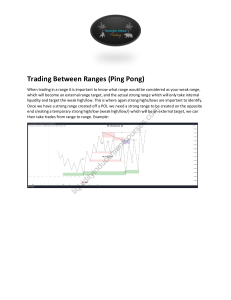
Smart Money Concepts (SMC) Strategy 1. Introduction to SMC Strategy The Smart Money Concepts (SMC) strategy is a trading approach that follows the activities of institutional investors, often referred to as "smart money," to make informed trading decisions. This strategy is based on the assumption that large financial institutions and professional traders have more information and influence over the market, and by understanding their actions, retail traders can gain an edge. 2. Market Structure Trends - Uptrend: A series of higher highs and higher lows. - Downtrend: A series of lower highs and lower lows. - Sideways/Range-bound Market: Prices oscillate between established levels of support and resistance. Ranges - Ranges are periods when the price moves sideways between support and resistance levels. - Identifying ranges can help traders spot potential breakout or breakdown points. Support and Resistance Levels - Support: A price level where a downtrend can be expected to pause due to a concentration of buying interest. - Resistance: A price level where an uptrend can be expected to pause due to a concentration of selling interest. 3. Liquidity Liquidity Zones - Areas in the market where there is a large concentration of buy or sell orders. - Typically found near significant support and resistance levels, previous highs and lows, and round numbers. Stop Hunts - Occur when the price moves to trigger stop-loss orders. - Smart money often pushes the price to these levels to gain liquidity for their positions. 4. Order Blocks Identifying Order Blocks - Order blocks are areas on the chart where institutional traders have placed large buy or sell orders. - These blocks can act as support or resistance in the future. Using Order Blocks in Trading - Look for large, sudden price movements to identify potential order blocks. - Use these blocks to predict future price movements and set entry/exit points. 5. Wyckoff Schematics Accumulation Phase - Period where smart money accumulates positions. - Characterized by relatively flat price movement within a range. Distribution Phase - Period where smart money distributes their positions. - Also characterized by relatively flat price movement within a range. Markup and Markdown - Markup: A period of rising prices following accumulation. - Markdown: A period of falling prices following distribution. 6. Practical Application Step-by-Step Guide 1. Identify Market Structure: Determine if the market is in an uptrend, downtrend, or range-bound. 2. Locate Liquidity Zones: Identify areas with high liquidity, such as previous highs and lows. 3. Spot Order Blocks: Look for significant price movements that suggest the presence of large institutional orders. 4. Apply Wyckoff Schematics: Determine if the market is in accumulation, distribution, markup, or markdown phase. 5. Set Entry and Exit Points: Use the identified levels to plan trades. Example Trades - Example 1: Buying at a support level within an accumulation phase. - Example 2: Selling at a resistance level within a distribution phase.