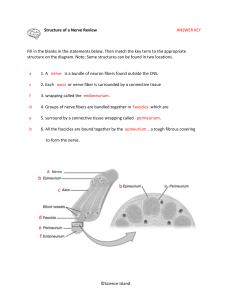
Gluteal Region By Dr. Khaled Saad Mohamed Assistant professor of Human Anatomy & Embryology Bones & Joints of the gluteal region • Dorsal surface of sacrum • Coccyx • Gluteal surface of Ilium • Ischium (ischial tuberosity) • Upper end of femur • Posterior aspect of hip joint • Sacrococcygeal & sacroiliac joint Gluteal Region 1-Gluteal Muscles . 2-Ligaments in Gluteal Region (2 Ligs) 3- Arteries in Gluteal Region (3 As) 4- Nerves in the Gluteal Region (7 Ns) 5- Hip Joint Gluteal Region (Muscles) Muscles Main Hip Extensor Gluteus Maximus Hip Abductors & medial rotators: ➢ Gluteus Medius ➢ Gluteus Minimus ➢ Tensor Fascia Lata Hip Lateral rotators 5 Muscles 1. Piriformis. 2. Obturator internus. 3. Quadrats femoris 4. Superior gemellus 5. Inferior gemellus. Gluteal Region Origin ➢ Sacrum ➢ Ilium Insertion Greater trochanter Except??? Gluteus Maximus ❖Origin: 1. gluteal surface behind posterior gluteal line. 2. back of sacrum & coccyx 3. sacrutuberous ligament ❖Insertion: 1. gluteal tuberosity (1/4). 2. Iliotibial tract (3/4) ❖Nerve supply: Inf. Gluteal nerve ❖Action: ➢ Powerful extensor of hip jointprincipally when strength is required eg. Lifting heavy weights from floor, rising from sitting position, running, climbing stairs)during normal walking extension -by hamstring muscles ➢ Powerful lateral rotator of thigh at the hip joint ➢ Acts with tensor fasciae latae stabilizes pelvis on thigh ➢ Acts with tensor fasciae latae to extend knee through iliotibial tract. Gluteus Maximus ❖Nerve supply: Inf. Gluteal nerve If gluteus maximus is paralyzed, patient can not stand up from sitting position without support Why ? Patient rises gradually from sitting posture supporting their hands first on their legs, then on their thighs to be able to rise up (They climb on themselves). Muscles Main Hip Extensor Gluteus Maximus Hip Abductors & medial rotators: ➢ Gluteus Medius ➢ Gluteus Minimus ➢ Tensor Fascia Lata Tensor Fascia Lata ❖Origin: Iliac crest behind ASIS ❖Insertion: Iliotibial tract ❖Nerve supply: Superior Gluteal nerve ❖Action: ➢ stabilizes pelvis on thigh ➢ extend knee through iliotibial tract. Gluteus Medius ❖Origin: Gluteal surface. between anterior (middle) & posterior gluteal lines ❖Insertion: Lateral surface of Greater trochanter ❖Nerve supply: Superior Gluteal nerve ❖Action: ➢ Powerful Abductor. ➢ The anterior fibers help in medial rotation of the thigh at the hip joint. ➢ During walking: Stabilize the pelvis (prevent tilting of the pelvis when the opposite limb is raised off the ground). ➢ On standing on one limb: Prevent tilting of pelvis towards unsupported side Gluteus Medius ❖Nerve supply: Superior Gluteal nerve Gluteus Minimus ❖Origin: Gluteal surface. between middle & inferior gluteal lines ❖Insertion: Anterior surface of Greater trochanter ❖Nerve supply: Superior Gluteal nerve ❖Action: ➢ Powerful Abductor. ➢ The anterior fibers help in medial rotation of the thigh at the hip joint. ➢ During walking: Stabilize the pelvis (prevent tilting of the pelvis when the opposite limb is raised off the ground). ➢ On standing on one limb: Prevent tilting of pelvis towards unsupported side If gluteus medius & minimis are paralyzed, patient can not walk normally. ➢ When the foot of the normal side is raised , the pelvis tilts to that side. ➢ If paralysis is on one side lurching gait. ➢ If on both sides waddling (Duck) ➢ gait. Gluteal Region 2 Hip Lateral rotators 5 Muscles 1. Piriformis. 2. Obturator internus. 3. Quadrats femoris 4. Superior gemellus 5. Inferior gemellus. Piriformis ❖Origin: ❖Action: By 3 digitations from pelvic surface of middle three pieces of sacrum. ➢ Lateral rotation of the thigh at the hip joint ❖Insertion: Apex of Greater trochanter Leaves the pelvis through Greater Sciatic notch ❖Nerve supply: Ventral rami S1, S2 Piriformis Origin: middle three pieces of sacrum 2 3 4 Insertion: Apex of Greater trochanter Piriformis Syndrome Sciatica like pain caused by compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle during running or sitting, can squeeze the sciatic nerve at the site where the nerve emerges from under the piriformis to over the gemellus and obturator internus muscles. Hip Lateral rotators Nerve Supply ➢Obturator Internus – Nerve to obturator internus ➢ Superior Gemellus - Nerve to obturator internus ➢ Inferior Gemellus - Nerve to quadratus femoris ➢ Quadratus femoris -Nerve to quadratus femoris Obt Superior Gemellus Inferior Gemellus Quad ➢ Structures passing through Greater sciatic foramen : Piriformis muscle. Above piriformis : ➢ Superior gluteal nerves & vessels. Below piriformis : ➢ Inferior gluteal nerves & vessels. ➢ Sciatic nerve. ➢ Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh. ➢ Nerve to quadratus femoris. ➢ Nerve to obturator internus. ➢ Pudendal N. ➢ Internal pudendal vessels. Post. cutaneous n. of thigh ➢ Structures passing through Lesser sciatic foramen : ➢ Tendon of obturator internus. ➢ Nerve to obturator internus. ➢ Pudendal N. ➢ Internal pudendal vessels. Obt Compartments of thigh Anterior compartment (Extensor group)(Quadriceps femoris muscle) Femoral nerve Deep fascia Femur Posterior compartment (Flexor group) (Hamstring muscles) Sciatic nerve Intermuscular septum Medial compartment (Adductor muscles) Obturator nerve Posterior Compartment Of The Thigh Contents ➢ Hamstring muscles: ➢ Biceps femoris. ➢ Semitendinosus. ➢ Semimembranosus. ➢ Ischial part of adductor magnus. ➢ Blood supply: Profunda femoris artery. ➢ Nerve supply: Sciatic nerve. Origin: ➢ The long head from the ischial tuberosity (lower part) ➢ The short head from the linea aspera . Biceps Femoris Insertion: Head of the fibula. Nerve supply: ❑ The long head is supplied by the Tibial branch of the sciatic nerve ❑ The short head is supplied by the common peroneal branch of the sciatic. Action : ❑Flexion of knee. ❑Lateral rotation of the leg (Locking of knee joint) ❑Long head: extends hip. Head of the fibula Origin: Ischial tuberosity (lower part) Insertion: Upper part of the medial surface of the shaft of the tibia (SGS). Nerve supply: Tibial branch of the sciatic nerve Action : ❑ Flexion and Medial rotation of knee. ❑ extends hip. Semitendinosus (SGS) Semimembranosus Origin: Ischial tuberosity (Upper part) Insertion: ❑ Posterior surface of the medial condyle of the tibia. ❑ It forms the oblique popliteal ligament, which reinforces the back of the knee joint. Nerve supply: Tibial branch of the sciatic nerve Action : ❑ Flexion and Medial rotation of the knee. ❑ extends hip. Sciatic nerve (L4,5 S1,2,3) ➢ The sciatic nerve, a branch of the sacral plexus (L4 and 5; S1, 2, and 3) ➢ Leaves the gluteal region below piriformis. ➢ It descends in midline of the back of the thigh. Sciatic nerve ➢ It is overlapped posteriorly semimembranosus muscles. by the biceps femoris ➢ It lies on the posterior aspect of the adductor magnus. ➢ In the lower third of the thigh it ends by dividing into the tibial and common peroneal nerves. and Sciatic nerve ends by dividing into the tibial and common peroneal (fibular) nerves. Branches of Sciatic Nerve 1. Cutaneous: To all leg & foot EXCEPT: ➢ Medial side of the leg ➢ Medial side of the foot till the big toe supplied by the saphenous nerve (branch of femoral nerve). 2. Muscular: •To Hamstrings: (flexors of knee & extensors of the hip). (through tibial part) to: ➢ Ischial part of Adductor Magnus. ➢ Long head of Biceps Femoris. ➢ Semitendinosus. ➢ Semimembranosus. NB. The short head of biceps receives its branch from the lateral popliteal (common peroneal) nerve. SCIATIC NERVE INJURY Causes: The sciatic nerve is most frequently injured by…? 1- Badly placed intramuscular injections in the gluteal region. To avoid this, injections should be done into the upper outer quadrant of buttock (into gluteus maximus or medius). Most nerve lesions are incomplete, and in 90% of injuries, the common peroneal nerve is mostly affected. Why? The common peroneal nerve fibers lie superficial in the sciatic nerve. SCIATIC NERVE INJURY Causes: 2-Herniation or rupture of the intervertebral disc 3 -Posterior dislocation of the hip joint. SCIATIC NERVE INJURY ❑Motor Effect: ➢ Marked wasting of all muscles below the knee. ➢ Weak flexion of the knee (sartorius & gracilis are intact). ➢ Weak extension of hip (gluteus maximus is intact). ➢ All the muscles below the knee are paralyzed, and the weight of the foot causes it to assume the plantar-flexed position, or Foot Drop. ➢ High steppage gait. High steppage gait Sciatica ➢ Sciatica describes the condition in which patients have pain along the sensory distribution of the sciatic nerve. ➢ The pain is experienced in the posterior aspect of the thigh, the posterior and lateral sides of the leg, and the lateral part of the foot. Causes of Sciatica : ➢Prolapse of an intervertebral disc, with pressure on one or more of the roots of the sciatic nerve (lower lumbar and sacral spinal nerves). ➢Pressure on the sacral plexus or sciatic nerve by an intrpelvic tumor, (Piriformis tumor). ➢Inflammation of the sciatic nerve or its terminal branches. Anterior Compartment Of The Thigh Contents Ilio psoas ➢ Muscles: ➢ Quadriceps femoris ➢ Sartorius ➢ Articularis Genu ➢ Ilio psoas ➢ Blood supply: Femoral artery. ➢ Nerve supply: Femoral nerve. Sartorius Muscles of Front of Thigh 1. Sartorius 2. Iliopsoas 3. Quadriceps femori s a) b) c) d) Rectus femoris Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis Vastus intermedius 4. Articularis genu Quadriceps femoris muscle It consists of 4 parts of different origin, but has a common tendon of insertion These 4 parts are: 1. Rectus femoris. 2. Vastus medialis 3. Vastus intermedius. 4. Vastus lateralis Origins of Quadriceps Femoris muscle 1- Rectus femoris: Arises by 2 heads (Hip bone): Straight head: From anterior inferior iliac spine. Reflected head: From impression above acetabulum 2- Vastus Lateralis ,Medialis and intermedius From the femur. Insertion of Quadriceps Femoris muscle ➢ The 4 heads of quadriceps femoris fuse to Tendon form a common tendon ((quadriceps tendon)) which is inserted into the upper border (base) of the patella and continued to the apex of the patella. Patella ➢ From the apex of the patella the ((Patellar ligament)) extends from the apex of the patella to be inserted into the tibial tuberosity (final insertion). Patellar ligament Quadriceps Femoris muscle Nerve supply: Femoral nerve Action: ➢ The main extensor of the leg at the knee joint. ➢ Rectus femoris assists in flexion of thigh at hip joint ➢ Keeps the patella in its position by contraction of the lower fleshy fibers of vastus medialis to prevent lateral displacement of the patella during extension of knee Origin: From anterior (A.S.I.S). Sartorius superior iliac spine Insertion: Upper part of the medial surface of the shaft of the tibia (SGS). Nerve supply: Femoral nerve Sartorius Action : (Tailors position) ➢ Flexion, Abduction & lateral rotation of thigh at hip j. ➢ Flexion of knee j. Articularis Genu Nerve supply: Femoral nerve Action: Elevates the synovial membrane of knee joint during extension of the knee to prevent it from being trapped (crushed) between tibial & femoral condyles Origin: ➢ The psoas major muscle In the abdomen from all lumbar vertebrae ➢ The iliacus muscle From Iliac fossa. Insertion: lesser trochanter of femur ➢ Nerve supply: ➢ The psoas major muscle lumbar Plexus ➢ The iliacus muscle Femoral nerve IlioPsoas IlioPsoas Action : ➢ The main flexor of the thigh at the hip joint. ➢ Acting from below: Flex the trunk as in raising from the recumbent position Medial compartment (Adductor muscles) Medial Compartment Of The Thigh Contents Muscles: ➢ Gracilis (medially) ➢ Pectineus. ➢ Adductor longus. ➢ Addutor brevis. ➢ Adductor magnus. ➢ Obturator externus Blood supply: Obturator artery. Nerve supply: Obturator nerve. Adductor Magnus Gracilis Action : Adduction Flexion Lat rotation Pectineus Adductor Brevis Adductor Longus Origin Superior pubic ramus Pubic body and inferior pubic ramus Pubic body Insertion Pectineal line of the femur Pectineal line of the femur linea aspera Origin Obturator externus Adductor Magnus Gracilis Obturator membrane (outer surface) ➢ Pubic part :From Lower border of pubic arch pubic arch ➢ Ischial part: From Ischial tuberosity Insertion Medial surface of ➢ Pubic part: Gluteal Upper part of the Greater trochanter of the femur tuberosity and linea medial surface of aspera. the shaft of the ➢ Ischial part: tibia (SGS). Adductor tubercle Adductor Magnus Pubic part Ischial part Origin Pubic arch Ischial tuberosity Insertion Posterior surface of shaft of femur Adductor tubercle N. supply Obturator nerve (posterior division) Sciatic nerve Action Adduction – flexion – lat rotation hip joint Extension of hip adductor magnus Ischial part Pubic part Obturator Externus Origin: Outer surface of obturator membrane Insertion: trochanteric fossa on the Medial surface of greater trochanter Nerve supply: Obturator nerve (posterior division) Action: Laterally rotates thigh Obturatot nerve (L2,3,4) ➢ The Obturator nerve, a branch of the Lumbar plexus (L1,2,3 and 4) ➢ It receives fibres from the anterior divisions of L2, L3 and L4 ➢ Divide into anterior and posterior divisions at obturator externus Branches of Obturator nerve Anterior division: Posterior division : ▪Muscular: gracilis, adductors longus & ▪Muscular: Obturator externus, adductors brevis magnus & brevis ▪Cutaneous: middle 1/3 of medial side ▪Cutaneous: No of thigh ▪Articular: to hip joint ▪Articular: to Knee joint ▪Vascular: to femoral artery ▪Vascular: to popliteal artery Femoral triangle site boundaries roof floor contents Inguinal ligament sartorius adductor longus. 3 2 1 Femoral sheath Femoral sheath Divided into three compartments by two fibrous septa ➢ Lateral compartment: femoral a. ➢ Middle compartment: femoral v. ➢ Medial compartment: femoral canal Femoral hernia • If a loop of intestine is forced into the femoral canal , it expands to form a swelling in the upper part of the thigh. Such a condition is known as a femoral hernia . • A femoral hernia is more common in women than in men (possibly because their wider pelvis and femoral canal ). Adductor canal Adductor canal Position: middle 1/3 of front of thigh. Boundaries ➢ Anterior wall: Sartorius ➢ Lateral wall : vastus medialis ➢ Posteomedial wall: adductors longus and magnus Adductor magnus Adductor canal • Contents: 1. Femoral artery. 2. Femoral vein 3. Saphenous nerve 4. Nerve to vastus medialis. Muscles of the Leg Compartments of the leg Anterior compartment 2 D (Extensor group) (Dorsiflextion) (Deep peroneal) nerve. Posterior compartment (Flexor group) (Planterflextion) Tibial nerve. Lateral compartment (Peroneal muscles) (Superfacial peroneal) nerve. Sciatic nerve ends by dividing into the tibial and common peroneal nerves. Common peroneal nerve divide into Deep peroneal nerve Superfacial peroneal nerve Common peroneal nerve Termination: It curves forwards on lateral side of neck of fibula where it terminates by dividing into: ➢ Superficial peroneal branch . ➢ Deep peroneal branch . Lateral Compartment Anterior Compartment Causes: ➢ Trauma or injury to the knee ➢ Compression of the fibula head during surgery e.g.tourniquet. ➢ Fracture neck of the fibula Motor Effect: Foot Drop. Anterior compartment (Extensor group) (Dorsiflextion) Tibialis anterior Extensor digitorum Extensor hallucis longus longus Origin ➢ Lateral surface of tibia. ➢ Interosseous membrane. ➢ Upper 3/4 of anterior surface of fibula. ➢ Interosseous membrane. ➢ Middle 2/4 of anterior surface of fibula. ➢ Interosseous membrane. Insertinon ❑ Medial cuneiform By 4 tendons into Distal phalanx of middle and distal big toe bone (main part). phalanges of lateral 4 ❑ Base of 1st metatarsal toes bone Peroneus tertius Origin ➢ Lower 1/4 of anterior surface of fibula. ➢ Interosseous membrane. Insertinon ❑ Base of 5th metatarsal bone Action Tibialis anterior ❑Dorsi flexion of foot at ankle joint. Extensor digitorum Extensor hallucis longus longus ❑Dorsi flexion of foot ❑Dorsi flexion of ❑Dorsi flexion of foot at at ankle joint. ❑Inversion of foot ❑Inversion of foot at at subtalar joints Peroneus tertius subtalar joints ❑Extension of lateral 4 toes foot at ankle joint. ❑Inversion of foot at subtalar joints ❑Extension of big toe ankle joint. ❑Eversion of foot at subtalar joints Extensor Retinaculae Superior Extensor Retinaculae Structures undercover it: (from medial to lateral): 1- Tibialis anterior. Tom 2- Extensor hallucis longus Has 3- Anterior tibial vessels Very 4- Anterior tibial nerve Nice 5- Extensor digitorum longus Dog 6- Peroneus tertius. Pigeon Lateral compartment (Peroneal group) (Eversion) Peroneus longus Peroneus brevis Origin From upper 2/3 of From lower 1/3 of lateral surface of fibula Insertinon ❑ Medial cuneiform bone ❑ Base of 1st metatarsal bone lateral surface of fibula ❑ Base of 5th metatarsal bone Peroneus longus Action: 1- Eversion of foot at subtalar joint. 2- Planter flexion of foot at ankle joint. 3- Maintains transverse arch of foot Peroneus longus tendon Peroneus brevis Action: 1- Eversion of foot 2- Planter flexion of foot Lateral compartments of leg Peroneal muscles 1 3 (Eversion) 2 1-Peroneus longus muscle. 2-Peroneus brevis muscle. 3-Peroneus tertius. Muscles of the Back of Leg Superficial Group: Deep Group: 1) Gastrocnemius 2) Soleus 3) Plantaris 1) Popliteus 2) Flexor Digitorum Longus 3) Flexor Hallucis Longus 4) Tibialis Posterior Gastrocnemius Origin: Medial Head medial condyle of the femur Insertion: Lateral Head lateral condyle of the femur. posterior surface of calcaneus (Tendon of Achilis) N.S: Tibial Nerve Action: 1- Chief plantar flexor 2- Flexion of knee 3 Propelling force in walking 4 Muscle pump for venous return Tendocalcaneous (Tendon of Achilis) Soleus Origin: 2- Tendinous arch between tibia & fibula 1- Upper part of head of the fibula 3- Soleal line & middle 1/3 of medial border of tibia Insertion: Posterior surface of calcaneus N.S: Tibial Nerve Action: 1 Plantar flexion 2 Steadies the leg on foot during standing 3 Propelling force in walking 4 Muscle pump for venous return Tendocalcaneous (Tendon of Achilis) Plantaris Origin: Popliteal surface of the femur just above the lateral condyle Insertion: posterior surface of calcaneus separately or with tendocalcaneus N.S: Tibial Nerve Action: 1- Plantar flexion of ankle 2- Flexion of knee Popliteus Origin: Popliteal groove below lateral epicondyle Insertion: Posterior surface of tibia above the soleal line N.S: Tibial Nerve Action: Unlocks The Knee Joint by initial medial rotation of tibia at the beginning of flexion of an extended limb Flexor Digitorum Longus Origin: Posterior surface of tibia (below soleal line) N.S: Tibial Nerve Action: 1- Flexion of all joints of lateral 4 toes 2- Plantar flexion of ankle joint 3 Inversion of foot at subtalar joint 4 Maintains the longitudinal arch of foot Insertion: Distal phalanges of lateral 4 toes Flexor Hallucis Longus Origin: Posterior surface of the fibula N.S: Tibial Nerve Action: Insertion 1- Flexion of all joints of the big toe. 2- Plantar flexion of ankle joint 3 Inversion of foot at subtalar joint 4 Maintains the longitudinal arch of foot Distal phalanx of the big toe. Tibialis Posterior Origin: ➢ Posterior surface of tibia (below soleal line) ➢ Posterior surface of the fibula ➢ Interosseous membrane N.S: Tibial Nerve Action: 1- Plantar flexion of ankle joint 2-Inversion of foot at subtalar joint 3-Maintains the longitudinal arch of foot Insertion 1- Navicular Bone (main site) 2- All Tarsal Bones except Talus 3- Bases of 2nd ,3rd and 4th Metatarsal Bones Flexor Retinaculum Definition: Thickened band of deep fascia at medial aspect of ankle joint. Function: They keep flexor tendons in contact with lower end of tibia during their contraction. Flexor Retinaculum Structures undercover it: (from medial to lateral): 1- Tibialis posterior 2- Flexor digitorum longus 3- Posterior tibial vessels 4- Tibial nerve 5- Flexor hallucis longus Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome • Entrapment of tibial nerve posterior to medial malleolus (flexor retinaculum) . • burning pain and paraesthesias along plantar aspect of foot. • pain may radiate to calf • worse with activity (walking), relieved by rest Popliteal Fossa Popliteal fossa is a diamond-shaped intermuscular space situated at the back of the knee It is more prominent when the knee is flexed. Boundaries: Laterally: Biceps femoris above and the lateral head of gastrocnemius and plantaris below Medially: the semimembranosus and the semitendinosus above and the medial head of the gastrocnemius below Medial head of gastrocnemius lateral head of gastrocnemius Popliteal Fossa The Roof Skin, superficial fascia, and the deep fascia of the thigh The Floor ➢ The popliteal surface of the femur . ➢ The oblique popliteal ligament of the knee joint . ➢ The popliteus muscle. Popliteal surface of the femur Contents 1-The popliteal vessels 2- The small saphenous vein 3-the common peroneal nerve 4-tibial nerve 5-the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh 6-the genicular branch of the obturator nerve 7- Popliteal lymph nodes