce the
outcome instead of a static page. It also works combined with a database. The database server could b ein the same system or be a network based
rresource the web server connects to. Most common set up for this is 'LAMP Stack'.
Stands for Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP. Apache is the web server, which runs a PHP file that contains instructions to connect and query a
MySQL database.
1. Exposed publicly or designed to be connected to througha firewall, 2. attackre may have more permissions than they need to enabeling lateral
movement, 3. Often connected w dynamic capabilities which allow attackers to supply tehir own codeor modify functions, 4. malicious code
distributions by having unaware visitors, 5. posibility of stealing database of usernames, passowrds, credit cards etc all at once, 6. Pivoting (Being able
to connect to other workstations or systems nearby/var; attacker tactic to reach all workstations and network (developers leave useful codes or code
repository keys on a web server thinking they will never be found bc they are outside /var/www/html, 7. 3erd party hosts many many websites, hacker
can gain access to one website, gain access to the server and compromise the rest f the websites on that server. *WEB SERVER SECURITY COMES
DOWN TO PATCHING SYSTEM AND BEING CAREFUL WITH CONFIGURATION.
Being able to connect to other workstations or systems nearby; attacker tactic to reach all workstations and network(developers leave useful codes or
code repository keys on a web server thinking they will never be found bc they are outside /var/www/html.
root front page
Front end, back end, and client side.
The client side is simply the web browser and your device. Is the device that is being used to connect to the website. Many things happen here: inputs to
be uploaded, requests of downloads etc.
For now lets assume front end=client side, and server side=back end. Computations happen here in servre sideusually in the form of a written scripting
language that does somehting. Ex. JavaScript, PHP, Pyhton, JAVA, Perl, ASP, Ruby, and Go. There are many more languages used to code
functionality on a website.
HTTPS tells the device how to write and send requests to get the document you need (document=webpage)
Calculated and logged remotely. There is another server elsewhere storing data collected about the system, application, users interactions even possibly
their locations. There are multiple types of analytics: some do automatically, others are by code written by programmers using API (Allows programmers
to write a few lines of code in their software that will call another application with a query and receive response.) It helps to track marketing campaings
and traffic flow all year and be prepared. Business often have the infrastructure to detect anomalies or unusual patterns like web users requets timing in
different periods of time. This is good to raise alarm and create action or drive automated response in an elastic infrastructure.
Allows programmers to write a few lines of code in their software that will call another application with a query and receive response.
330
1
330
1
330-331
1
331
1
331
1
330-331
332
1
1
332
1
333-334
1
333
1
335
1
335
1
Error/Server/Client/Success/Informational
Response Codes
Response headers
Private Mode
My Referer URLs
Web Server Common Failures/Prevention
Apache Signature & more
Some of these codes can tell a hacker wether there is a firewall & how things are config in the system. INFORMATIONAL: 100 Continue - Everything
is looking smooth. Continue as you were. SUCESS: 200 OK-Request has been completed with no errors. It varies slighly depending on HTTP method
used (GET, POST, HEAD, TRACE). You might not necessarily see a 200 code and the page just loads but they are still being received by the by the
browser (check respose header to verify this). 202 Acepted-Received buthave not yet done anything about it. REDIRECTION: 301 Moved permanentlyUsually the new URL is given in the response. CLIENT ERRORS: 400 Bad Requests-Invalid Syntax error. 401 Unauthorized-You are not allowed into
this site without logging in. unauthenticated. 403 Forbidden-Same as 401 but server knows the clients identity. Usually means you dont have enough
privilege. 404 Not Found-Nobody knows that site. Mayb eyou type it wrong way. 408 Request Timeout-The server is shutting you down for idleness.
SERVER ERRORS: 500 Internal server error-Server does not know what to do, so it took a nap. Typuically happens d/t bad code or failure to handle
data or an exception. These are often worth investigating. Bad Gateway-Issue with the servers connection. 503 Service Unavailable-Overloaded server.
504 Gateway Timeout-Your servers are too slow. probably a connection problen somewhere in the network.
A form of HTTP header that do not carry information about the content but rather the status of the request one has sent. They come from the web server
themselves. The client sends an HTTP request and the web server replies with an HTTP response.
Doesn’t make you anonymous to website and internet providers for their marketing campaings. It does deletes cookies, cache, and other artifacts
associated with the session after one leaves. You can add individual extentions and ad blockers to stop trackers and a VPN to mask network traffic.
Tracks the page address where I came from. URL Tracker.
IT hygiene failures. Also check periodically with vendors of your selected technology for new config options, defaults, and bug advisory, along with
releases. 1.Check over your defaul config: Most modern systems do a good job bringing in a lower priviledged user like www-data and config
appropiatedly. In Apache default set up does not enable HTTPS so all communications will be unencrypted when echanging ingo, also number of
workers are set up low, it might need scalability tweeks 2. Validate web server permissions: Most default setups today will create a separate user and a
group like www-data which should have overall low priviledges on the system. However, to troubleshoot issues like a permission error, some people
google how to upgrade the permissions on a user by adding them to another group on the system that has real power but now this person will get used to
fix issies with code instructiones online opening a way for hackers to gain access and priviledges. Another example is administrators doing: chmod 777
/var/wwwhtml This indeed fixes permission errors but now everyone can do everything, all access. We should see restrictive permissions set for each
specific user, which should be the lowest overall. 3. Disable the banner/versioning: Depending on the web server, like in the case of APAche and Nginx
will output their version number and some basic config info valuable to attackers as it can leak that you are runnning a specific version that may be
vulnerable to a specific exploit. In Apache this is called the signature. 4. Using Checklists: Vendors publish specific info and checklists you can use to
secure thier servers. Also look for resources with CIS Benchmarks to further restrict them.
Version number of apache you are running. Good info for attackers to know if you are running a web server with known vulnerabilities they can exploit.
Comes with a large amount of pre-set functionality by default. Apache and Nginx, both are configured to use a folder as the web root; that folder will
contain the files needed to run the website. The folder should include an index file named either index.html or index.php: this is the file that is sent when
a request is made to '/'. Ex. visit https://www.google.com/ you will get the index page at the top level of the web root directory. Apache loads PHP really
simple, just run a to EN Mode with PHP and everything works.
336
1
337
1
338
1
338
1
340
1
341, 234
1
Hygiene in IT/Cyber
Nginx
Remote Web server config
index.html
certbot
Multiple sites in same server
Database Server & as Software
DBMSs or DBMS
MySQL
DSDs
Front End-Client Server Model
Back End - Client Server Model
Codd's Relational Model for database
management
Peter Chen, Charles Bachman
IT hygiene failures. Also check periodically with vendors of your selected technology for new config options, defaults, and bug advisory, along with
releases. 1.Check over your defaul config: Most modern systems do a good job bringing in a lower priviledged user like www-data and config
appropiatedly. In Apache default set up does not enable HTTPS so all communications will be unencrypted when echanging ingo, also number of
workers are set up low, it might need scalability tweeks 2. Validate web server permissions: Most default setups today will create a separate user and a
group like www-data which should have overall low priviledges on the system. However, to troubleshoot issues like a permission error, some people
google how to upgrade the permissions on a user by adding them to another group on the system that has real power but now this person will get used to
fix issies with code instructiones online opening a way for hackers to gain access and priviledges. Another example is administrators doing: chmod 777
/var/wwwhtml This indeed fixes permission errors but now everyone can do everything, all access. We should see restrictive permissions set for each
specific user, which should be the lowest overall. 3. Disable the banner/versioning: Depending on the web server, like in the case of APAche and Nginx
will output their version number and some basic config info valuable to attackers as it can leak that you are runnning a specific version that may be
vulnerable to a specific exploit. In Apache this is called the signature. 4. Using Checklists: Vendors publish specific info and checklists you can use to
secure thier servers. Also look for resources with CIS Benchmarks to further restrict them.
Comes pretty lean, you can customize it as you see fit. It uses PHP FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) to be able to run server side code and PHP. Apache
and Nginx, both are configured to use a folder as the web root; that folder will contain the files needed to run the website. The folder should include an
index file named either index.html or index.php: this is the file that is sent when a request is made to '/'. Ex. visit https://www.google.com/ you will get
the index page at the top level of the web root directory.
If you accidentally cut off the relevant port (ex. 22) during configuration you wont be able to connect anymore.
it can be set even empty, when you access it is blank.
Can manage the automatic renewal of security certificates for you withou needing authorization each time. You can change an option so that you have
more control over the configurations or you can allow Certbot full access to edit the configurations of the web server. For TLS certificates renewal.
Yes you can separated by name or port for ex.
Computer system that provides other computers or programs with services related to accessing and retrieving data from a database. As a software, it is
the back-end portion of a database application following the client server model. They are used to store and manage the databases stored on server ,to
provide access to the different types of users in different ways depending on what they are trying to achieve. Database management systems or DBMSs
often provide this server functionality. Ex. MySQL The Front end displays requested data running on users computer, the back end tackles tasks like
data analysis and storage running on server itself.
Ex. MySQL Database management systems or DBMSs often provide this server functionality. Ex. MySQL The Front end displays requested data
running on users computer, the back end tackles tasks like data analysis and storage running on server itself. Over 300s DBMSs.
Is a freely open source Relational Dabase Management System that uses Structured Query Language (SQL).
Data Structure Diagrams. First conception of database server by Charles Bachman in 1969. These diagrams provided a mean to to graphically represent
relashionships between data entities which formed the basis of Codd's Relational Model for database management in the 70's.
For now lets assume front end=client side, and server side=back end.
For now lets assume front end=client side, and server side=back end.
Data Structure Diagrams. First conception of database server by Charles Bachman in 1969. These diagrams provided a mean to to graphically represent
relashionships between data entities which formed the basis of Codd's Relational Model for database management in the 70's. Further resarch using this
model culminated with Peter's Chen proposal of the Entity Relashionship Model- An abstract data model defining a data or information structure that
can be implemented in a database. This model is more 'real world applicable' and became th emost used model to describe relational databases. Main
principle of this model is that front-end database users should not have to know how databases work behind the scenes. Still used by most databases
today.
Data Structure Diagrams. First conception of database server by Charles Bachman in 1969. These diagrams provided a mean to to graphically represent
relashionships between data entities which formed the basis of Codd's Relational Model for database management in the 70's. Further resarch using this
model culminated with Peter's Chen proposal of the Entity Relashionship Model- An abstract data model defining a data or information structure that
can be implemented in a database. This model is more 'real world applicable' and became th emost used model to describe relational databases.
340
1
234, 341
1
test q
test q
1
1
test q
1
tets q
1
343
1
343
1
343
1
343
1
1
1
343
1
343
1
Entity Relashionship Model
SQL
Database design & Logic
Database Tools
SQL Server Demo
PHPMyAdmin & Adminer Functions
Adminer
PHPMyAdmin
Data Structure Diagrams. First conception of database server by Charles Bachman in 1969. These diagrams provided a mean to to graphically represent
relashionships between data entities which formed the basis of Codd's Relational Model for database management in the 70's. Further resarch using this
model culminated with Peter's Chen proposal of the Entity Relashionship Model- An abstract data model defining a data or information structure that
can be implemented in a database. This model is more 'real world applicable' and became th emost used model to describe relational databases.
Structured Query Language-is the most common language for adding, accessing, and managing content in a database. Popularity d/t reliability, speed of
processing, and flexiblity. Used in mysql database, SQL server
Logic requiered to design databases to ensure all statements are complete, no redundancy, efficient to use, help us strucuture databases betterwrite more
efficient query statements, think through relashionships, model the relashionships between all the data, helps a business potentially grow, crucial in
business developmentand analytics. Primarily databses are use dby a company to to store information about their business crucial for their day to day
dealings. Bad datase design= can function but make every task hard and future upgrade paths painful. Good database design= make for extensible
business systems and easy to exytract data.
PHPMyAdmin & Adminer Functions. These tools provide a graphical front end to manage the contents of MYSQL database. Ex. Back up database.
These tools are written in PHP easy to integrate with a web server and user friendly interface for simplicity of tasks. It will allow you to (only a few
examples): Run SQL Commands, Export Tables into differetn file types such as PDF, search the database, create, copy, and drop tables, mantain server,
administer multile servers, and Adminer allows theh use of CSS skinds. Administer can manipulate the entire database with these tools. *These tools
should NEVER be used on a production databseor, if they must be used only leave them up for as long they are needed to avoid an exploit in one f these
tools that can lead to the compromise of the database it connects to.
Most widespread type of database server and their relational structure and intuitive language make them compelling choices for developers. Here there
are valuable conecpts to learn wether in offensive security and finding flaws, or defensive security and locking down unauthorized paths to data. Root
user should always connect through the local box/host via SSH (never from over the network to the database), get access to the system and connect. By
default mysql has an anonymous user-remove asap.
PHPMyAdmin & Adminer Functions. These tools provide a graphical front end to manage the contents of MYSQL database. Ex. Back up database.
These tools are written in PHP easy to integrate with a web server and user friendly interface for simplicity of tasks. It will allow you to (only a few
examples): Run SQL Commands, Export Tables into differetn file types such as PDF, search the database, create, copy, and drop tables, mantain server,
administer multile servers, and Adminer allows theh use of CSS skinds. Administer can manipulate the entire database with these tools. *These tools
should NEVER be used on a production databseor, if they must be used only leave them up for as long they are needed to avoid an exploit in one f these
tools that can lead to the compromise of the database it connects to.
Supports many databases compared to PHPMyAdmin which only supports the management of MySQL and MariaDb databases. Allows the use of CSS
skins.
Supports only MySQL and MariaDB databases.
343
1
343
1
344
1
345
1
346
1
345
1
345
1
345
1
SQL Server Set Up Considerations
ufw
mysqldump
SQL Alter Command
SQL Update Command
SQL Insert Command
SQL Exporting Dangers
IP 127.0.0.1 vs. 0.0.0.0
Amazon RDS
Aurora
DNS Servers-Intro
Command -h (MySQL in Linux)
They will depend on the SQL server and its specific best practice & security config. But some are standard like the CIS Guides. Few Important Setup
Considerations: 1. Validate the IP connectivy rules-common mistake for sql servers running in cloud like AWS, sets them to make them accessible to the
open internet allowing port 3306(for MySQL) to be connected to anyone in the world. 2. Remember to run the 'mysql_secure_installation' to remove the
test database, anonymous accounts that come with set up, and enforce credentials on the root user. Improves security instantly. 3. Validate that MySQL
is running with an appropiately privileged restricted user. Specific lower privileged mysql user is really common and useful. Linux will do this for you
but check. 4. Consider removing mysql history file located at ~/.mysql_history it can expose credentials or config to users of the system. 5. Ask yourself
if you need remote logins at all? If you dont need more broad access, you can reduce the surface fof an attack. ( ip address 127.0.0.1 used to connect
database on local host. 0.0.0.0 means try to connect to all IP addresses on the local machine all ipv4 are allowed.) 6. Conduct MySQL verb restrictions.
Ex. limit the use of 'SHOW DATABASES' attacker will have less info. 7. Update-to eliminate security vulnerabilities. Patches might change how SQL
works and the language specifics which means one will also have to make changes to the application or update web frameworks. A good test
environment where you can validate changes helps. 8. Check the Linux File Permissions-Check that my.cnf is accesible from the root user or admin user
via sudo. make sure MySQL data directory (typically '/usr/local/mysql/data' is accessible for the mysql user but not others. 9. Consider use of a
managed SQl platform that does a lot of this for you ex. Amazon RDS, Aurora (managed SQL platform. Automatically apply updates, restric access to
the backend systemand simply operational and security ownership at no cost, you still have to config credentials and the service appropiately. ), 10.
Make sure you have adequately sized your system to the requirements and configured monitoring so you know if disk space is low. Use MSQL and CIS
guides. (keep permissions tight, users and roles specific and software updated.)
347-348
1
firewall. Used on sql databased using linux
A database backup program
Change sthe structure of a table. Ex. Add or delete columns, create or destroy indexes, rename columns or table itself
Modify rows in a table. Ex. Professor added email to an existing emplyee on database where the space for email was already created in table.
Inserts new rows to exisiting table. Requieres privileges.
Exports are in text based, plain text formet. Make sure to use encryption. It can be intercepted or stolen.
IP address used to connect database on local host. 0.0.0.0 means try to connect to all IP addresses on the local machine all ipv4 are allowed.
managed SQL platform. Automatically apply updates, restric access to the backend systemand simply operational and security ownership at no cost, you
still have to config credentials and the service appropiately.
managed SQL platform. Automatically apply updates, restric access to the backend systemand simply operational and security ownership at no cost, you
still have to config credentials and the service appropiately.
DNS = Domain Name System. Is the Phone book of the internet. Translates typed domain name sinto numreic IP addresses; from human language to
computer language. Abstracting DNS has 2 types: Authoritative servers & Cient-Facing servers (ex. Googles's DNS that recursively resolves requests by
pivoting around the DNS insfractructure). Why DNS is neded? Humans cannot recall all those IP #s and much more we cant do reverse lookup. There
are 4 types of DNS Servers. 1. Recursive Resolver/DNS Recursor: Receives the query from the client machine via applications like internet browser.
Querys the root nameserver first. Also stores IP on cache 2. Root Nameserver: Is the first port call of the resolver to query directs the resolver to the TLD
nameserver thta stores the information for its domain. There are 13 decentralizes & distributed clusters root serves strategically placed all over the world
acting as index, reference, for locating the IP address for a site host. 3. TLD (top level domain) nameserver: The resolver then queries the provided TLD
server which will respond wit the IP address o the domains authoritative nameserver. TLD servers differentiate between .com, .net, and .org. 4.
Authoritative Nameserver: Will retrieve teh specific IP address of the origin server for the provided web domain name, which the resolver will pass
down to the client. Once a query has passed all four servers, the client can query directly to origin server and this one will respond by sending data to be
displayed in web browser. This process with all four servers happens the first time you query a site, after that the resolver will store theorigins server on
cache for a certain period or until cleared, after that th eprocess starts all over again.
video
346
346
346
346
346
347
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
348
1
348
1
350
1
MySQL client can be told to connect to remote systems with -h.
346
1
DNS Servers Types:
Browser
Resolver/DNS Recursor, DNS
Root Namserver, DNS
TLD - Top Level Domain, DNS
Authoritative Name Servers, DNS
Amplification Factor, DNS server Security
DNS Benefits & Danger to Users
DNS Demo set up
DNS Security-Free Wifi Traps
ISP
There are 4 types of DNS Servers. 1. Recursive Resolver/DNS Recursor: Receives the query from the client machine via applications like internet
browser. Querys the root nameserver first. Also stores IP on cache 2. Root Nameserver: Is the first port call of the resolver to query directs the resolver to
the TLD nameserver thta stores the information for its domain. There are 13 decentralized & distributed clusters root serves strategically placed all over
the world acting as index, reference, for locating the IP address for a site host. 3. TLD (top level domain) nameserver: The resolver then queries the
provided TLD server which will respond wit the IP address o the domains authoritative nameserver. TLD servers differentiate between .com, .net, and
.org. 4. Authoritative Nameserver: Will retrieve teh specific IP address of the origin server for the provided web domain name, which the resolver will
pass down to the client. Once a query has passed all four servers, the client can query directly to origin server and this one will respond by sending data
to be displayed in web browser. This process with all four servers happens the first time you query a site, after that the resolver will store theorigins
server on cache for a certain period or until cleared, after that th eprocess starts all over again.
Allows a user to input a human readable domain name and the computer will query dns servers to find that IP for that address.
There are 4 types of DNS Servers. 1. Recursive Resolver/DNS Recursor: Receives the query from the client machine via applications like internet
browser. Querys the root nameserver first. Also stores IP on cache
Root Nameserver: Is the first port call of the resolver to query directs the resolver to the TLD nameserver thta stores the information for its domain.
There are 13 decentralized & distributedclusters root serves strategically placed all over the world acting as index, reference, for locating the IP address
for a site host.
TLD (top level domain) nameserver: The resolver then queries the provided TLD server which will respond wit the IP address o the domains
authoritative nameserver. TLD servers differentiate between .com, .net, and .org.
Authoritative Nameserver: Will retrieve the specific IP address of the origin server for the provided web domain name, which the resolver will pass
down to the client. Once a query has passed all four servers, the client can query directly to origin server and this one will respond by sending data to be
displayed in web browser. This process with all four servers happens the first time you query a site, after that the resolver will store theorigins server on
cache for a certain period or until cleared, after that th eprocess starts all over again.
The recursive resolver will send all the servers queries at the same time. This gives rise to the so called 'amplification factor.' It is easy to appreciate hpw
it would be possible to attack this system effectively.
DNS servers are not all the same, and can filter or block. DNS traffic is unencrypted, it takes more than than just changing your DNS to give you
anonymity. Your ISP (internet service provider) may block access to to specific sites using DNS. You can change your DNS to another one and you will
bypass the blockage. Another benefit of changing DNS is speed since often ISP DNS are slower compared to CloudFlare, OpenDNS, or Google DNS.
Of course your ISP company will still know what you are doing since they are the one routing your traffic. Cloudflare and others provide special rules
and filtering to redirect you away from malicious sites and jail you in a page to protect you, they are customizable. If an atacker controls your DNS they
win, they can redirect you werever they want.
See notes in book
Localized thread as attacker needs to be in the communication path. DNS is crucial to networks but vulnerable to attacks and observation. By default
DNS is not encrypted but some DNS use some form of encryptoin. Dangers using free wi-fi at a shop: 1. Others on the network can 'sniff' the network
traffic of the wireless nertwork, see your DNS requests and lean about where you are visiting, this will leak info about software you are running when it
updates or phones home. Not necessarily means they can they can redirect you to whicever website they want. Danger 2: Connecting to a wi-fi that has
been compromissed and controlled by a devious party. in this case your traffic passes through the router and your DNS is provided by it. The devious
people controlling the wifi router could send you somewhere else (not autherntic place) instead of where you want to go.
Internet Service Provider
350-351
1
350
1
350
1
350
1
350
1
350-351
1
352
1
353
1
354
1
355
1
353
1
DNS over HTTPS vs TLS (Security)
Man in the middle attack, DNS
DoT - DNS over TLS
DoH - DNS over HTTPS
Port 853
Port 443
DNSSEC
DNS Cache Poisoning
DNS Admin monitorin/blocking
Oblivious Extension
DNSKEY RRset
DNSSEC Root Signing Ceremony
Patches, Missing patches
Log Servers
Central Loggin capability
By default DNS is sent in plain text which allows it to be monitored by anyone in the path of transit. Privacy problem that becomes a security problem;
also a global problem=government use DNS to to censor the internet. Attacker use it too for many reasons:can be used as man in the middle attack or
simply to gather info about person u organization. Base of security is Encryption. Encrypted DNS comes in: DoT & DoH! Both use TLS to encrypt. A.
DNS over TLS- (DoT) is a way to encrypt DNS using TLS. In DoT, the DNS sits on top of the UDP which is simply wrapped with encryption via TLS.
This provides a mechanism to hide the contents of the quesry and makes tampering detectable as th eencryption will be corrupted through modification.
DoT uses port 853 so you get a dedicated port for visibility & network filtering but it may be more restricted. B.DNS over HTTPS (DoH)-Is an
alternative to DoT, runs on port 443 which is a standard port used by most websites for secure web connections and often available. In this instance
DNS queries are sent over HTTP/2 instead of over UDP. This provides the same features as DoT and makes sure an attacker cant see inside the requests
or responses as well as protecting them from tampering. This has become an increasingly defaut protocol for many browsers and users. Still overall, you
have to trust the DNS server even when you transit is encrypted, you can query an evil attacker DNS Server.
DNS over TLS- (DoT) is a way to encrypt DNS using TLS. In DoT, the DNS sits on top of the UDP which is simply wrapped with encryption via TLS.
This provides a mechanism to hide the contents of the quesry and makes tampering detectable as th eencryption will be corrupted through modification.
DoT uses port 853 so you get a dedicated port for visibility & network filtering but it may be more restricted.
DNS over HTTPS (DoH)-Is an alternative to DoT, runs on port 443 which is a standard port used by most websites for secure web connections and
often available. In this instance DNS queries are sent over HTTP/2 instead of over UDP. This provides the same features as DoT and makes sure an
attacker cant see inside the requests or responses as well as protecting them from tampering. This has become an increasingly defaut protocol for many
browsers and users. This one is better for users concerned with privacy since all requets will be sent using regulat HTTPS (p.357). Oblivious Extensionfor DoH. Effectively route the traffic through a proxy server so the DNS servers do not know who sent the request. Hence more rivacy to the user.
DoT uses port 853 so you get a dedicated port for visibility & network filtering but it may be more restricted.
DoH)-Is an alternative to DoT, runs on port 443 which is a standard port used by most websites for secure web connections and often available.
DNS Security Extensions is a security protocol focused on: criminals taking DNS offline, trick DNS servers to caching and serving bad entries, or
hijacking domains. This is NOT used to encrypt communications or solve the problem of interception or monitoring on a café with Wi-fi connection for
example. This is actually related to DNS root server lookups and how authoritative name servers correspond with DNS resolvers. Is more focused on
problems like DNS cache poisoning. DNSSEC verifies the DNS servers identity in commnication with the DNS resolver. Does it by allowing them to
sign the DNS resposes digitally. Needs to be implemented at every level of the DNS to protect the esolver as it communicates with different server.
DNSSEC root signing ceremony to sign the DNSKEY RRset, (this makes it thrustworthy) humans are able to verify this.
DNSSEC deals with this issue.
Oblivious Extension- for DoH. Effectively route the traffic through a proxy server so the DNS servers do not know who sent the request. Hence more
privacy to the user.
DNSSEC verifies the DNS servers identity in commnication with the DNS resolver. Does it by allowing them to sign the DNS resposes digitally. Needs
to be implemented at every level of the DNS to protect the esolver as it communicates with different server. DNSSEC root signing ceremony to sign the
DNSKEY RRset, (this makes it thrustworthy) humans are able to verify this.
DNSSEC verifies the DNS servers identity in commnication with the DNS resolver. Does it by allowing them to sign the DNS resposes digitally. Needs
to be implemented at every level of the DNS to protect the esolver as it communicates with different server. DNSSEC root signing ceremony to sign the
DNSKEY RRset, (this makes it thrustworthy) humans are able to verify this.
Most common root causes of compromise. Make sure you stay on top of updates is one of the best ways to keep your systems secure.
Log events of different severity levels is very important to maintain goof IT hygiene and for cyber security incident response.
Enable us to immediately start an investigation and source potential impacted systems. This capability extends to the cloud too with a variety of products
known as LaaS (loggin as service), becoming very popular, LaaS platforms provide pre built-in capabilities to set up and you can just focus on analysing
the logs instead. (save your time in set up) ending log entries to a secure 'write only' remote log source makes tampering with logs harder.
356
1
356
1
356
1
356
1
356
356
1
1
357-358
1
357
357
1
1
357
1
358
1
358
1
quiz
360
1
1
360
1
Loggin in local systems
LaaS Platform, Log Server in Cloud
log entries, Log Server
Rsyslog, Log Servers
SIM
SIEM
SEM
Rsyslog Legacy to declare template
SIM vs SEM vs SIEM
ISO 27000
Log Servers, Free Tools vs Commecial
(SIEMs)
Log Servers, ELk vs SIEM
not trusthworthy. Not a good practice. Attacker can modify logs to hide presece or actions. If logs events are immediately sent from a system to central
log server this is much more difficult to do. ending log entries to a secure 'write only' remote log source makes tampering with logs harder.
Central Loggin capability enable us to immediately start an investigation and source potential impacted systems. This capability extends to the cloud too
with a variety of products known as LaaS (loggin as service), becoming very popular, LaaS platforms provide pre built-in capabilities to set up and you
can just focus on analysing the logs instead. (save your time in set up) ending log entries to a secure 'write only' remote log source makes tampering with
logs harder.
Sending log entries to a secure 'write only' remote log source makes tampering with logs harder.
RocketFast Syslog Server. Is the rocket fast system for log processing. You will see this dealing with Linux devices, IoT devices, and Industrial Control
Systems. Receives all security messages (log information from the local system & the broader system), you can filter by time, and hostname, if a
message was a debug or critical message. (severity of message) You can store data under /var/log or MySQL in tables. How you store the data files is
very configurable with many plug ins available. In Rsyslog config using the old $template or the new template(parameters), both will still work. In
configiurating Rsyslog: *,* (first asterisk means collect all mesages and second is for selecting the severity of messages you want to log). Enables very
high performance ingestion of alerts at over 1Million per second. You can ingest the record from a variety of sources, filtering by application type, and
severity. You can then store the data in all manor of databases or services, even piping it out to LaaS providers to ease your analysis.
Security Information Management. Tools of platforms used to collect and stored all the security data that is logged within an organization. It can collect
all sorts of data and become huge really quickly. Data like: Changes to operating systems, web servers (if in house), firewalls, IDS & IPS logs, router
info, terminal commands, changes to an employees computer, antivirus logs, DNS servers, Authertication Servers, Data base access. Hence is not
uncommon to be a little more selective on what you will want to collect.
Security Information Management & Event Management. Rather than having 2 separate tools that do practically the same thing, you have SIEM which
automate much of this process and comes pre-packaged with rues & flows designed to make processing data and reacting to it easier. It has become
popular. Useful in security but also when auditors come and check on compliance, this is for things like Information Security Management systems and
ISO 27000 certificates. Great SIEM set up will react to breaches, understand whathappened, and investigate restrospectively. These platfoems include
more and more clever techniques to react to data and baselining with machine learning & heuristic mechanisms is finding more suspicious entries than
ever. There are default set ups for different type of business fro the to collect the data but it always need some customization to your environment. These
can be installed in the network or in the cloud (goo since you can have support but handles your event data to a third party).
Security Event Management. These tools provide real time analysis of all the SIM data with the added benefit of sending alerts about any security
abnormalities. The putput to a console where a human gets an alert to be investigated. This can be used to trip alerts but also provide bigger picture
insights in to the network and trends. The console tend to have displays such as charts, and pictorial presentation. Log data can provide invaluable data
of what attackers are doing inside network.The ability to analyse this data quickly as opposed to in 30 days makes a difference.
Old way: $template & new way: template(parameters)
All refer to a type of tool that will store and process logs or even data. The quick difference is that SIM deals with storing log data for long term analysis,
Sem is concerned with live action processing, and SIEM combines both.
"SIEM is useful in security but also when auditors come and check on compliance, this is for things like Information Security Management systems and
ISO 27000 certificates."
Splunk; very popular product in the commercial space. Open source projects: Apache Metron that evolved out of the CISCO OpenSOC platform.
Metron uses other Apache projects such as Kafka (Open source distributed event streaming platform), and analysis via tools like Apache Hadoop (Open
source framework used to efficiently store and process large datasets). It has a very extensive architecture but doesnt have the easy out of the box
coverage of a commercial tool. Some other platforms offer free & as a premium paid products like SIEMonster. Most companies prefer a commercial
product due to the benefit of support.
ELK stack combine Elasticsearch, Logstash, & Kibana. Powerful stack with massive capabilities on the processing and query side. Builds dashboards,
grab logs, process & store them. You can add some other tools to get it close to performing like a SIEM solution, however, you will find alerting and
correlation capabilities missing which makes it fall short compared to what commercial SIEMs offer. Not a full SIEM but very helpful. one example of
the utility of this platform is SOF-ELK. This big data analytics platform is optimized towards security operations and forensic investigator roles.
Developed by Phil Hagen for a SANS class but has grown in to broader use.
360
1
360
1
360
1
360-361
1
362
1
362-363
1
362
1
361
1
362
1
363
1
364
1
364
1
ELK vs SIEM
ElK
SPLUNK
Apache Metron
SIEMonster
KAFKA
Apache Hadoop
Metron , Apache
Elasticsearch, ELK
Logstash, ELK
Kibana, ELK
SOF-ELK
Phil Hagen
Heuristics base security
GDPR
AI behavioral Profiling Learning Model
Security vs Privacy, Log Servers
PII
ELK stack combine Elasticsearch, Logstash, & Kibana. Powerful stack with massive capabilities on the processing and query side. Builds dashboards,
grab logs, process & store them. You can add some other tools to get it close to performing like a SIEM solution, however, you will find alerting and
correlation capabilities missing which makes it fall short compared to what commercial SIEMs offer. Not a full SIEM but very helpful. one example of
the utility of this platform is SOF-ELK. This big data analytics platform is optimized towards security operations and forensic investigator roles.
Developed by Phil Hagen for a SANS class but has grown in to broader use.
ELK stack combine Elasticsearch (Distributed, free and open, search and analytics engine for all types of data including textual, numerical, geospatial,
structures and unstructures. Built on Aache Lucene and releasedin 2010), Logstash (Is a free open source server side data processing pipeline that ingest
data from a multitude of sources, transforms it, and the sends it to your favorite stash), & Kibana (Free and open user interface that lets you visualize
your Elasticsearch data and navigate the Elastic Stack). Powerful stack with massive capabilities on the processing and query side. Builds dashboards,
grab logs, process & store them. You can add some other tools to get it close to performing like a SIEM solution, however, you will find alerting and
correlation capabilities missing which makes it fall short compared to what commercial SIEMs offer. Not a full SIEM but very helpful. one example of
the utility of this platform is SOF-ELK. This big data analytics platform is optimized towards security operations and forensic investigator roles.
Developed by Phil Hagen for a SANS class but has grown in to broader use.
SIEM commercial popular platform tool.
Open source SIEM platform tool.
SIEM platform that is both offered as Free & as paid premium paid product.
Open source distributed event streaming platform.
Open source framework used to efficiently store and process large datasets.
open source framework SIEM from Apache. Open source projects: Apache Metron that evolved out of the CISCO OpenSOC platform. Metron uses
other Apache projects such as Kafka (Open source distributed event streaming platform), and analysis via tools like Apache Hadoop (Open source
framework used to efficiently store and process large datasets). It has a very extensive architecture but doesnt have the easy out of the box coverage of a
commercial tool.
Part of ELK stack. Distributed, free and open, search and analytics engine for all types of data including textual, numerical, geospatial, structures and
unstructures. Built on Aache Lucene and releasedin 2010.
Part of ELK stack. Is a free open source server side data processing pipeline that ingest data from a multitude of sources, transforms it, and the sends it
to your favorite stash.
Part of ELK stack. Free and open user interface that lets you visualize your Elasticsearch data and navigate the Elastic Stack.
ELK is not a full SIEM but very helpful. One example of the utility of this platform is SOF-ELK. This big data analytics platform is optimized towards
security operations and forensic investigator roles. Developed by Phil Hagen for a SANS class but has grown in to broader use.
ELK is not a full SIEM but very helpful. One example of the utility of this platform is SOF-ELK. This big data analytics platform is optimized towards
security operations and forensic investigator roles. Developed by Phil Hagen for a SANS class but has grown in to broader use.
Extremely popular bc it works well. 'form of behavioral analysis' 'AI'
General Data Protection Regulation. Legislation that updated and unified data privacy laws across the European Union. Approved on April 14, 2016, in
effect since May 25, 2018.
With AI software that learns your behavior and watches everything on the network for your security, it is imposible to have privacy.
AI behavioral Profiling Learning Model. With AI software that learns your behavior and watches everything on the network for your security, it is
imposible to have privacy. On top of that, many models are not trained on the computerbut requiere data to be sendt to a remote server to be processed.
Also how much oversight do users will accept on thier devices?The problems with logs potentially containing sensitive data (passwords, PII (Personal
Identifiable Information) that needs to be purged. Also users invoking their rights to be forgotten under GDPR: Easy on a SQL database but not that easy
on log files. How to identify them? It gets very difficult to comply with law in this case when you can id people. Difficult to balance security and
privacy. More monitoring = better attacker prevention, but can also leave open to legal or ethical constraints. Needs to be owned and worked by security
teams.
Personal Identiafiable Information
364
1
364
1
364
364
364
364
364
1
1
1
1
1
364
1
364
1
364
1
364
1
364
1
364
1
365
1
365
1
365
1
365
1
365
1
Log Server, Best Practices
EICAR Test Virus
1. Do not start by logging everything, build up, not collect evrything and reduce backdown. 2. Consider compliance as well. GDPR? HIPAA? Know
your organization rules and change your set up. 3. Considere collection efficieny and safety. Careful collecting PII or sensitive info introducing
additional risk for your systems and the users data. Exclude these events. 4. Consider key business and security events. Authorization sucess and failure
attempts are particularly important. Changes in user rights, errors from key applications, high privilege users data access & rights and how they are
logged. 5. Retention strategy: How long you neeed this data? Archive less importnat data? 6. Run a test! Try and create a mini incident ex. EICAR Test
Virus. Does an alert get sgenerated? Are the right people notified? 7. Consider data transport security & encryption at rest: Does data contain sensitive
info? How is the data then trasnsported safely? You dont want observers on the network to 'casually' read your log entries. 8. Validate if log server is
operational as expected. Interact regularly with them, dont let the logs fill up in a corner; a malicious event hidden in a log server sorrounded by million
other events with no alerting is not of much use but more useful for retrospective incident analysis than NO logs at all!
The European Institute for Computer Antivirus Research (EICAR) has developed a test virus to test your antivirus appliance. The test virus is not a virus
and does not contain any program code.
Email Servers Intro
Also known as mail server. Is a computer system that sends and receives email using standard email protocols. The SMTP (Simple Mail transfer
Protocol) deals with the outgoing email messages and the IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP3 (Post Office Protocol) deal with
incoming email. All these behind the scenes. Many business and individuals use web-based email clienta which wont requiere separate config on a email
server, but business often choose invest their own servers for reasons of space and security. Is often the case that email is used as a delivery mechanism
in attacks. A further dimmension to email servers is that they are very often provided via cloud services (Microsoft Office365). These SaaS models for
email can provide lots of capabilities, providing reliability and and functionality it can however compromise in the areas of forensics and investigation if
you need to extract specific data; classic trade off between cloud and SaaS services and On-site hosting.
Email Server, Cloud SaaS vs On Site Hosting Is often the case that email is used as a delivery mechanism in attacks. A further dimmension to email servers is that they are very often provided via
cloud services (Microsoft Office365). These SaaS models for email can provide lots of capabilities, providing reliability and and functionality it can
however compromise in the areas of forensics and investigation if you need to extract specific data; classic trade off between cloud and SaaS services
and On-site hosting.
Microsoft Office 365
email servers provided via cloud
Mac Mail
Email client.
MX Records
Domain query on DNS server in the process of sending email to identify server.
Email Server Steps Behind Scenes When
Step1: Email client- Compose email hit send. Emial client connects to sending server on your domain. Email client shares relevant info that has been
Sending Email
packaged and added correct routing and decoded so it reaches the other side, in email header you have who is it coming from, where is going, info
about sending email client and content and info about the origins of the message. These headers are key to process message but also used a spart of
authenticity checks with spam filters. Email client shares all that info with your sending server. 2. Sending server processes the email address of the
recipient to see if it is or not on the same domain of the sender. If it is: then no routing between servers is needed; message goes straight to the domains
Incomins mail server (IMAP) or (POP3). This is the end for this message and and can be read by recipient. If the recipient is a different domain to the
sender then the sending server identifies wher ethe recipients mail server is using DNS. 3. The message is usually routed along a series of servers until it
reaches the recipients mail server. 4. The incoming message is scanned by recipients email server, if it passes filtres and other checks and is validated is
then forwarded to the users mailbox. DNS is CRUCIAL to be routed to right place!
Email Server, Headers
Step1 to send email and behind the scenes: Email client- Compose email hit send. Emial client connects to sending server on your domain. Email client
shares relevant info that has been packaged and added correct routing and decoded so it reaches the other side, in email header you have who is it
coming from, where is going, info about sending email client and content and info about the origins of the message. These headers are key to process
message but also used a spart of authenticity checks with spam filters.
Spam Filters, Encoding And Variability
Another tactic in spamming is encoding or using unusual characters or symbols to avoid matching filters. Sometimes they don’t want to catch anyone
but to see if they can bypass spam filters.
366
1
366
1
369
1
369
1
369
372
372
1
1
1
372-373
1
372-373
1
375
1
Spam Filters
IP Reputation
Spam Filter, Email wa still delivered
Spam Filter Behavior/flaw
BotNets
Credential Harverster
MIRAI Bot case
Spam Filter, Global spam Filter Updates
SMTP Response Codes Definition
SMTP Response Codes
Enhanced Status Codes
Tend to be send by BotNets. Spam has many forms, but in general is either adverts from companies, cyber criminals trying to get you to click links with
malicious code behind or just a credential harverster that tries to trick you in to hand over data. How do spam filers work? 1. Examine the IP reputation
data or the sender information. 2. Looks at headers for suspect fields or odd values that dont look like real clients. 3. Share data between many users to
find attacks that have been reported. 4. Scan the contents of emails to find common hooks or attacks. 5. Examine attachements, links and other parts of
the email to see if it identifies suspicious next step. Spammers only need a mnority of people to scam, those few that click on obvious spam emails are
their prey bc they follow to the second step. Spam messages tend to be send by BotNets wich are effectively massive networks of computers that have
been hacked. Desktops, computers, internet connected fridges, doorbells, anything with a processor and connected to the internet. Using lots of
legitimate devices that have been compromised is actually a tactic to defeat detection on itself. Spam filters will even check links to see if link will take
you where it says it will.
Lots of spam filters also look for suspicious IP ranges on the internet that should not be sending email. If the attacker has a larger number of systems
they can also send the spam in small bursts and avoid poisoning the reputation of the compromised device. IP reputtaion is a very effective mechanism
in modern spam filters.
Lots of email systems can actually identify spam campaings after thay have passed in to some user mailbox. Based on config they can quarantine or
remove these emails.
1. Tend to get constant updates on blacklists of known bad senders. 2. They will get many updates a day on rules to identify text patterns associated with
known campaigns. 3. They will feed suspicious samples into a lab so that systems or humans can spot errors and update detection. The flaw? when
campaings are low volume from a good reputation account-difficult to detect. Often depends on the user or detection of the payload that follows.
Spam messages tend to be send by BotNets wich are effectively massive networks of computers that have been hacked. (Desktops, computers, internet
connected fridges, doorbells, anything with a processor and connected to the internet. Using lots of legitimate devices that have been compromised is
actually a tactic to defeat detection on itself.
tricks you with spam for ex. To hand over data
interesting historical case reading about BotNet devices. Mirai is a piece of malware designed to hijack busybox systems commonly used on IoT devices
in order to perform DDoS attacks. Responsible for largest DDoS attack.
Are made up of 3 digits, each individual number means a different thing. First digit=What class of status is. (it may accept the command, or have a
temporary error and so on). Second digit=Explains a bit more about what kind of problem is encountered (Syntax error, connection problem). Third
digit=the specific detail about whatthe code is.
220=SMTP service ready.The server can process the following command. 250=Requested action taken and completed. Most common response. (client
data) 421=The service is not available, and the connection will be closed. Your destination server is probably not reachable. 450=The requested
command failed because the user's mailbox was unavailable. Try again later. 451=The command has been aborted due to an error from the recipients
server. 452=The command has been aborted because the server has insufficient system storage. maybe you have overloaded the server by sending too
many messages at once. 500=The server could not recognize the command due to a syntax error. Could be caused by filtering issues with your security
software or similar. 501=A syntax error was encountered in command arguments. Caused mainly by invalid mailing addreses. 503=The server has
encountered a bad sequence of commands. Usually an authentication error. The commands are not executing in the correct order. 550=The requested
command failed because the user's mailbox was unavailable. This can indicate no email address or spam. 551=The recipient is not local to the server.
The server then gives a forward address to try. Commonly used as a strategy for spam prevention. 552=The action was aborted due to exceeded storage
allocation. The recipient's email was full. This could have been an attack or simply you are sending files that are too big. 554=Delivery error: Sorry your
message cannot be delivered. This mailbox is disabled. Either blacklisted your IP or thinks the email is SPAM. See also Enhanced Status Codes
This addition was brought in to fix some of the uncontrolled growth of use cases. RFC3463 "SMTP suffers from scars from history most notaly the
unfortunate damage to the replay code extension mechanism by uncontrolled use." This organizes messages in to a structure of: CLASS (2 = denotes a
positive or succesful message, class 4 =transient or temporary, class 5=permanent error), SUBJECT (is 1 to 3 digits, and DETAIL can be 1 to 3 digits.
Ex. 5.1.1 tell us that a permanent issue has been raised (5), The first 1 tell us thisis an addressing subject, the final 1 tell us the user is not found or the
recipient is rejected. *Also subject field could be x.2.xxx for the mailbox status, or x.4.xxx for network and routed related responses.
374-376
1
374-375
1
376
376
1
374-375
1
374
1
374
1
376
1
377
1
377-378
1
378-379
1
RFC3463, Enhance Status Codes
Enhanced Status Codes, Subject Fields
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail
Extension) Definition
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail
Extension) How it Works?
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail
Extenstion) What Could Go Wrong?
MIME Encoding
This addition was brought in to fix some of the uncontrolled growth of use cases. RFC3463 "SMTP suffers from scars from history most notaly the
unfortunate damage to the replay code extension mechanism by uncontrolled use."
subject field could be x.2.xxx for the mailbox status, or x.4.xxx for network and routed related responses.
Behind the scenes when you send pictures in an email, MIME provides a mechanism to be able to transfer non ASCII data as well suggesting to
receiving clients whether it should be displayed inline or as an attachement. In order to achieve this we need a set of headers to describe the content and
also encoding mechanisms to get the data to transmit over the protocol. It provides the capabilites to allow you to send HTML, images, audio, and video
in messages. In later times it has also become key to supporting security use cases too.
Mime has headers like 'Content-Type' header which might stipulate text/plain, or text/html. The more interesting is 'multipart' which enables multiples
parts of messages to exists with different encoding standards being used; useful for messages with an embedded image and zip file attached for ex.
Another common header is 'Content-Transfer-Encoding' header which stipulates how the data will be enclosed. Since email only supports text to include
files as an attachment they must be encoded. Typically MIME attachments like images are encoded in base64, which produces a loooong weird string.
The email client then recognizes is an attachment and decodes it back into a file you can download through the email client. There are other schemes
used such as 7bit, 8bit, printedquotable, or binary. It depends on the email client and transfer mechanism. Check online RFC for MIME.
MIME has quite a few different features and headers. Over time some clients have handled the data differently to a given server despite pretty clear
guidance in the standard. Leading to ocassions where a security scanner fails to parse the MIME and allows it through but the client then renders the
malicious content. This is becoming less common but is a constant reminder protocols for exchanging data and consistency accross multiple applications
interacting with a standard are not simple to achieve.
Another common header is 'Content-Transfer-Encoding' header which stipulates how the data will be enclosed. Since email only supports text to include
files as an attachment they must be encoded. Typically MIME attachments like images are encoded in base64, which produces a loooong weird string.
The email client then recognizes is an attachment and decodes it back into a file you can download through the email client. There are other schemes
used such as 7bit, 8bit, printedquotable, or binary. It depends on the email client and transfer mechanism. Check online RFC for MIME.
base64,
Another comon header is 'Content-Transfer-Encoding' header which stipulates how the data will be enclosed. Since email only supports text to include
7bit,8bit,printedquotable,binary/MIME Email files as an attachment they must be encoded. Typically MIME attachments like images are encoded in base64, which produces a loooong weird string.
Attachement
The email client then recognizes is an attachment and decodes it back into a file you can download through the email client. There are other schemes
used such as 7bit, 8bit, printedquotable, or binary. It depends on the email client and transfer mechanism. Check online RFC for MIME.
Email Server Setup-Basic Demo
Postfix
MTA's (Mail Transfer Agents)
ESMTP
RCPT TO
MAIL FROM
SMTP Banner
main.cf
Postfix is one of many MTA's (Mail Transfer Agents) that has an SMTP server designed to send and receive email. Others are 'sendmail', 'Exim', and
'Qmail'. These servers can be configured in a variety of modes:ex. Receiving email and simply forwarding it on to some other MTA- a kind of stream
forwarder. They can also be local only, or configured to work just within a specific IP range in the local network. In this demo, we config a SMTP
server that works with the network but sends email between local users on the Linux system. This is the basis of more advanced config wher we can
layer on webmail services that can be accessed with a browser. We can also bring in POP3 and IMAP which are designed to enable clients to get access
to their email once Postfix has put it in the right place!
Postfix is one of many MTA's (Mail Transfer Agents) that has an SMTP server designed to send and receive email. Others are 'sendmail', 'Exim', and
'Qmail'. These servers can be configured in a variety of modes:ex. Receiving email and simply forwarding it on to some other MTA- a kind of stream
forwarder. They can also be local only, or configured to work just within a specific IP range in the local network.
a kind of stream forwarder. Postfix, sendmail, Exim, Qmail.
Extended SMTP adds additional commands to the protocol in 8bit ascii code to help with the spam problem. Provides authentication of the sender, SSL
encryption of emails, etc.
RCPT To comes after MAIL FROM. The wrong order will terminate connection.
RCPT To comes after MAIL FROM. The wrong order will terminate connection.
main.cf is the primary Postfixconfig file where you can configure the SMTP banner. It is included in the main.cf under /etc/postfix by default. You can
customize it here.
main.cf is the primary Postfixconfig file where you can configure the SMTP banner. It is included in the main.cf under /etc/postfix by default. You can
customize it here.
378
1
379
1
380
1
380
1
380
1
380
1
380
1
381
1
381
1
381
1
1
1
1
1
1
Sync Servers (Synchronization Servers)
Definition
Sync Servers (How do they work?)
Sync Servers (Asymmetric cryptography)
Sync servers are not as specific as others bc there are so many types but they enable us to synchronize data between one or more locations. Perhaps the
service spans multiple devices types such as moving data btween a laptop and a phone. This is an increasingly capability for photos, files, and all manner
of other data. Is the synchronization continuos? Triggered? How does it transfer info? What data is sync? Sync in one directoin or archive? and so many
other questions when it comes to the different types of sync servers. REAL TIME OR DEMAND BASIS
Co-lab with team in a Word document ex. All the individuals simply are connecting to one central device using something like remote desktop protocol
and opening the document simultaneously. Each time they edit the document the changes are saved instantly. Thisis the general principle. The sync
server is the centrally located computer that everyone works on and gets uploaded to each persons screen. Ex. 2 The linked device example is similar in
that there is one central server processing all of the accounts and uploading traffic to each device on that account. Further we need to look at: Assymetric
cryptography, and Public key infrastructure. REAL TIME OR ON DEMAND BASIS *A call back is When the sync server asks the OS API to let them
know when a file has been updated. This is for real time syncronization.
You have two keys; a public and a private. You can lock the message with whichever one you would like but you must unlock it with the opposite key.
Cryptography ex: 1. Bob encrypts his message with Alice public key. Since Alice is the only person with the private key (remember when you lock with
one you must unlock with the other) then Bob knows Alice is the only person who can unlock and read that message. He also knows that the reader will
be Alice and no one else. 2. Bob encrypts with his private key. This would allow Alice to know that the messsage definitely came from Bob. Everyone
knows Bob's public key and since Bob is the only one taht coud have locked the message then it must be Bob sending it. 3. Bob can encrypt with his
public key. The only person that can unlock this message is Bob. There are a couple of usus for this.
Sync Servers (Public Key Infrastructure-PKI) When the public and private keys are generated, the public key must get out to the world to see by going on relevant servers usually, although you may
also see a PGP key at the bottom of some emails. The distribution of these public keys is stored on the same sync servers for this particular use. The
public key infrastructure (PKI) is the service where all the public keys are stored. If you wanted to message a friend, you would have to go to some PKI
to get their key to encrypt the message and and send it to them. All this DEPENDING on how the server controls this. It is possible for the server itself
to snoop on the messages or processes happening. The flaw is in knowing excactly whose private, and public key are being used. If the server controls
this then there is a possibility they could forward the message to themselves.
Remote Desktop Protocol
Sync servers word document example.
Assymetric Cryptography
You have two keys; a public and a private. You can lock the message with whichever one you would like but you must unlock it with the opposite key.
Cryptography ex: 1. Bob encrypts his message with Alice public key. Since Alice is the only person with the private key (remember when you lock with
one you must unlock with the other) then Bob knows Alice is the only person who can unlock and read that message. He also knows that the reader will
be Alice and no one else. 2. Bob encrypts with his private key. This would allow Alice to know that the messsage definitely came from Bob. Everyone
knows Bob's public key and since Bob is the only one taht coud have locked the message then it must be Bob sending it. 3. Bob can encrypt with his
public key. The only person that can unlock this message is Bob. There are a couple of uses for this.
Symmetric Cryptography
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
PKI
PGP Key
Delta
call back
rsync
You lock and unlock the message with the same key.
When the public and private keys are generated, the public key must get out to the world to see by going on relevant servers usually, although you may
also see a PGP key at the bottom of some emails. The distribution of these public keys is stored on the same sync servers for this particular use. The
public key infrastructure (PKI) is the service where all the public keys are stored. If you wanted to message a friend, you would have to go to some PKI
to get their key to encrypt the message and and send it to them. All this DEPENDING on how the server controls this. It is possible for the server itself
to snoop on the messages or processes happening. The flaw is in knowing excactly whose private, and public key are being used. If the server controls
this then there is a possibility they could forward the message to themselves.
Public key infrastructure
When theh public and private keys are generated, the public key must get out to the world to see by going on relevant servers usually, although you may
also see a PGP key at the bottom of some emails. The distribution of these public keys is stored on the same sync servers for this particular use.
Building a Delta where results of updates/syncronization after checksum files match. Deltas can apply at the file level or at the data level
When the sync server asks the OS API to let them know when a file has been updated. This is for real time syncronization.
tool on linux to sync files. Transfers and syncs files between a computer and a storage drive and across networked computers by comparing
modifications times and sizes of files.
384
1
385
1
385
1
385-386
1
385
1
385
1
385
1
385-386
1
385
1
385
1
1
1
1