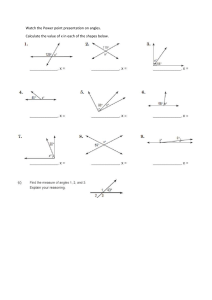
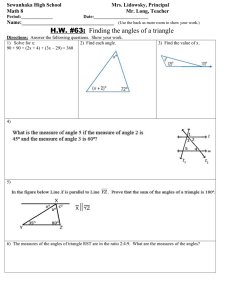
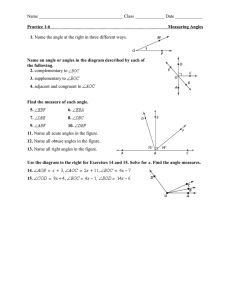
Jay Vrba SRVY 1341 Test 1 15 February 2016 List the three basic requirements to determine an angle. Reference starting line, direction of turning, angular distance What is the name of the number system used to measure angles in the United States? Sexagesimal system What kinds of horizontal angles are most commonly observed? Interior angles, deflection angles, angles to the right What is a closed polygon? A line that begins and ends on the same point, closed traverse In surveying, what is closing the horizon? Using the direction method to include all of the angles around a point List six different types of meridians. Central meridian, deed meridian, record meridian, assumed meridian, reference meridian, magnetic meridian How is a deflection angle observed? Route surveys are commonly run by deflection angles observed to the right or left from the lines extended. A deflection angle is not complete without a designation R or L and it cannot exceed 180°. Each angle should be doubled or quadrupled and an average value determined . the angle should be observed an equal number of times in face left and face right to reduce instrumental errors. Deflection Angles can be obtained by subtracting 180° from angles to the right. Positive values so obtained denote right deflection angles; negative ones are left. What is a closed traverse? Two categories of closed traverse exist: polygon and link. In the polygon traverse the lines return to the starting point thus forming a closed figure that is both geometrically and mathematically closed. Link traverses finish upon another station that should have a positional accuracy equal to or greater than that of the starting point. The Link type (geometrically open, mathematically closed) must have a closing reference direction. Closed traverses provide checks on the observed angles and distances, Jay Vrba which is an extremely important consideration. They are used extensively in control, construction, property, and topographic surveys. What is an open traverse? Open Traverse (geometrically and mathematically open) consists of a series of lines that are connected but do not return to the same starting point or close upon a point of equal or greater-order of accuracy. Open traverses should be avoided because they offer no means of checking for observational errors and mistakes. What is the largest possible angle in bearings? 90° What is the formula to calculate the sum of all the interior angles of a closed polygon? (n-2)180° How is a back bearing calculated? Same numerical values as forward bearings but opposite letters How is a back azimuth calculated? By adding or subtracting 180° (depending on size of the angle) What is the sum of the interior and exterior angles at any given station? 360° In what planes do surveyors measure angles? Horizontal and vertical For each problem, draw a quadrant diagram and label the given information and the location of the angle to be calculated, show all mathematical computations and draw a box around the answer. Convert the following Azimuths to Bearings 72° 33’ 27” Jay Vrba 131° 48’39” 206° 47’ 43” 332° 39’ 32” 4 47’ 48” 120° 36’ 24” 3 46’ 31” 281° 29’ 39” 55° 48’ 24” 143° 36’ 38” Jay Vrba Convert the following Bearings to Azimuths N 56° 47’ 37” E S 42° 31’ 36” E S 62° 12’ 34” W N 51° 48’ 36” W N 47° 41’ 32” E S 43° 32’ 47” E S 61° 46’ 41” W Jay Vrba N 53° 35’ 37” W N 71° 42’ 34” E S 43° 28’ 46” E Line AB = N 61° 31’ 44” E Angle BAC = 75° 25’ 21” Calculate the Bearing of Line AC Line JK = S 56° 42’ 37” E Angle KJL = 49° 34’ 48” Calculate the Bearing of Line JL Line PQ = S 52° 42’ 33” W Angle QPR = 73° 36’ 36” Calculate the Bearing of Line PR Jay Vrba Line ST = N 59° 28’ 58” W Angle TSU = 86° 14’ 32” Calculate the Bearing of Line SU Line XY = S 63° 16’ 48” W Angle YXZ = 214° 31’ 46” Calculate the Bearing of Line XZ Adjust the following traverse Calculate the area in square feet and acres Calculate the Closure Error Calculate the Ratio of Error Calculate the coordinates of each station Calculate the corrected Bearings and Distances AB = S 45°15’14” E 149.83’ BC = N 71°49’00” E 135.96’ CD = N 11°28’37” W 168.26’ DE = N 68°44’24” W 145.27’ EA = S 23°20’37” W 168.24’ Coordinates of Point A = N 10000.00, E 10000.00