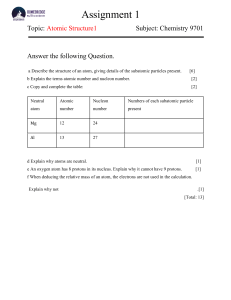
Detailed Lesson PLAN IN Science 8 - Atomic Structure secondary education (Universidad de Zamboanga) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 School Teacher Teaching Date: Alegria National High School Roselyn B. Batal April 5, 2023 Grade Level 8 Learning Area Quarter Chemistry 3rd A. Content Standard The learner demonstrates understanding of how the concept of the element evolved from Ancient Greek to the present B. Performance Standards The learner should be able to make a creative representation of the historical development of the atom or the chemical element in a timeline. C. Learning Competency Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a particular atom (S8MT-IIIe-f-10) I.OBJECTIVES II.CONTENT (Indicator 4.1.2) At the duration of the lesson, learners are expected to: a. describe atom and its subatomic particles; b. locate the subatomic particles; c. infer which subatomic particle contributes to the atomic number and mass of the atom; d. give the importance of being a part of a whole; and e. create atomic model of a certain atom/ element. ATOMIC STRUCTURE III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. Reference 1. Teacher’s guide pages 2. Learner’s Manual pages Unit 3, pages 136 – 140 3. Other Learning Materials Laptop Activity sheets Google.com Youtube.com Self-Learning Module Microsoft PowerPoint https://www.scribd.com/document/600420677/DLP-Atomic-Structure Abamongga, Mary Lou, et al. Science – Grade Quarter 3 - Module 3, First Edition, 2020 Manila paper, pentil pen, scotch tape, scissors, crayons, colored paper Unit 3, pages 194 – 203 IV. PROCEDURE A. Preparatory Activities (5 minutes) Student’s Activity Teacher’s Activity a. Prayer Era Areana, kindly lead the prayer. b. Greetings Good morning everyone! Everybody please take your sit. Good morning Ma’am Roselyn! Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) PPST C.O Indicators c. Checking Attendance d. Setting of Standards Class monitor, who is absent today? Please list down who is absent for this afternoon. And mark absent also for those students who are not in their proper chair. Now class, what should a good student do when the teacher is discussing her in front? What else! Ma’am sit properly and no extra movement. Keep quit ma’am. This time class let me introduce to you our classroom rules. Everybody read. • • • • • • • Classroom Rules Treat others with respect at all times. Listen to the teacher when s/he speaks. Ask for help when you need it. Be prepared every day with required items. Respect other people's property. Listen and follow directions. Raise your hand before speaking or leaving your seat Can I expect all of that from you class? Yes ma’am. Very good! This is a reminder for everyone to please pass your output on or before the deadline to get the proper credit for your work, Okay? We understood ma’am. e. Review Previous Lesson Last meeting we discussed about the Phase Change of Matter. Now, who can recall the different changes taking place when matter changes its state? Is there any question or clarification regarding to our last topic? (Students’ answers). None ma’am Very good! B. Presenting New Lesson ( 7 minutes) a. Motivation Before we proceed to our lesson today, group your selves into five groups. The same group we had yesterday. Our activity is called “Who Am I?”. Now, I’ll show you pictures or phrases. Just raise your hands if you know the Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) Indicator 5.1.2 (leads to diagnostic) Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) answers. Does anyone from the class have a question? Okay, is everyone ready? None ma’am. Yes, we are ready! Let us start then. b. Presentation of the Lesson From the activity, what do you think is our topic for today? c. State the objectives of the lesson That’s right. Our topic for today is about atom, its structure and its sub- atomic particles. Now, cl ass let me intro duce to you our objectiv es for t h is after noon. • He discovered electron. • He studied how alpha particles interact with a gold foil. • They disagreed with Aristotle and said that matter could be divided Our topicufnotril it gets to the smallest part today is acbaloleudt “atomos” the a t o•m Hs e discovered the electron charge ma’am. using his oil drop experiment. • He is best known for introducing the atomic theory into chemistry. Everyb ody rea d . At the duration of the lesson, learners are expected to: a. describe atom and its subatomic particles; b. locate the subatomic particles; c. infer which subatomic particle contributes to the atomic number and mass of the atom; d. give the importance of being a part of a whole; and e. create atomic model of a certain atom/ element. d. Purpose of the Lesson This time class, I will group the class into five groups. This will be your permanent all throughout the session. Understood? Indicator 1.1.2 (Integration of English) What you will be going to do is to read poem entitled “Little Things” by Julia Carney. Each group shall read stanza. Is everyone ready? Indicator 1.4.2 Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) Indicator 1.5.2 Alright! Let’s start with Group 1. GUIDE QUESTIONS: 1. What makes the ocean mighty? 2. What are the little grains? 3. What makes our earth happy? 4. Why do little things make part of the whole? 5. If you are given a chance to play a role in the community, what role would you choose to help our community a better place? Our lesson for today introduces a discussion of purpose in the context of the concept of parts in their relation to the whole. We think of parts as serving a purpose, or perhaps it would be more accurate to say, as fulfilling a function within a greater whole. Just like the atom, it has fundamental parts called the subatomic particles. C. Presentation (7 minutes) Class, I will present to you the short video about Atoms and Its Subatomic Particles. D. Lesson Proper (5 minutes) Based on the video I presented, what is an atom? Indicator 1.4.2 Atom is the smallest particle and the building blocks of matter ma’am. Very good, that is correct. All matters are made up of atoms. Even us humans are made up of atoms. What makes up an atom? It is made up of Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) its sub-atomic particles called electron, proton, and neutron. Very good. What are the charges of this sub-atomic particles? Does anyone from the class have any questions or clarification? Electron (e) has negative charge, proton (p) has a positive charge, and neutron (n) has no electric charge. None ma’am. Let’s now proceed to the other part of our lesson. E. Application (27 minutes) Indicator 1.4.2 (Integration of Mathematics) Indicator 1.1.2 Now, class! We will have a group activity. Form a circle with your group. I will distribute a copy of Activity sheet, Group Activity Rubric, and materials in each group. (Attached after the lesson plan) Make sure to scan/ skim the activity. If you have questions, feel free to ask. If none, proceed and do your tasks. Later, post your outputs here on the board. Choose/ assign representative/s from your group who will explain your output in front of the class. You will be graded using the Rubrics for Group Activity. Indicator 5.1.2 (leads to formative) Yes ma’am! Am I understood class! Very good. (Each group will now do their tasks for 15 minutes.) Alright, time is up! Make sure to clean your area. Each group will now present their assigned tasks through their Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) representative. Let’s start with group 1. (Each group shall present each of their outputs.) Congratulations, everyone. Let’s clap our (Students’ clap hands for all the good works. Well done! their hands.) Inquiry-Based Questions • Why do we need to study atoms and elements? • Why are they important even though we cannot see them? • Can you use the things that you have learned in your everyday living? How? (Answers may vary. The teacher may also lead the answer to practicing their critical thinking. Investigating things like these will develop their scientific mind. The teacher may also lead the students to the earlier poem – being a part of something bigger) F. Generalization (2 minutes) Indicator 1.5.2 Now let’s summarize our lesson for today through a Venn Diagram and strips of sentences about the lesson Put the strips of sentences on the Venn Diagram according to your understanding of the lesson. 1. Makes up an atom 2. Found inside the nucleus of an atom 3. Found outside the nucleus of an atom. 4. Positively-charged 5. Negatively-charged 6. Neutral 7. Have charges Indicator 5.1.2 (leads to formative) None ma’am Well done! All of your entries are correct. Do you still have any questions? G. Evaluation (5 minutes) To test if you really understand our discussion this morning. Answer the activity sheet I have given to you. You have 5 minutes to answer this one. You can start now. Do not forget to write your name, grade, and section. Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) Indicator 5.1.2 (leads to summative assessment) Direction: Read each statement below. Choose the letter of the best answer that described by each statement inside the box below. Each letter may be used once, more than once, or not at all. 1. It has a neutral charge. 2. It has a charge that would repel an electron. 3. It has a positive charge and found in the nucleus. 4. It moves randomly around the nucleus of an atom. 5. This is where the negatively-charged particle can be found. 6. This subatomic particle determines the identity of the atom. 7. This subatomic particle has a charge that attracts an electron. 8. An atom with 3 protons & 2 electrons will have this overall charge. 9. This is the region of the atom where almost all of the atoms mass is located. 10. Other than the answer to #3 it is another subatomic particle found in the nucleus. H. Assignment (1 minute) Follow-up activity: Research/ read more on the history of the discovery of atoms. Take notes of the important dates / years and scientists/persons involved. Create a timeline using what they have search in a long bond paper. Write a short explanation on how scientist studied atoms/ elements even without seeing them. V. Reflect and Understand (1 minute) Below are open-ended statements. Complete the statement based on your perception, opinion and concepts about atomic structure. Pass your reflection tomorrow together with your assignment output. Before, I thought that But now, I have difficulty in I can Prepared by: ROSELYN B. BATAL JHS Teacher 1 Applicant Republic of the Philippines Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) . . . . Department of Education CARAGA Region DIVISION OF AGUSAN DEL SUR ALEGRIA NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Alegria, San Francisco Agusan del Sur Group Activity – Quarter 3 Science 8 GRADE & SECTION: GROUP MEMBERS’ NAMES: SCORE: DATE: _ _ ACTIVITY: Count Me In! I. OBJECTIVES: At the end of the activity, the learners should be able to: A. Describe atom and its subatomic particles; B. Locate the subatomic particles; C. Infer which subatomic particle contributes to the atomic number and mass of the atom; D. Create atomic model of a certain atom/ element II. MATERIALS: ➢ Manila paper ➢ Scissors ➢ Marker ➢ Ballpen III. PROCEDURES: A. If you look closely at the tip of sharpened pencil, you will see that it is made of graphite. Going deeper, graphite is made of carbon atoms. Deeper still, each carbon atom is made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ➢ Crayons/ coloring materials ➢ Activity sheet ➢ Bond Papers ➢ Colored papers Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) 1) Draw the carbon atom from the box on the previous page. 2) Label the drawing of a carbon atom. All labels must be used: ➢ Proton ➢ Neutron ➢ Electron ➢ Nucleus ➢ Positive (+) ➢ Negative (-) ➢ Neutral (0) ➢ Electron Cloud 3) Color each particle (Red – protons, Yellow – neutrons, Green – electrons). GUIDE QUESTION: Q1: What are the three (3) subatomic particles? Q2: What do neutrons and protons have in common? How are they different? B. Particles that are smaller than the atom are called subatomic particles. The three main subatomic particles that form an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. The center of the atom is called the nucleus. Complete the table below. PROPERTIES Electrons Neutrons Proton s Symbol Charge Location in the atom Mass GUIDE QUESTION(s): Q3: What are the properties you could use to distinguish a proton from an electron? Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) Q4: What property do protons and electrons have that neutron don’t? C. Atomic Number & Mass Number. Complete the table below. Take note that: • Atomic Number = number of protons = number of electrons • Mass Number = number of protons + number of neutrons Element A B C D E Atomic Number 13 Mass Number Proton (p+) Neutron (n0) 14 87 136 50 Electron (e-) 20 20 45 207 82 GUIDE QUESTION(s): Q5: How can atoms be neutral if they contain charged particle? Q6: Why isn’t possible for an atom to have a mass number of 14 and an atomic number of 13? D. Complete the table below. Find the element and its symbol. Use the data and the periodic table of elements at the last page of this activity. Proton Element Symbol Atomic Number Mass Number Neutron (n0) Electron (e-) (p+) 38 50 31 15 22 18 19 20 64 29 GUIDE QUESTION(s): Q7: Are the number of protons and neutrons for each element always the same? Q8: What is the mass number? Why aren’t electrons included in the mass number? E. In the earlier discussion, you have encountered Bohr’s Planetary Model of an atom. Create your very own atomic model using any materials that can be found in the classroom or the materials that you have with you and your group. Take a picture of it and send it to your teacher so that your teacher can project it on the monitor for your other classmates to see. Write a short explanation of your model on the space provided below. Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com) F. Rewrite the data you gathered in the Manila paper. ➢ Group 1 – details of Activity A only and the answers for Q1 and Q2 ➢ Group 2 – details of Activity B only and the answers for Q3 and Q4 ➢ Group 3 – details of Activity C only and the answers for Q5 and Q6 ➢ Group 4 – details of Activity D only and the answers for Q7 and Q8 ➢ Group 5 – send your picture to your teacher, be ready for your explanation GROUP WORK RUBRIC GROUP NO.: CRITERIA DATE: EXEMPLARY (5) Decision Making All members of the group contribute to the decision-making. SCORE: LEARNED (4) BASIC (3) APPRENTICE (1) Most students contribute to decision-making. Some students contribute to decision-making. One person dominates decision-making. Social Interaction Students respect and encourage the views of others. Students ask questions or clarification. Students build on others comments. Most students ask questions and build on others comments. Students pay attention to the group discussion. Some students ask questions and build on other comments. Students frequently interrupt and/ or put down the views of others. Students do not ask questions or clarification. On Task Behavior All students exhibit their best behavior while doing the task. Most students exhibit on-task behavior most of the time. Students exhibit on-task behavior some of the time. Students exhibit on-task behavior inconsistently. Group Structure and Functioning Students complete a clear and logical sequence of steps. Complete task with form and reflection and revision. Members volunteer to take responsibilities and roles. Students complete a sequence of steps. Complete task on time. the leader assigns responsibilities and tasks. With assistance, students are able to sequence steps. Rush to complete task. Division of tasks and responsibilities is inefficient and wastes time. With assistance, students have difficulty sequencing steps. Task is not completed on time. Correct Answers All answers are correct. One or two incorrect answers/ mistakes. Three or four incorrect answers/ mistakes. Five or more incorrect answers/ mistakes. Timeliness Finished the task before/ ahead the given time. Finished the task on time. Finished the task two minutes after the given time. Finished the task five minutes after the given time. Downloaded by Marybeth Marciano (marybethmarciano.07@gmail.com)